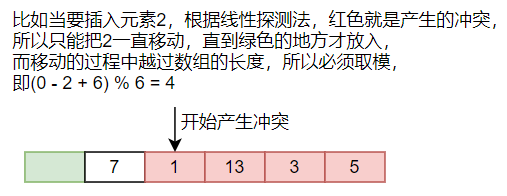
Given a hash table of size N, we can define a hash function H(x)=x%N. Suppose that the linear probing is used to solve collisions, we can easily obtain the status of the hash table with a given sequence of input numbers.
However, now you are asked to solve the reversed problem: reconstruct the input sequence from the given status of the hash table. Whenever there are multiple choices, the smallest number is always taken.
Each input file contains one test case. For each test case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤ 1000), which is the size of the hash table. The next line contains N integers, separated by a space. A negative integer represents an empty cell in the hash table. It is guaranteed that all the non-negative integers are distinct in the table.
For each test case, print a line that contains the input sequence, with the numbers separated by a space. Notice that there must be no extra space at the end of each line.
11
33 1 13 12 34 38 27 22 32 -1 21
1 13 12 21 33 34 38 27 22 32
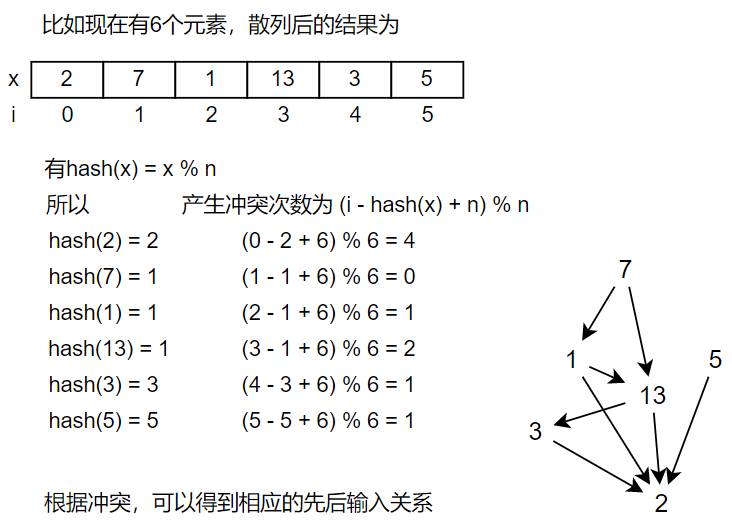
这道题目通过hash函数 H(x) = x % N 映射,得到相应的一组序列,要求我们给出元素输入的顺序。因为输入的顺序可以有多种,所以题目要求我们总是选择最小的那个元素。
这道题当时想了好久,完全没有思路,当看到姥姥说是拓扑排序后都惊呆了。
“当你处理的元素之间有非常明确的先后顺序关系,就要考虑是否与拓扑排序有关系。”姥姥如是说。
确实,之所以会产生冲突是因为部分元素通过hash函数得到的值是相同的,如果是线性探测法的话,就必须从得到的hash值开始一直往后移直到有空位才放入这个元素。而这个过程中移动的次数就是产生冲突的次数。这些产生冲突的元素必须要先于这个元素输入。可以看到,这些产生冲突的元素就与这个元素产生了先后顺序关系,他们必须要先于这个元素输入,才会产生冲突。
举个例子:
通过上面的例子,你可能会说要建个图,但事实上,我们并不需要建图。下面来介绍不需要建图的做法思路。(当然,建图也是可以做的)
为了方便,我们先定义一个结构体,存放着元素的值value,元素散列后的下标位置pos,以及对应的hash值mod(mod = value % n)。用一个vector存放这个结构体类型的节点。
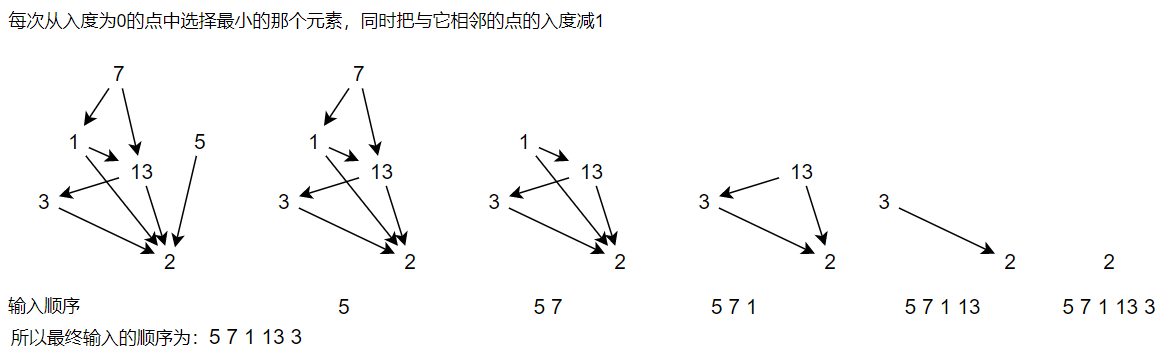
可以发现,点的入度就是冲突的次数。这样每个元素所对应的那个点的入度为 indegree[i] = (v[i].pos - v[i].mod + n) % n ,注意这里应该考虑到冲突可能越过数组长度,这种写法是错误的: indegree[i] = (v[i].pos - v[i].mod) % n
同时,可以看到,我们每次都是选入度为0,并且元素值最小的那个值出来,这里我们就不再使用队列queue,而是改用priority_queue,可以实现每次都弹出元素值最小的那个元素。
最后一个问题是,由于我们不建图,如何知道弹出的点与哪些点相邻呢。为了表述方便,用t代表弹出的那个元素,i代表某一个元素。
我们要找的点其实就是形成先后关系的元素,必须要在t输入后,再输入的那个元素。所以,我们可以遍历一遍vector,去看每个元素i产生的冲突是否包含t。如果t与i产生冲突,那么t的下标位置与i的下标位置及其hash值应该满足这个关系: v[i].mod <= t.pos < v[i].pos 。
但我们还需要考虑到越过数组长度的情况,所以不可以直接用这个表达式来判断。换一种思想,如果t会在这个范围内,那么它的某一个距离也会是在某范围内。而这个所说的某一距离,其实就是t.pos到v[i].mod的距离,如果满足 (t.pos - v[i].mod + n) % n < (v[i].pos - v[i].mod + n) % n ,就说明t导致i产生冲突,也就是说t先于i输入,也就是说t与i相邻,即有t -> i。
最后AC代码如下:
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <queue> 3 #include <vector> 4 5 struct Node { 6 int value, pos, mod; 7 }; 8 9 bool operator<(const Node &a, const Node &b) { 10 return a.value > b.value; 11 } 12 13 void topSort(std::vector<Node> &v, int n) { 14 int indeg[v.size()]; 15 for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) { 16 indeg[i] = (v[i].pos - v[i].mod + n) % n; // 计算入度,其实就是产生冲突的次数,因为可能会越过数组长度,所以要取模 17 } 18 19 std::priority_queue<Node> pq; 20 for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) { 21 if (indeg[i] == 0) pq.push(v[i]); // 把入度为0的元素压入队列 22 } 23 24 bool flag = false; // 打印空格标识符 25 while (!pq.empty()) { 26 Node t = pq.top(); 27 pq.pop(); 28 if (flag) printf(" "); 29 flag = true; 30 printf("%d", t.value); 31 32 for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) { 33 if ((t.pos - v[i].mod + n) % n < (v[i].pos - v[i].mod + n) % n) { // 遍历找到与弹出元素形成先后关系的元素 34 indeg[i]--; // 该元素入度减1 35 if (indeg[i] == 0) pq.push(v[i]); // 同时如果入度为0将其压入队列 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 41 int main() { 42 int n; 43 scanf("%d", &n); 44 std::vector<Node> v; // 不定长数组v,用来存放每个元素的值,散列后的下标位置,及hash值 45 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 46 int value; 47 scanf("%d", &value); 48 if (value != -1) { 49 int mod = value % n; 50 v.push_back({value, i, mod}); 51 } 52 } 53 54 topSort(v, n); 55 56 return 0; 57 }
浙江大学——数据结构:https://www.icourse163.org/course/ZJU-93001?tid=1461682474
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/onlyblues/p/14805848.html