IO:Java对数据的操作是通过流的方式,IO流用来处理设备之间的数据传输,上传文件和下载文件,Java用于操作流的对象都在IO包中。
图示:(主要IO流)
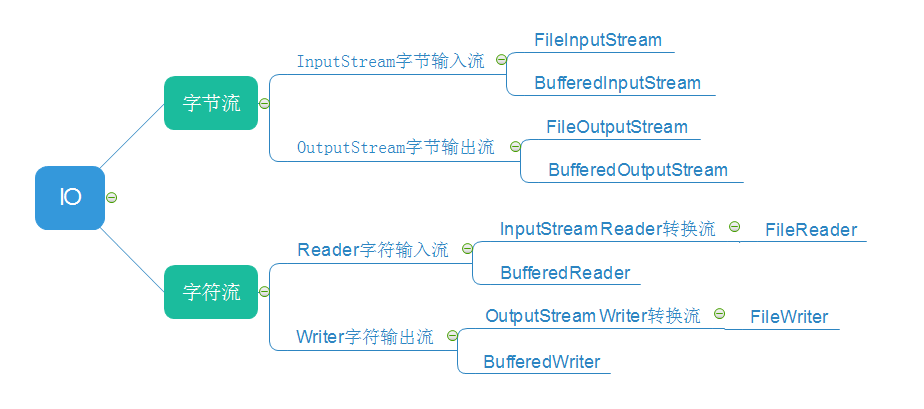
InputStream:字节输入流基类,抽象类是表示字节输入流的所有类的超类。
常用方法:
// 从输入流中读取数据的下一个字节
abstract int read()
// 从输入流中读取一定数量的字节,并将其存储在缓冲区数组 b中
int read(byte[] b)
// 将输入流中最多 len 个数据字节读入 byte 数组
int read(byte[] b, int off, int len)
// 跳过和丢弃此输入流中数据的 n个字节
long skip(long n)
// 关闭此输入流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源
void close()
OutputStream:字节输出流基类,抽象类是表示输出字节流的所有类的超类。
常用方法:
// 将 b.length 个字节从指定的 byte 数组写入此输出流
void write(byte[] b)
// 将指定 byte 数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字节写入此输出流
void write(byte[] b, int off, int len)
// 将指定的字节写入此输出流
abstract void write(int b)
// 关闭此输出流并释放与此流有关的所有系统资源
void close()
// 刷新此输出流并强制写出所有缓冲的输出字节
void flush()
FileInputStream:字节文件输入流,从文件系统中的某个文件中获得输入字节,用于读取诸如图像数据之类的原始字节流。
构造方法:
// 通过打开一个到实际文件的连接来创建一个FileInputStream,该文件通过文件系统中的File对象file指定
FileInputStream(File file)
// 通过打开一个到实际文件的连接来创建一个FileInputStream,该文件通过文件系统中的路径name指定
FileInputStream(String name)
常用方法:覆盖和重写了父类的的常用方法。
// 读取f盘下该文件f://hell/test.txt
//构造方法1
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("f://hello//test.txt"));
int i = 0;
//一次读取一个字节
while ((i = inputStream.read()) != -1) {
// System.out.print(i + " ");// 65 66 67 68
//为什么会输出65 66 67 68?因为字符在底层存储的时候就是存储的数值。即字符对应的ASCII码。
System.out.print((char) i + " ");// A B C D
}
//关闭IO流
inputStream.close();
// 读取f盘下该文件f://hell/test.txt
//构造方法2
InputStream inputStream2 = new FileInputStream("f://hello/test.txt");
// 字节数组
byte[] b = new byte[2];
int i2 = 0;
// 一次读取一个字节数组
while ((i2 = inputStream2.read(b)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(b, 0, i2) + " ");// AB CD
}
//关闭IO流
inputStream2.close();
注: 一次读取一个字节数组,提高了操作效率,IO流使用完毕一定要关闭。
FileOutputStream:字节文件输出流是用于将数据写入到File,从程序中写入到其他位置。
构造方法:
// 创建一个向指定File对象表示的文件中写入数据的文件输出流
FileOutputStream(File file)
// 创建一个向指定File对象表示的文件中写入数据的文件输出流
FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append)
// 创建一个向具有指定名称的文件中写入数据的输出文件流
FileOutputStream(String name)
// 创建一个向具有指定name的文件中写入数据的输出文件流
FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append)
常用方法:覆盖和重写了父类的的常用方法。
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File("test.txt"));
// 写出数据
outputStream.write("ABCD".getBytes());
// 关闭IO流
outputStream.close();
// 内容追加写入
OutputStream outputStream2 = new FileOutputStream("test.txt", true);
// 输出换行符
outputStream2.write("\r\n".getBytes());
// 输出追加内容
outputStream2.write("hello".getBytes());
// 关闭IO流
outputStream2.close();
注;输出的目的地文件不存在,则会自动创建,不指定盘符的话,默认创建在项目目录下;输出换行符时一定要写\r\n不能只写\n,因为不同文本编辑器对换行符的识别存在差异性。
BufferedInputStream:字节缓冲输入流,提高了读取效率。
构造方法:
// 创建一个 BufferedInputStream并保存其参数,即输入流in,以便将来使用。
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in)
// 创建具有指定缓冲区大小的 BufferedInputStream并保存其参数,即输入流in以便将来使用
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size)
InputStream in = new FileInputStream("test.txt");
// 字节缓存流
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(in);
byte[] bs = new byte[20];
int len = 0;
while ((len = bis.read(bs)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(bs, 0, len));
// ABCD
// hello
}
// 关闭流
bis.close();
BufferedOutputStream:字节缓冲输出流,提高了写出效率。
构造方法:
// 创建一个新的缓冲输出流,以将数据写入指定的底层输出流
BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out)
// 创建一个新的缓冲输出流,以将具有指定缓冲区大小的数据写入指定的底层输出流
BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size)
常用方法:
// 将指定 byte 数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字节写入此缓冲的输出流
void write(byte[] b, int off, int len)
// 将指定的字节写入此缓冲的输出流
void write(int b)
// 刷新此缓冲的输出流
void flush()
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("test.txt", true));
// 输出换行符
bos.write("\r\n".getBytes());
// 输出内容
bos.write("Hello Android".getBytes());
// 刷新此缓冲的输出流
bos.flush();
// 关闭流
bos.close();
Reader:读取字符流的抽象类.
常用方法:
// 读取单个字符
int read()
// 将字符读入数组
int read(char[] cbuf)
// 将字符读入数组的某一部分
abstract int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
// 跳过字符
long skip(long n)
// 关闭该流并释放与之关联的所有资源
abstract void close()
Writer:写入字符流的抽象类.
常用方法:
// 写入字符数组
void write(char[] cbuf)
// 写入字符数组的某一部分
abstract void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
// 写入单个字符
void write(int c)
// 写入字符串
void write(String str)
// 写入字符串的某一部分
void write(String str, int off, int len)
// 将指定字符添加到此 writer
Writer append(char c)
// 将指定字符序列添加到此 writer
Writer append(CharSequence csq)
// 将指定字符序列的子序列添加到此 writer.Appendable
Writer append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end)
// 关闭此流,但要先刷新它
abstract void close()
// 刷新该流的缓冲
abstract void flush()
InputStreamReader:字节流转字符流,它使用的字符集可以由名称指定或显式给定,否则将接受平台默认的字符集。
构造方法:
// 创建一个使用默认字符集的 InputStreamReader
InputStreamReader(InputStream in)
// 创建使用给定字符集的 InputStreamReader
InputStreamReader(InputStream in, Charset cs)
// 创建使用给定字符集解码器的 InputStreamReader
InputStreamReader(InputStream in, CharsetDecoder dec)
// 创建使用指定字符集的 InputStreamReader
InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName)
特有方法:
//返回此流使用的字符编码的名称
String getEncoding()
//使用默认编码
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("test.txt"));
int len;
while ((len = reader.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) len);//爱生活,爱Android
}
reader.close();
//指定编码
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("test.txt"),"utf-8");
int len;
while ((len = reader.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) len);//????????Android
}
reader.close();
注:Eclipse默认使用GBK编码,test.txt文件所以是GBK编码,当指定utf-8编码时所以会乱码。
OutputStreamWriter:字节流转字符流。
构造方法:
// 创建使用默认字符编码的 OutputStreamWriter
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out)
// 创建使用给定字符集的 OutputStreamWriter
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, Charset cs)
// 创建使用给定字符集编码器的 OutputStreamWriter
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, CharsetEncoder enc)
// 创建使用指定字符集的 OutputStreamWriter
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, String charsetName)
特有方法:
//返回此流使用的字符编码的名称
String getEncoding()
BufferedReader:字符缓冲流,从字符输入流中读取文本,缓冲各个字符,从而实现字符、数组和行的高效读取。
构造方法:
// 创建一个使用默认大小输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流
BufferedReader(Reader in)
// 创建一个使用指定大小输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流
BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz)
特有方法:
// 读取一个文本行
String readLine()
//生成字符缓冲流对象
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("test.txt")));
String str;
//一次性读取一行
while ((str = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(str);// 爱生活,爱Android
}
//关闭流
reader.close();
BufferedWriter:字符缓冲流,将文本写入字符输出流,缓冲各个字符,从而提供单个字符、数组和字符串的高效写入。
构造方法:
// 创建一个使用默认大小输出缓冲区的缓冲字符输出流
BufferedWriter(Writer out)
// 创建一个使用给定大小输出缓冲区的新缓冲字符输出流
BufferedWriter(Writer out, int sz)
特有方法:
// 写入一个行分隔符
void newLine()
FileReader:InputStreamReader类的直接子类,用来读取字符文件的便捷类,使用默认字符编码。
FileWriter:OutputStreamWriter类的直接子类,用来写入字符文件的便捷类,使用默认字符编码。
读取f盘下的一个视频文件到项目中:文件大小29.5 MB
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("f://滑板//HEEL_FLIP.mp4");
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("HEEL_FLIP.mp4");
int len;
// 开始时间
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 一次读取一个字节
while ((len = inputStream.read()) != -1) {
outputStream.write(len);
}
// 用时毫秒
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - begin);// 213195
//关闭流释放资源
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("f://滑板//HEEL_FLIP.mp4");
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("HEEL_FLIP.mp4");
int len;
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
// 开始时间
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 一次读取一个字节数组
while ((len = inputStream.read(bs)) != -1) {
outputStream.write(bs, 0, len);
}
// 用时毫秒
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - begin);// 281
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("f://滑板//HEEL_FLIP.mp4");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(inputStream);
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("HEEL_FLIP.mp4");
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(outputStream);
int len;
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
// 开始时间
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
while ((len = bis.read(bs)) != -1) {
bos.write(bs, 0, len);
}
// 用时毫秒
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - begin);// 78
bis.close();
bos.close();
注:由此可以看出高效缓冲流读写速度是非常快的,建议使用。
public String picUpload(MultipartFile file) throws Exception {
String epId = getLoginUser.getEpId();
String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename();
//后缀名
String nameSuffix = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("."));
//保存路径
String path = uploadPath + "/" + "/" + "APP" + "/" + epId + "/" + "/" + GetTime.time() + "/";
File file1 = new File(path);
//如果目录不存在 则创建
if (!file1.exists()) {
file1.mkdirs();
}
//生产新文件名
String name = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + nameSuffix;
String newFileName = name.replace("-", "");
InputStream in = null;
BufferedOutputStream out = null;
try {
//输入流
in = new BufferedInputStream(file.getInputStream());
//输出流
out = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(path + newFileName));
//一次读取的字节数
byte[] temp = new byte[1024];
int leng = in.read(temp);//每次读取的字节数
while (leng != -1) {
//写入
out.write(temp, 0, leng);
out.flush();
leng = in.read(temp);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new Exception("上传失败");
} finally {
//关流
out.close();
in.close();
}
return newFileName;
}
public String picUpload(MultipartFile file) throws Exception {
String epId = getLoginUser.getEpId();
String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename();
//后缀名
String nameSuffix = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("."));
//保存路径
String path = uploadPath + "/" + "APP" + "/" + epId + "/" + GetTime.time() + "/";
File file1 = new File(path);
//如果目录不存在 则创建
if (!file1.exists()) {
file1.mkdirs();
}
//生产新文件名
String name = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + nameSuffix;
String newFileName = name.replace("-", "");
BufferedInputStream in = null;
BufferedOutputStream out = null;
try {
//输入流
in = new BufferedInputStream(file.getInputStream());
//输出流
out = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(path + newFileName));
byte[] temp = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = in.read(temp)) != -1) {//每次读取的字节数
//写入
out.write(temp, 0, len);
out.flush();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new Exception("上传失败");
} finally {
//关流
out.close();
in.close();
}
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
stringBuffer.append("/" + "APP" + "/" + epId + "/" + GetTime.time() + "/" + newFileName);
String newName = stringBuffer.toString();
return newName;
}
public String picUpload(MultipartFile file) throws Exception {
String epId = getLoginUser.getEpId();
String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename();
//后缀名
String nameSuffix = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("."));
//保存路径
String path = uploadPath + "/" + "/" + "APP" + "/" + epId + "/" + "/" + GetTime.time() + "/";
File file1 = new File(path);
//如果目录不存在 则创建
if (!file1.exists()) {
file1.mkdirs();
}
//生产新文件名
String name = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + nameSuffix;
String newFileName = name.replace("-", "");
InputStream in = null;
BufferedOutputStream out = null;
try {
//输入流
in = new BufferedInputStream(file.getInputStream());
byte[] temp = new byte[1024];
int i = in.read(temp);
//输出流
out = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(path + newFileName));
while (i != -1) {
//写入
out.write(temp, 0, i);
out.flush();
i = in.read(temp);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new Exception("上传失败");
} finally {
//关流
in.close();
out.close();
}
return newFileName;
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/TTCherry/p/14814206.html