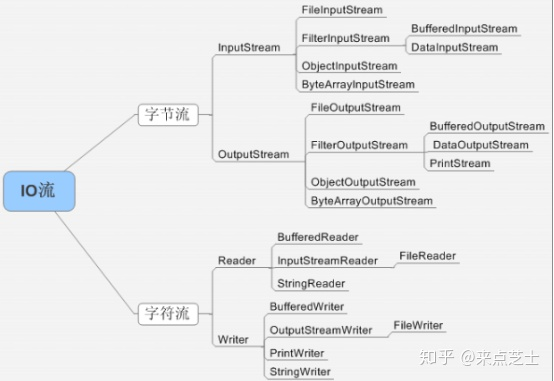
1、字符流处理的单元为2个字节的Unicode字符,分别操作字符、字符数组或字符串,而字节流处理单元为1个字节,操作字节和字节数组。
所以字符流是由Java虚拟机将字节转化为2个字节的Unicode字符为单位的字符而成的,所以它对多国语言支持性比较好!如果是音频文件、图片、歌曲,就用字节流好点,如果是关系到中文(文本)的,用字符流好点.
所有文件的储存是都是字节(byte)的储存,在磁盘上保留的并不是文件的字符而是先把字符编码成字节,再储存这些字节到磁盘。在读取文件(特别是文本文件)时,也是一个字节一个字节地读取以形成字节序列.
2、字节流可用于任何类型的对象,包括二进制对象,而字符流只能处理字符或者字符串; 字节流提供了处理任何类型的IO操作的功能,但它不能直接处理Unicode字符,而字符流就可以。
字节流转换成字符流可以用 InputSteamReader OutputStreamWriter
//字节流转换成字符流 InputStreamReader
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(fileInputStream);
//InputStreamReader 转换成带缓存的bufferedReader
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputSteamReader);
下面首先是通过字符流对文件进行读取和写入:
1 package lib;
2
3 import java.io.BufferedReader;
4 import java.io.File;
5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
6 import java.io.FileReader;
7 import java.io.FileWriter;
8 import java.io.IOException;
9 import java.io.PrintWriter;
10
11 public class Test {
12 // 定义文件路径
13 File f = new File("F:\\test.txt");
14 //字符流读取的方法
15 public String read() throws IOException{
16 String str = "";
17 String count = "";
18 try {
19 // 使用字符流对文件进行读取
20 BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));
21 while (true) {
22 //读取每一行数据并将其赋值给str
23 if ((count = bf.readLine()) != null) {
24 str += count;
25 } else {
26 break;
27 }
28 }
29 // 关闭流
30 bf.close();
31 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
32 e.printStackTrace();
33 }
34 return str;
35 }
36 //字符流写入方法
37 public void Write(){
38 try {
39 //其中true表示在原本文件内容的尾部添加,若不写则表示清空文件后再添加内容
40 PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(f,true));
41 pw.write("测试输入字符串到文件中2");
42 pw.close();
43 } catch (IOException e) {
44 e.printStackTrace();
45 }
46 }
47 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
48 Test test=new Test();
49 //将字符串输入到文件中
50 test.Write();
51 //读取相对应的字符串
52 String str=test.Read();
53 //将文件中内容在控制台输出
54 System.out.println("文件内容为:"+str);
55 }
56 }
上述代码的关键地方都有注释,就不再一一赘述了,主要就是在使用完流之后不要忘记关闭就好(行30,行42)
然后是通过字节流的方式对文件进行操作,将一个文件中的内容复制到另一个文件中:
1 package com.file.test2;
2
3 import java.io.File;
4 import java.io.FileInputStream;
5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
6 import java.io.FileOutputStream;
7 import java.io.IOException;
8
9 public class TestFile2 {
10 //使用字节流读取并写入文件,将一个文件复制到另一个文件中
11 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
12 //要复制的源文件
13 File f=new File("D:\\test.txt");
14 //目标文件
15 File f2=new File("D:\\test2.txt");
16 //定义一个byte类型的数组,用于存储读取到的内容
17 byte [] b=new byte[1024];
18 int length;
19 try {
20 //定义读取的流
21 FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(f);
22 //定义输出到文件的流
23 FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream(f2);
24 //将文件内容输出到另一个文件中
25 while((length=in.read(b))!=-1){
26 out.write(b, 0, length);
27 }
28 out.close();
29 in.close();
30 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
31 e.printStackTrace();
32 }
33 }
34 }
在字节流的操作中,第13行的源文件必须存在,可以根据需要自行更改文件路径,只需要存在即可,否则会报文件找不到的错误,同时若想在控制台输出读取到的字节流的内容则可以在第27和28行之间加两句代码:in.read(b, 0, b.length);System.out.println(new String(b));
以上就是字符流和字节流的相关操作,其实代码不难,主要是自己的理解,相同的问题每个人都会有不同的理解方式,当然,对于我们编程人员来说,除了要多思考之外还要多动手。最后希望以上内容能对大家有所帮助
Java:字节流读写文件
针对文件的读写,JDK专门提供了两个类,分别是 FileInputStream 和 FileOutputStream ,它们都是InputStream 的子类。
Example01:以字节流形式读取文件中的数据
Example02:将数据以字节流形式写入文件(覆盖文件内容)
Example03:将数据以字节流形式写入文件(追加文件内容)
1.FileInputStream 是操作文件的字节输入流,专门用于读取文件中的数据。
public class Example01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("Example1.txt"); int b = 0; while(true) { b = in.read(); if(b == -1) { break; } System.out.println(b); } in.close(); } }
注意:首先要确保文件 Example1.txt 存在并且可读,否则会抛出文件找不到的异常 FileNotFoundException
2.FileOutputStream 是操作文件的字节输出流,专门用于把数据写入文件。
public class Example02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //创建一个文件字节输出流 FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("Example2.txt"); String str = "****写入数据****"; byte[] b = str.getBytes(); for(int i=0; i<b.length; i++) { out.write(b[i]); } out.close(); } }
注意:程序运行后,会自动生成一个新的文本文件 Example2.txt 。如果 Example2.txt 已经存在数据,那么该文件中的数据会先被清空,再写入新的数据。
3.FileOutputStream 的构造函数 FileOutputStream(String fileName,boolean append) ,用于把数据追加写入文件。
public class Example03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("Example2.txt", true); String str = "----追加数据----"; byte[] b = str.getBytes(); for(int i=0; i<b.length; i++) { out.write(b[i]); } out.close(); } }
注意:程序通过字节输出流对象向文件 Example2.txt 追加了数据。
由于IO流在进行数据读写操作时会出现异常,如果一旦遇到异常,IO流的 close() 方法将无法得到执行,流对象所占有的系统资源将得不到释放,因此,为了保证IO流的 close() 方法必须执行,通常将关闭流的操作写在 finally 代码块中。
finally{ try{ if(in != null) in.close(); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } try{ if(out != null) out.close(); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } }
1. 字节流的读写。
package com.main.stream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; /** * 字节流文件读写 * @author PC * */ public class FileRwByByte { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 定义源文件 File file = new File("D:\\springboot学习\\34116codes.zip"); InputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); // 获取文件名 String fileName = file.getName(); // 定义写文件路径 String aimPath = "E:\\stream\\" + fileName; OutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(aimPath); // 定义字节,接收读取到的源文件字节内容 int by; while ((by = fis.read()) != -1) { fos.write(by); } fos.flush(); fis.close(); fos.close(); } }
这里按照一个字节一个字节的读取,将读取到的字节写入到新的文件中,达到文件复制粘贴的效果。
上面程序可以正常执行,但是执行过程中,如果遇到10MB 以上的文件,可能会感觉特别的慢,原因就在于,程序中一个字节一个字节的读取,会增大文件读写的次数。
如何改进,使用字节数组,一次读取多个字节,减少文件读写次数,提交程序执行效率。
将程序中,按照字节单字节读取的部分,修改为按照字节数组读取。这时,输入流一次读取1024个字节,然后将读取到的字节直接输出写到文件中,大大增加程序的整体效率。
// 定义字节数组,接收读取到的源文件字节内容 byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; while (fis.read(bytes) != -1) { fos.write(bytes); }
附整段代码
package com.main.stream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; /** * 字节流文件读写 * @author PC * */ public class FileRwByByte { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 定义源文件 File file = new File("D:\\springboot学习\\34116codes.zip"); InputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); // 获取文件名 String fileName = file.getName(); // 定义写文件路径 String aimPath = "E:\\stream\\" + fileName; OutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(aimPath); // 定义字节数组,接收读取到的源文件字节内容 byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; while (fis.read(bytes) != -1) { fos.write(bytes); } fos.flush(); fis.close(); fos.close(); } }
上面看了字节流的读写,有单字节的读写和读取字节数组两种方式。同样,字符流的读写也有单字符读写和字符数组两种方式。
package com.main.stream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Reader; import java.io.Writer; /** * 字符流文件读写 * @author PC * */ public class FileReaderDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 定义源文件 File file = new File("E:\\test.txt"); Reader reader = new FileReader(file); // 获取文件名 String fileName = file.getName(); // 定义写文件路径 String aimPath = "E:\\stream\\" + fileName; Writer writer = new FileWriter(aimPath); // 定义字符,接收读取到的源文件字符内容 int ch; while ((ch = reader.read()) != -1) { writer.write(ch); } writer.flush(); writer.close(); reader.close(); } }
同样的原因,单字符读写会稍微慢一点,那么换字符数组读取呢?
// 定义字符数组,接收读取到的源文件字符内容 char[] chars = new char[1024]; while (reader.read(chars) != -1) { writer.write(chars); }
只需要将读写操作方式的按单字符读写修改为按照数组的方式即可。
附完整代码:
package com.main.stream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Reader; import java.io.Writer; /** * 字符流文件读写 * @author PC * */ public class FileReaderDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 定义源文件 File file = new File("E:\\test.txt"); Reader reader = new FileReader(file); // 获取文件名 String fileName = file.getName(); // 定义写文件路径 String aimPath = "E:\\stream\\" + fileName; Writer writer = new FileWriter(aimPath); // 定义字符数组,接收读取到的源文件字符内容 char[] chars = new char[1024]; while (reader.read(chars) != -1) { writer.write(chars); } writer.flush(); writer.close(); reader.close(); } }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/lixiaochong/p/14825204.html