1、c语言中字符串的复制
#include <stdio.h> char *copy(char *d, const char *s) { char *t = d; // 定义指向传入的字符串首字符的指针 while(*d++ = *s++) //当指针s所指元素不为null时,将s所指元素赋值给d所指元素 ; return t; //返回指针 } int main(void) { char str1[] = "abcd"; char str2[128]; printf("str2: "); scanf("%s", str2); copy(str1, str2); printf("str1 after replication: %s\n", str1); return 0; }
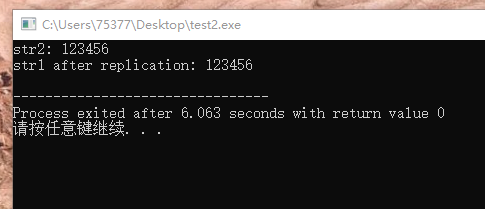
2、不正确的字符串复制
#include <stdio.h> char *copy(char *d, const char *s) { char *t = d; while(*d++ = *s++) ; return t; } int main(void) { char *str1 = "abcd"; // 不正确的原因出现在这里!!!复制的目的字符串是使用指针创建的!!!! 使用指针实现的字符串,每一个字符相当于字符串字面量,
//而不像是字符串数组中字符保存为数组元素,因此复制过程会出现 //改写字符串字面量的错误,也可能会写入非空的内存空间, 引发异常。 char str2[128]; printf("str2: "); scanf("%s", str2); copy(str1, str2); printf("str1 after replication : %s\n", str1); return 0; }
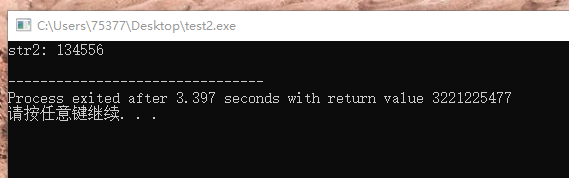
3、
#include <stdio.h> char *copy(char *d, const char *s) { char *t = d; while(*d++ = *s++) ; return t; } int main(void) { char str1[6] = "abcd"; // 会不会写入非空的内存空间???? char str2[128] = "abcdefghijklm"; copy(str1, str2); printf("str1 after replication : %s\n", str1); return 0; }
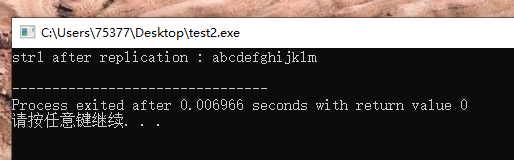
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/liujiaxin2018/p/14842707.html