package org.example;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileInputStreamTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//main方法里的代码,IO的这块的代码处理异常的大概框架都是这样的,之后就只截取主要代码了
/*
FileInputStream :文件字节输入流,可以读任何类型的文件,读取方向为从硬盘向内存
*/
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
/*
文件路径:D:\tempDir\tempFile.txt java中 \ 代表转义,所以IDEA自动将路径替换为 \\。
路径也可以写成反斜杠的形式 D:/tempDir/tempFile.txt
*/
fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\tempDir\\tempFile.txt");
int read = fis.read();
System.out.println(read);
read = fis.read();
System.out.println(read);
read = fis.read();
System.out.println(read);
read = fis.read();
System.out.println(read);
read = fis.read();
System.out.println(read);
read = fis.read();
System.out.println(read);
read = fis.read();
System.out.println(read);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// close()方法放在finally块中,确认一定会执行。
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}


为啥程序最终输出的为数字,而不是文件中的字母。
这是因为FileInputSream是字节输入流,每次读取一个字节。
所以每次读取,刚好读完文件中的每个字母的字节,也就是八位二进制数所代表内容的ASCII值。
通过最后一个 -1 可以发现当字节流将文件读取完后,再次读取会返回 -1。根据这个可以改进以上程序。
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\tempDir\\tempFile.txt");
while (true) {
int readData = fis.read();
if (readData == -1) {
break;
}
System.out.println(readData);
}
将程序改进为while循环,对文件进行读取。但是循环体还是有冗余代码,继续改进。
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\tempDir\\tempFile.txt");
int readData = 0;
while ((readData = fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(readData);
}
现在循环体已经很简洁了,下面使用 byte 数组提升读取数据。
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\tempDir\\tempFile.txt");
byte[] bytes = new byte[4];
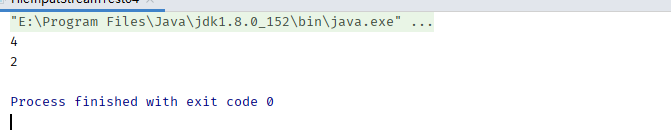
int readCount = fis.read(bytes);
System.out.println(readCount);
readCount = fis.read(bytes);
System.out.println(readCount);
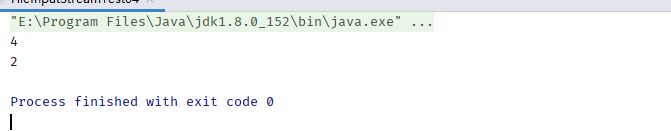
通过打印结果发现,第一次读取到4个字节,第二次只读取到2个字节。
再通过 new String(bytes) 将byte数组转换成字符串,可以发现第二次读取的两个字节将第一次读取的四个字节的前两个覆盖了,而后两个没变。
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\tempDir\\tempFile.txt");
byte[] bytes = new byte[4];
int readCount = 0;
while ((readCount = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
//使用这个new String方法 读多少转换多少
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, readCount));
}
JavaSE - IO流 - FileInputSream初步
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/LNpig/p/14901321.html