valueOf() intValue()
package com.cnblogs;
//本类用于实现
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
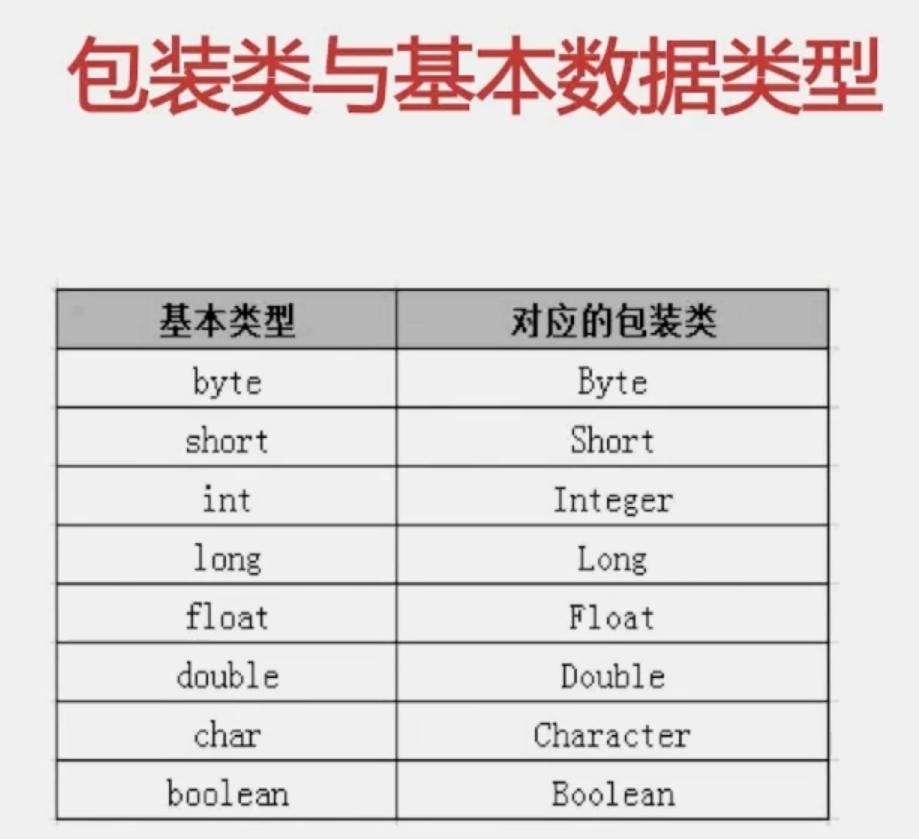
//装箱:基本类型转成引用类型的过程
//基本类型
int num1 = 18;
//使用Integer类创建对象
Integer integer1 = new Integer(num1);
Integer integer2 = Integer.valueOf(num1);
System.out.println("======装箱=======");
System.out.println(integer1);
System.out.println(integer2);
//类型转换,拆箱,引用类型转成基本类型
Integer integer3 = new Integer(100);
int num2 = integer3.intValue();
System.out.println("======拆箱=======");
System.out.println(num2);
//JDK1.5之后,提供自动装箱和拆箱
int age = 30;
//自动装箱
Integer integer4 = age;
System.out.println("======自动装箱=======");
System.out.println(integer4);
//自动拆箱
int age2 = integer4;
System.out.println("======自动拆箱=======");
System.out.println(age2);
/*
======装箱=======
18
18
======拆箱=======
100
======自动装箱=======
30
======自动拆箱=======
30
*/
}
}
package com.cnblogs;
//本类用于实现
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//基本类型和字符串之间转换
//基本类型转成字符型
int num1 = 100;
//方法一
String str1 = num1 + "";
//方法二
String str2 = Integer.toString(num1);
System.out.println(str1);//100
System.out.println(str2);//100
//字符型转成基本类型
String str3 = "150";
//使用Integer.parseInt();
int num2 =Integer.parseInt(str3);
System.out.println(num2);//150
//boolean字符串形式转成基本类型,“true” ---> true 非“true” ---> false
String str4 = "true";
String str5 = "hello";
boolean flag1 = Boolean.parseBoolean(str4);
boolean flag2 = Boolean.parseBoolean(str5);
System.out.println(flag1);//true
System.out.println(flag2);//false
}
}
package com.cnblogs;
//本类用于实现
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//面试题
Integer integer1 = new Integer(100);
Integer integer2 = new Integer(100);
System.out.println(integer1 == integer2);//false
Integer integer3 = 100;//自动装箱
Integer integer4 = 100;
System.out.println(integer3 == integer4);//true 在整数缓冲区中,地址相同
Integer integer5 = 200;
Integer integer6 = 200;
System.out.println(integer5 == integer6);//false 不在整数缓冲区中,地址不相同
}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/fangweicheng666/p/14984482.html