


逆波兰表达式的代码实现

package com.model.stack; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Stack; /** * @Description:测试类 * @Author: 张紫韩 * @Crete 2021/7/10 7:58 * 演示逆波兰表达式实现的计算器 */ public class StackDemo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { String suffixExpression="30 4 + 5 * 6 -"; // 1+2+3*4-5+6 1 2 + 3 4 * + 5 - 6 + String str="1 2 + 3 4 * + 5 - 6 +"; List<String> list = strToList(suffixExpression); List<String> list1 = strToList(str); System.out.println(calculator(list1)); System.out.println("计算结果:"+calculator(list)); } public static List<String> strToList(String str){ ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); String[] strings = str.split(" "); for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) { list.add(strings[i]); } return list; } // 实现计算器 public static int calculator(List<String> list){ int num1=0; int num2=0; Stack<Integer> numStack = new Stack<>(); Stack<Character> operatorStack = new Stack<>(); for (String str:list){ if (str.matches("\\d+")){ //正则表达式,匹配多个数字 numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(str)); }else{ num2=numStack.pop(); num1=numStack.pop(); int res1 = res(num1, num2, str); numStack.push(res1); } } return numStack.pop(); } public static int res(int num1,int num2,String operator){ int res=0; switch (operator){ case "+": res=num1+num2; break; case "-": res=num1-num2; break; case "*": res=num1*num2; break; case "/": res=num1/num2; break; default: break; } return res; } }

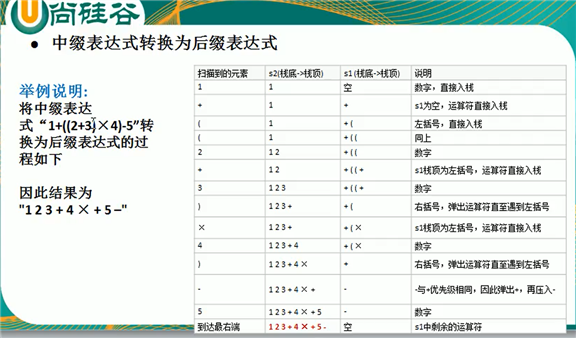
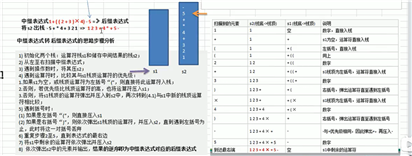
中缀转后缀代码实现:
package com.model.stack; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import java.util.Stack; /** * @Description:测试类 * @Author: 张紫韩 * @Crete 2021/7/10 9:48 * 中缀表示转为后缀表达的代码实现 */ public class StackDemo05 { public static void main(String[] args) { String infixStr = "10+((2+3)*4)-20";//中缀表达式 List<String> list = strToList(infixStr); for (String str : list) { System.out.println(str); } System.out.println(infixToPostFix(list)); } public static List<String> strToList(String str) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); String strKeep = ""; for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) { if (!(str.charAt(i) >= ‘0‘ && str.charAt(i) <= ‘9‘)) {//是字符直接加入 list.add(String.valueOf(str.charAt(i))); } else {//不是操作符,需要判断是否是多位数 strKeep += str.charAt(i); if (i == str.length() - 1) { list.add(strKeep); } else if (!(str.charAt(i + 1) >= ‘0‘ && str.charAt(i + 1) <= ‘9‘)) { list.add(strKeep); strKeep = ""; } } } return list; } public static String infixToPostFix(List<String> list) { String postfixStr = ""; Stack<String> stack1 = new Stack<>(); Stack<String> stack2 = new Stack<>(); for (String str : list) { if (str.matches("\\d+")) { stack2.push(str); } else if (str.equals("(") || str.equals(")")) {//小括号 if (str.equals("(")) { stack1.push(str); } else { while (true) { String str1 = stack1.pop(); if (str1.equals("(")) { break; } stack2.push(str1); } } } else {//运算符,其他情况都是直接压入栈1, while (stack1.size() != 0 && priority(stack1.peek()) >= priority(str)) { stack2.push(stack1.pop()); } stack1.push(str);// } } while (true) { if (stack1.isEmpty()) { break; } stack2.push(stack1.pop()); } while (true) { if (stack2.isEmpty()) { break; } postfixStr = stack2.pop() + " " + postfixStr; } return postfixStr.trim(); } // public static void operator(Stack<String> stack1, Stack<String> stack2, String str) { // try { // if (stack1.peek().equals("(") || stack1.isEmpty()) { // stack1.push(str); // } else if (priority(stack1.peek()) < priority(str)) {//大于栈顶的优先级 // stack1.push(str); // } else {//小于等于栈顶的优先级 // stack2.push(stack1.pop()); // operator(stack1, stack2, str); // } // } catch (Exception e) { // System.out.println(e.getMessage()); // } // } // 返回操作符的优先级 public static int priority(String str) { if (str.charAt(0) == ‘+‘ || str.charAt(0) == ‘-‘) { return 0; } else if (str.charAt(0) == ‘*‘ || str.charAt(0) == ‘/‘) { return 1; } else { return -1; } } }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/zzhAylm/p/14993471.html