面向对象与面向过程
面向对象编程(Object-Oriented Programming,OOP )
break 跳出switch语句、结束循环return 结束方法,返回一个结果static
package com.kuang.oop.demo01;
/**
* 值传递与引用传递
*
* @author maple_w
* Created on 21/07/12 012 15:08
*/
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
System.out.println(a); // 1
Demo01.change(a);
System.out.println(a); // 1
Person person = new Person();
System.out.println(person.name); // null
Demo01.change(person);
System.out.println(person.name); // name
}
// 值传递
public static void change(int a) {
a = 10;
}
// 引用传递,但本质上还是值传递
// 这里的person是一个对象,指向的是new出来的person,可以改变其属性
public static void change(Person person) {
person.name = "name";
}
}
class Person {
String name;
}
类与对象的关系:
初始化与创建对象:
new关键字创建对象
在新建类时,即使什么内容不不写,也会自动创建一个构造器方法。
public class Person(){
// 编译时默认自动生成
public Person(){}
}
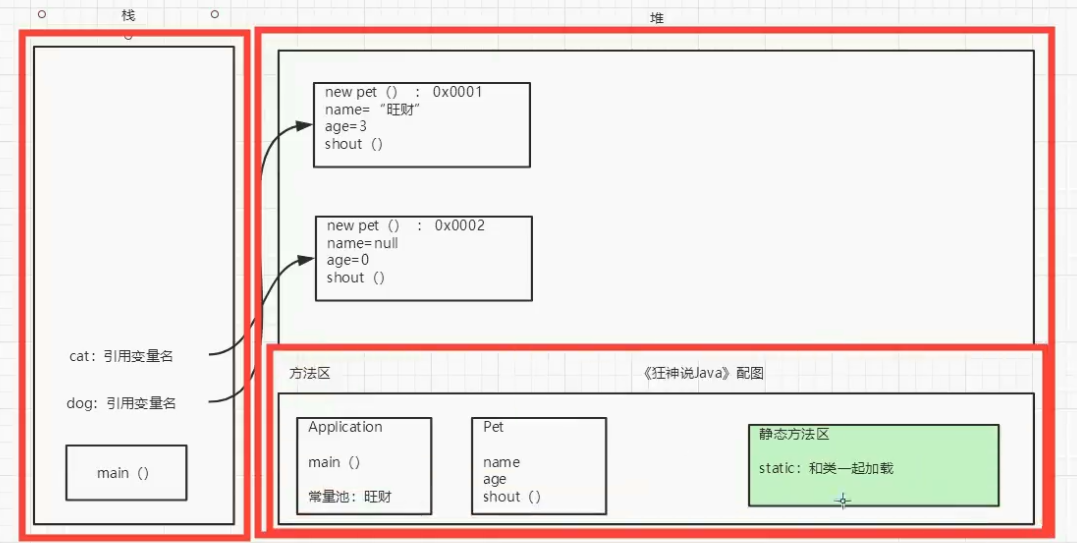
修饰符 属性类型 属性名 = 属性值new 关键字创造对象,要有构造器优点:
extends 的意思是“扩展”,子类是父类的扩展。关系:
extends来表示Java中所有的类都继承自object类;
super;
方法重写;
private 私有的东西无法被继承super:
public class A extends B{}
public class B{}
B b = new A(); // b会调用B的静态方法
重写:需要有继承关系,子类重写父类的方法。方法必须一致,方法体不同。
为什么需要重写:
package com.kuang.oop.demo02;
/**
* 测试类
*
* @author maple_w
* Created on 21/07/12 012 21:50
*/
public class application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 一个对象的实际类型是确定的
// new Student();
// new Person();
// 可以指向的引用类型就不确定了
Student s1 = new Student();
// 父类的引用指向子类
Person s2 = new Student();
Object s3 = new Student();
// 子类重写了父类的方法,执行子类的方法
s2.run(); // son
s1.run(); // son
// s2.eat(); // 无法直接执行
// 对象能够执行的方法主要看左边的类型,和右边关系不大。
// Student 子类,能调用的方法都是自己的或者继承父类的
// Person 父类,可以指向子类,但是不能调用子类独有的方法
}
}
package com.kuang.oop.demo02;
/**
* 人物类
*
* @author maple_w
* Created on 21/07/12 012 21:50
*/
public class Person {
public void run(){
System.out.println("run");
}
}
package com.kuang.oop.demo02;
/**
* 学生类
*
* @author maple_w
* Created on 21/07/12 012 21:50
*/
public class Student extends Person{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("son");
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("eat");
}
}
instanceof 判断类型
package com.kuang.oop.demo03;
/**
* 测试类
*
* @author maple_w
* Created on 21/07/12 012 22:04
*/
public class application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Object > String
// Object > Person > Student
// Object > Person > Teacher
Object o = new Student();
System.out.println(o instanceof Student); // true
System.out.println(o instanceof Person); // true
System.out.println(o instanceof Teacher); // false
System.out.println(o instanceof Object); // true
System.out.println(o instanceof String); // false
System.out.println("==================");
Person p = new Student();
System.out.println(p instanceof Student); // true
System.out.println(p instanceof Person); // true
// System.out.println(p instanceof Teacher); // 编译报错
System.out.println(p instanceof Object); // true
// System.out.println(p instanceof String); // 编译报错
System.out.println("==================");
Student s = new Student();
System.out.println(s instanceof Student); // true
System.out.println(s instanceof Person); // true
// System.out.println(s instanceof Teacher); // 编译报错
System.out.println(s instanceof Object); // true
// System.out.println(s instanceof String); // 编译报错
}
}
package com.kuang.oop.demo04;
/**
* static
*
* @author maple_w
* Created on 21/07/12 012 22:42
*/
public class Student {
private static int age; // 静态变量
private double score; // 非静态变量
public void run(){} // 非静态方法
public static void go(){} // 静态方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
go();
Student.go();
new Student().run();
Student s1 = new Student();
System.out.println(Student.age);
System.out.println(s1.age);
System.out.println(s1.score);
}
}
package com.kuang.oop.demo04;
// 静态导入包
import static java.lang.Math.random;
import static java.lang.Math.PI;
/**
* 静态代码块
*
* @author maple_w
* Created on 21/07/12 012 22:44
*/
public class Person {
{
// 匿名代码块
System.out.println("匿名代码块"); // 2.
}
static {
// 静态代码块 只会执行一次
System.out.println("静态代码块"); // 1.
}
public Person(){
System.out.println("构造方法"); // 3.
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
random();
Person person = new Person();
// 静态代码块
// 匿名代码块
// 构造方法
System.out.println("================");
Person person1 = new Person();
// 匿名代码块
// 构造方法
}
}
abstract 修饰符可以用来修饰方法,也可以修饰类。如果修饰方法,该方法就是抽象方法,如果修饰类,该类就是抽象类。new关键字来创建对象,它是用来让子类继承的。类与接口:
class,声明接口的关键字 interface接口相关:
implements 可以实现多个接口内部类:在一个类的内部再定义一个类
package com.kuang.oop.demo07;
/**
* 外部类
*
* @author maple_w
* Created on 21/07/13 013 8:28
*/
public class Outer {
private int id = 10;
public void out(){
System.out.println("外部类方法");
}
public class Inner{
public void in(){
System.out.println("内部类方法");
}
// 获得外部类的私有属性
public void getID(){
System.out.println(id);
}
}
}
package com.kuang.oop.demo07;
/**
* 测试类
*
* @author maple_w
* Created on 21/07/13 013 8:29
*/
public class application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Outer outer = new Outer();
// 通过外部类实例化 成员内部类
Outer.Inner inner = outer.new Inner();
inner.in(); // 内部类方法
inner.getID(); // 10
}
}
public static class Inner1{
public void in(){
System.out.println("静态内部类");
}
// 无法获取到外部类的属性
}
// 一个java类中可以有多个class类,但只能有一个public class
class A{
}
public class Ounter{
public void method(){
class Inner{
}
}
}
package com.kuang.oop.demo07;
/**
* 匿名内部类
*
* @author maple_w
* Created on 21/07/13 013 8:38
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 匿名内部类,没有名字的初始化类,不用将实例保存到变量中
new Apple().eat();
}
}
class Apple{
public void eat(){
System.out.println("1");
}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/maple-w/p/15004836.html