

package com.model.algorithm; /** * @Description:测试类 * @Author: 张紫韩 * @Crete 2021/7/17 20:04 * 常用的算法---非递归式的二分查找算法 */ public class AlgorithmDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; System.out.println("index="+binarySearch(array, 5)); } public static int binarySearch(int[] array,int targetNum){ if (array.length !=0) { int left = 0; int right = array.length; int mid; while (left <= right) { mid = (left + right) / 2; if (targetNum > array[mid]) { left = mid + 1; } else if (targetNum < array[mid]) { right = mid - 1; } else { return mid; } } } return -1; } }
分治算法:




package com.model.algorithm; /** * @Description:测试类 * @Author: 张紫韩 * @Crete 2021/7/17 21:14 * 常用算法---分治算法 * 汉诺塔 */ public class AlgorithmDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { hanoiTower(4, ‘A‘, ‘B‘, ‘C‘); } public static void hanoiTower(int num,char one,char two,char three){ if (num==1){ System.out.println("移动第"+num+"盘"+one+"->"+three); }else { hanoiTower(num-1, one, three, two); System.out.println("移动第"+num+"盘"+one+"->"+three); hanoiTower(num-1, two, one, three); } } }
动态规划算法:
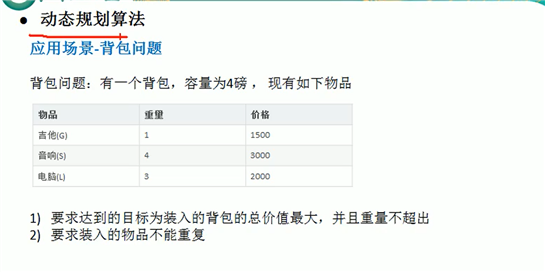



package com.model.algorithm; /** * @Description:测试类 * @Author: 张紫韩 * @Crete 2021/7/18 10:51 * 十种常用算法--动态规划算法 */ public class AlgorithmDemo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] value = {0, 1500, 3000, 2000}; int[] weight = {0, 1, 4, 3}; int m = 4;//背包的重量 int[][] res = new int[value.length][m + 1]; int[][] path = new int[value.length][m + 1]; // 初始化 for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {//第一列的,重量为0 res[i][0] = 0; } for (int i = 0; i < res[0].length; i++) { res[0][i] = 0; } for (int i = 1; i < res.length; i++) { for (int j = 1; j < res[0].length; j++) { if (weight[i] > j) { res[i][j] = res[i - 1][j]; } else { if (value[i]+res[i-1][j-weight[i]]>res[i-1][j]){ res[i][j]=value[i] + res[i - 1][j - weight[i]]; path[i][j]=1; }else { res[i][j]=res[i-1][j]; } } } } for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < res[0].length; j++) { System.out.print(res[i][j] + "\t"); } System.out.println(); } int i = path.length-1; int j=path[0].length-1; while(i>=0&&j>=0){ if (path[i][j]==1){ System.out.printf("第%d个物品放入了背包\n",i); j-=weight[i]; } i--; } } }
KMP算法:


package com.model.algorithm; /** * @Description:测试类 * @Author: 张紫韩 * @Crete 2021/7/18 16:38 * 十种常用算法---KMP算法 */ public class AlgorithmDemo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str2="wxiz"; String str1="aaawxiz"; System.out.println(math01(str1, str2)); } // 暴力匹配,str1中是否包含str2 public static boolean math(String str1,String str2){ for (int i = 0; i < str1.length()-str2.length()+1; i++) { int length = str2.length(); if (str2.equals(str1.substring(i, i+length))){ return true; } } return false; } public static int math01(String str1,String str2){ int i=0; int j=0; char[] char1 = str1.toCharArray(); char[] char2 = str2.toCharArray(); int len1=char1.length; int len2=char2.length; while(i<len1&&j<len2){ if (char1[i]==char2[j]){ i++; j++; }else { i=i-j+1; j=0; } } if (j==len2){ return i-j; }else { return -1; } } }




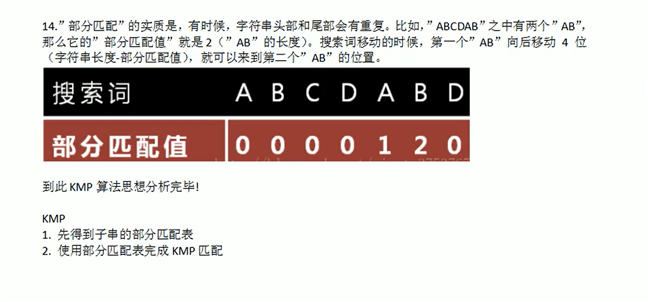

package com.model.algorithm; import java.util.Arrays; /** * @Description:测试类 * @Author: 张紫韩 * @Crete 2021/7/18 16:38 * 十种常用算法---KMP算法(字符串匹配问题) */ public class AlgorithmDemo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("暴力匹配算法"); String str2 = "wxiz"; String str1 = "aaawxiz"; System.out.println(math01(str1, str2)); System.out.println("KMP算法的使用"); String string1 = "BBC ABCDAB ABCDABDABDE"; String string2 = "ABCDABD"; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(kmpNext(string2))); int[] kmpNext = kmpNext(string2); System.out.println(kmpSearch(string1, string2, kmpNext)); } // KMP搜索算法 public static int kmpSearch(String str1,String str2,int[] next){ int j=0; int len2 = str2.length(); for (int i = 0; i < str1.length();i++) { if (str1.charAt(i)==str2.charAt(j)){ j++; }else { // KMP算法的核心,调整j的位置 while(j>0&&str1.charAt(i)!=str2.charAt(j)){ j=next[j-1]; } } if (j==len2){ return i-j+1; } } return -1; } // 得到一个字符串的部分匹配表 public static int[] kmpNext(String str) { int[] next = new int[str.length()]; next[0] = 0;//如果字符串的长度是1返回的部分匹配之就是0 for (int i = 1, j = 0; i < str.length(); i++) { // 当匹配到str.charAt(i)!=str.charAt(j)满足时,我们需要从 next[j-1]获取新的j的值, // 知道我们发现str.charAt(i)==str.charAt(j)成立才退出 // 这时KMP的核心语法 while (j > 0 && str.charAt(i) != str.charAt(j)) { j = next[j - 1]; } // 当匹配到str.charAt(i)==str.charAt(j)满足时,部分匹配表就+1 if (str.charAt(i) == str.charAt(j)) { j++; } next[i] = j; } return next; } // 暴力匹配,str1中是否包含str2 public static boolean math(String str1, String str2) { for (int i = 0; i < str1.length() - str2.length() + 1; i++) { int length = str2.length(); if (str2.equals(str1.substring(i, i + length))) { return true; } } return false; } public static int math01(String str1, String str2) { int i = 0; int j = 0; char[] char1 = str1.toCharArray(); char[] char2 = str2.toCharArray(); int len1 = char1.length; int len2 = char2.length; while (i < len1 && j < len2) { if (char1[i] == char2[j]) { i++; j++; } else { i = i - j + 1; j = 0; } } if (j == len2) { return i - j; } else { return -1; } } }
贪心算法:
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/zzhAylm/p/15025282.html