package com.FirstStage.FifthModule.One;
/**
* 单例设计模式
*/
public class Singleton {
// 2.声明本类类型的引用指向本类类型的对象并使用private static关键字修饰
private static Singleton singleton = null; // 懒汉式
//private static Singleton singleton = new Singleton(); // 饿汉式
// 1.私有化构造方法,使用private关键字修饰
private Singleton() {}
// 3.提供公有的get方法负责将上述对象返回出去,使用private static关键字修饰
private static synchronized Singleton getInstance() { // 懒汉式
/*synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if (null == singleton) {
singleton = new Singleton();
}
return singleton;
}*/
if (null == singleton) {
synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if (null == singleton) {
singleton = new Singleton();
}
}
}
return singleton;
}
/*public static Singleton getInstance() { // 饿汉式
return singleton;
}*/
public void show() {
System.out.println("单例设计模式!");
}
}
package com.FirstStage.FifthModule.One;
public interface Sender {
// 自定义抽象方法来描述发送行为
void send();
}
package com.FirstStage.FifthModule.One;
public class MailSender implements Sender {
@Override
public void send() {
System.out.println("正在发送邮件...");
}
}
package com.FirstStage.FifthModule.One;
public class SmsSender implements Sender {
@Override
public void send() {
System.out.println("正在发送短信...");
}
}
package com.FirstStage.FifthModule.One;
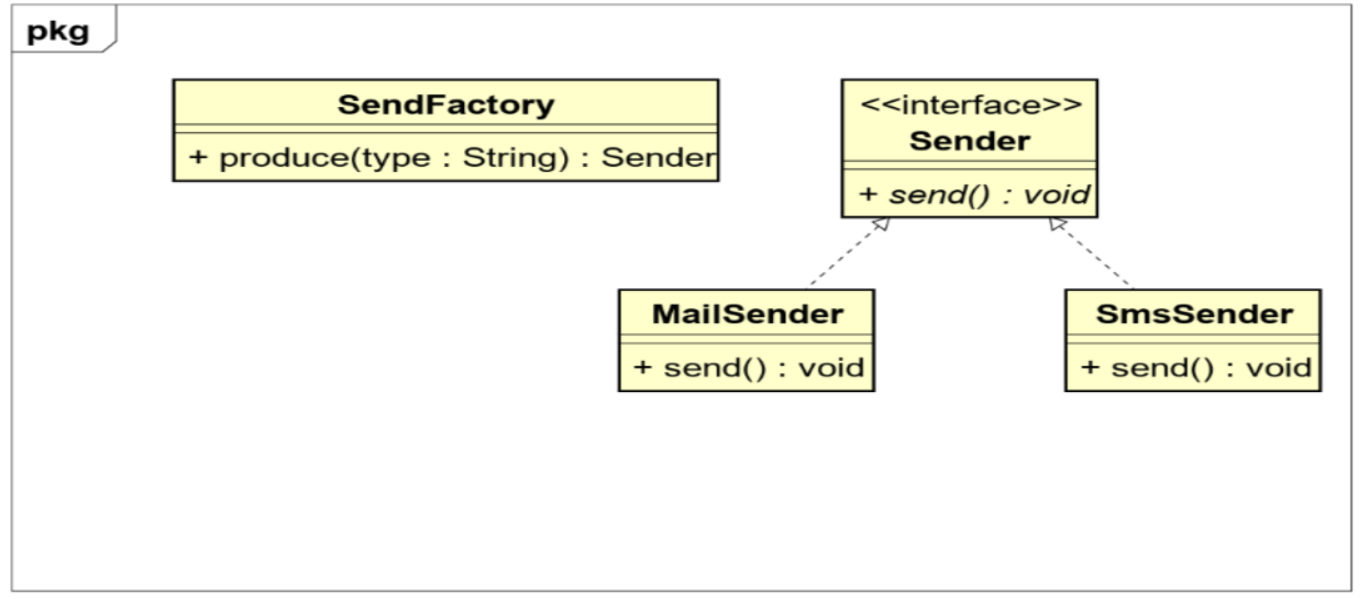
public class SendFactory {
// 自定义成员方法实现对象的创建
// 普通工厂方法模式
public Sender produce(String type) {
//System.out.println("随便");
if ("mail".equals(type)) {
return new MailSender();
}
if ("sms".equals(type)) {
return new SmsSender();
}
return null;
}
// 多个工厂方法模式
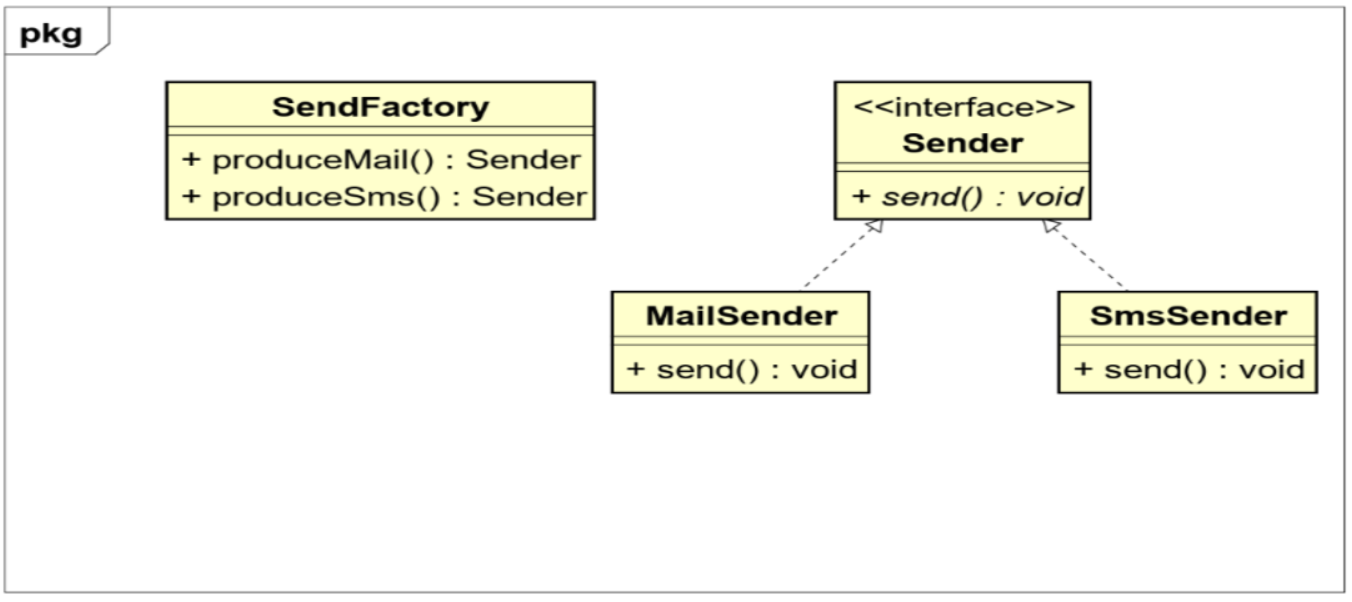
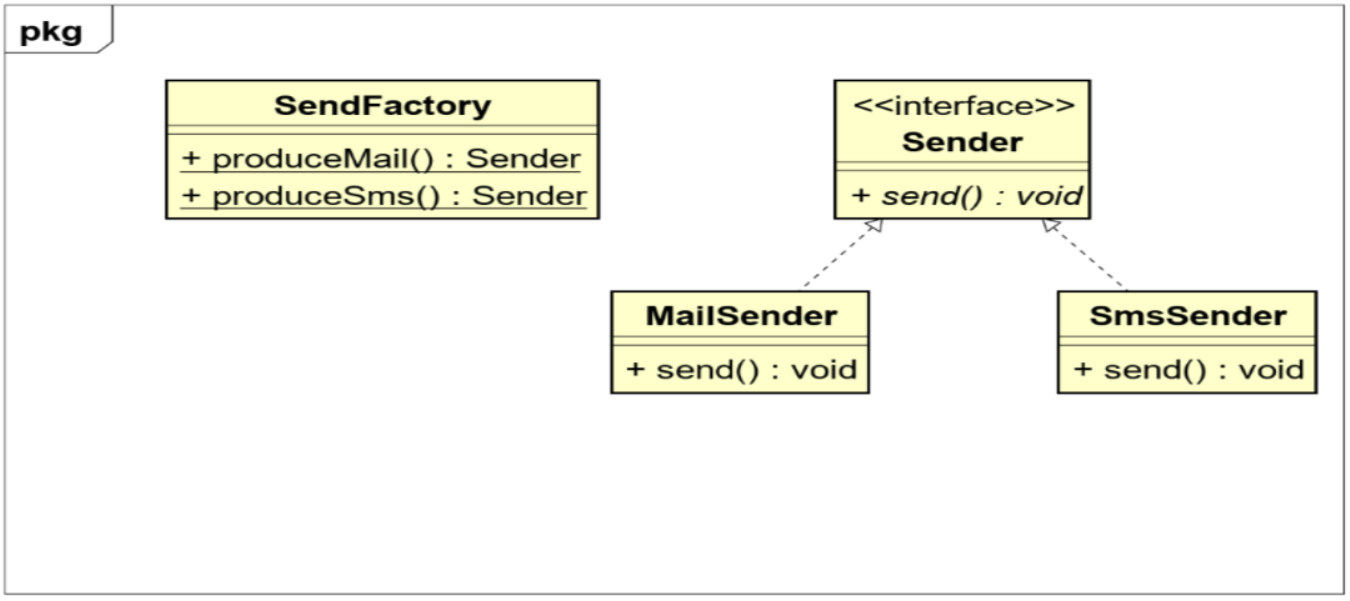
// 加上static静态工厂方法,类层级
public static Sender produceMail() {
return new MailSender();
}
public static Sender produceSms() {
return new SmsSender();
}
}
package com.FirstStage.FifthModule.One;
public class SendFactoryTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 缺点:代码复杂,可读性略差
// 优点:扩展性和可维护性更强! 尤其是在创建大量对象的前提下
// 1.声明工厂类类型的引用指向工厂类的类型的对象
//SendFactory sendFactory = new SendFactory();
// 2.调用生产方法来实现对象的创建
//Sender sender = sendFactory.produce("mail");
//Sender sender = sendFactory.produce("maill");
//Sender sender = sendFactory.produceMail();
Sender sender = SendFactory.produceMail();
// 3.使用对象调用方法来模拟发生的行为
sender.send();
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
// 优点:代码简单,可读性强
// 缺点:拓展性和可维护性略差
Sender sender1 = new MailSender();
sender1.send();
}
}
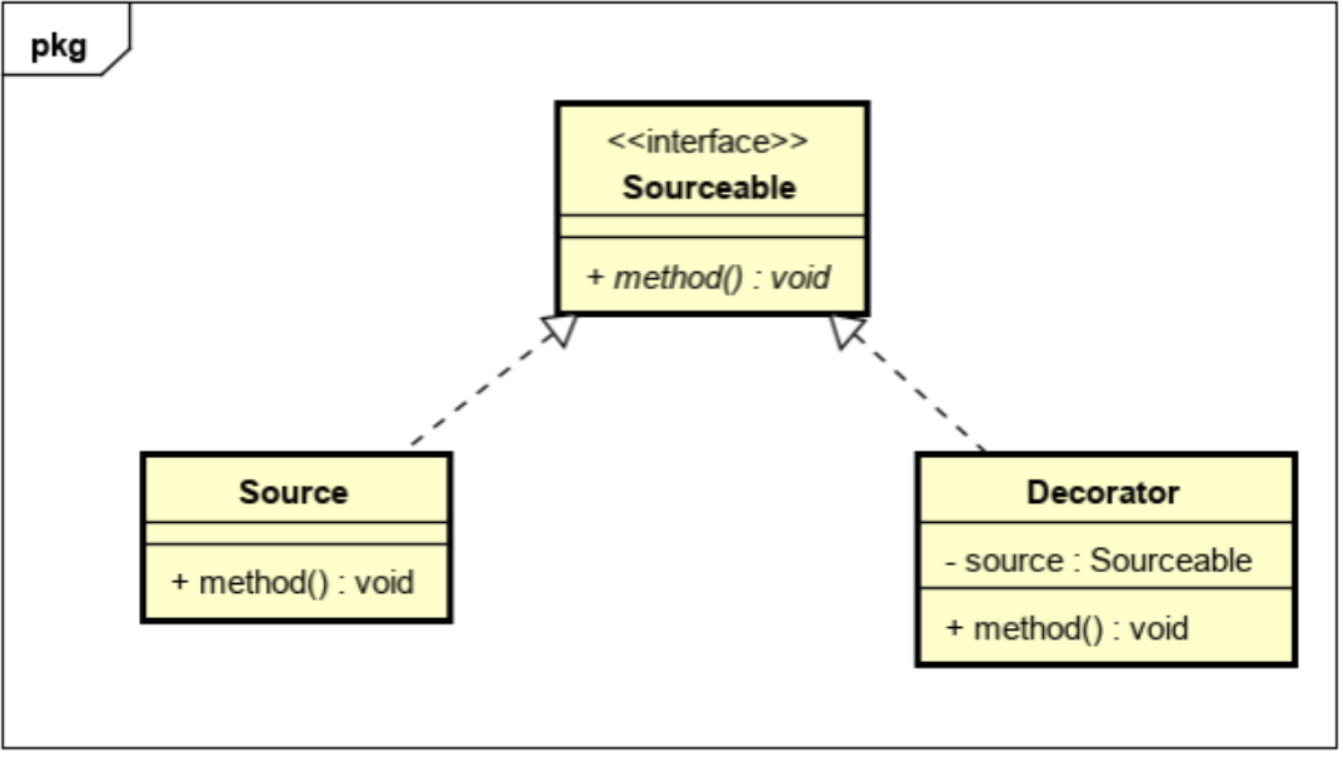
package com.FirstStage.FifthModule.One;
public interface Sourceable {
// 自定义抽象方法
void method();
}
package com.FirstStage.FifthModule.One;
public class Source implements Sourceable {
@Override
public void method() {
System.out.println("素颜美可以如此之美!");
}
}
package com.FirstStage.FifthModule.One;
public class Decorator implements Sourceable {
private Sourceable source; // 合成复用原则
public Decorator(Sourceable source) {
this.source = source;
}
@Override
public void method() {
source.method(); // 保证原有功能不变
System.out.println("化妆之后更美...");
}
}
package com.FirstStage.FifthModule.One;
public class SourceableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sourceable sourceable = new Source();
sourceable.method();
System.out.println("------------------------");
//Sourceable sourceable1 = new Decorator(new Source());
Sourceable sourceable1 = new Decorator(sourceable);
sourceable1.method();
System.out.println("------------------------");
Sourceable sourceable2 = new Proxy();
sourceable2.method();
}
}
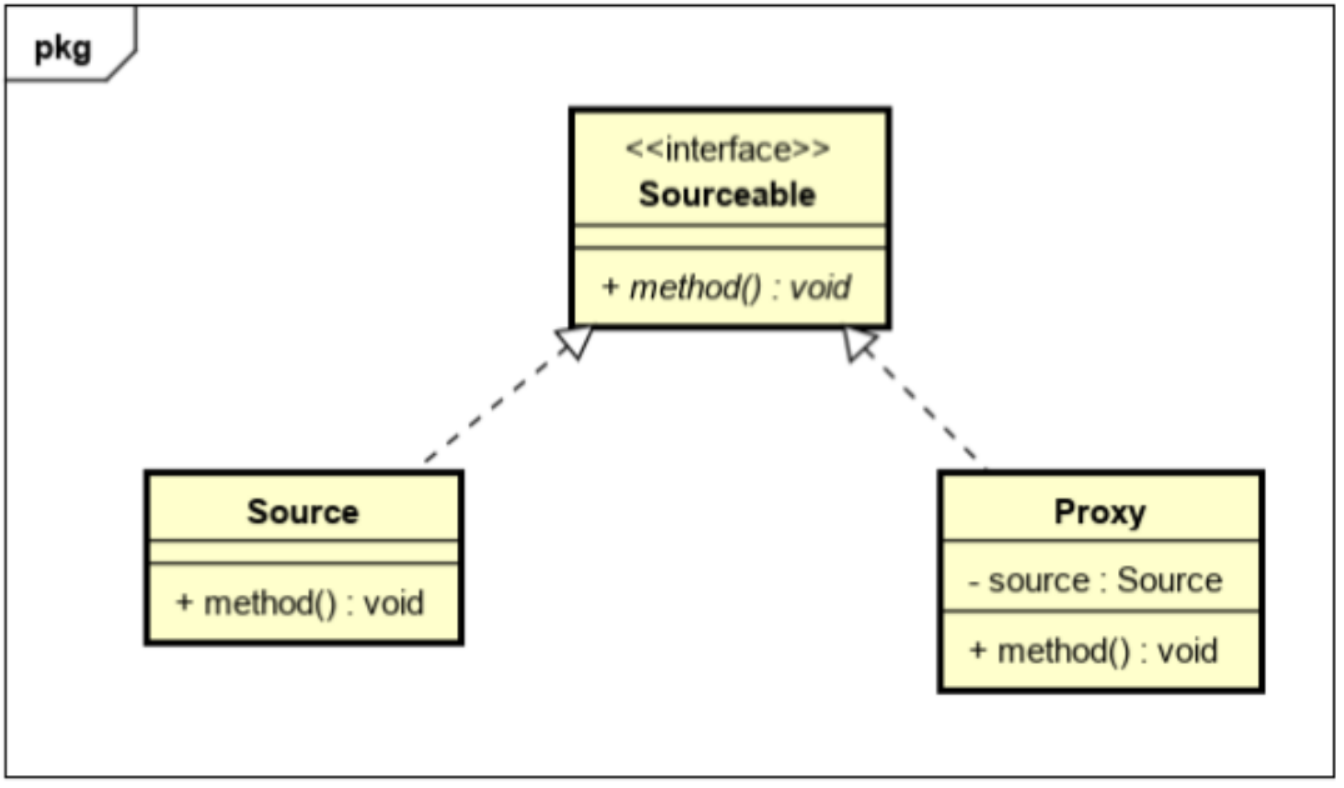
package com.FirstStage.FifthModule.One;
public class Proxy implements Sourceable {
private Source source;
public Proxy() {
source = new Source();
}
@Override
public void method() {
source.method();
System.out.println("我和装饰器模式其实是不一样的!");
}
}
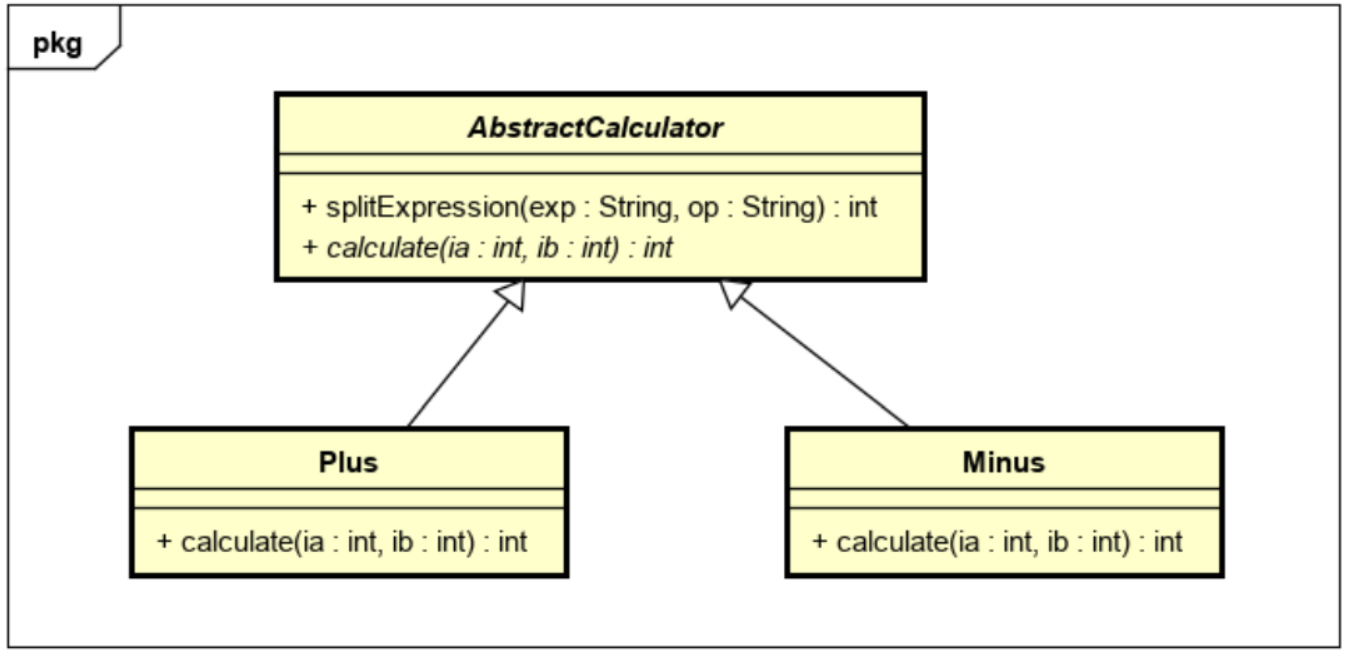
package com.FirstStage.FifthModule.One;
public abstract class AbstractCalculator {
// 自定义成员方法参数指定的表达式按照参数指定的规则进行切割并返回计算结果
public int splitExpression(String exp, String op) {
String[] sArr = exp.split(op);
return calculate(Integer.parseInt(sArr[0]), Integer.parseInt(sArr[1]));
}
// 自定义抽象方法实现运算
public abstract int calculate(int ia, int ib);
}
package com.FirstStage.FifthModule.One;
public class Plus extends AbstractCalculator {
@Override
public int calculate(int ia, int ib) {
return ia + ib;
}
}
package com.FirstStage.FifthModule.One;
public class Minus extends AbstractCalculator {
@Override
public int calculate(int ia, int ib) {
return ia - ib;
}
}
package com.FirstStage.FifthModule.One;
public class AbstractCalculatorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractCalculator abstractCalculator = new Plus();
int res = abstractCalculator.splitExpression("1+1", "\\+");
System.out.println("最终的运算结果是: " + res); // 2
}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/china-soldier/p/15031805.html