了解什么是注解? Annotation
Annotation是从JDK5.0 开始引入的技术
注解的作用:
注解的格式:
以 @[注释名] 的形式在代码中存在,并且还可以添加一些参数
e.g. @SuppressWarnings(value = "unchecked")
注解 可以用在哪?
package annotation;
// 什么是注解
public class Demo01 extends Object{
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
// 重写的注解
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString();
}
}
内置注解
1、 @Override : 定义在java.lang. 包下,此注释只适用于修饰方法,表示一个方法声明打算重写超类/父类中的另一个方法声明
2、@Deprecated : 定义在java.lang.Deprecated中,可以用于修饰方法、属性、类,表示不鼓励程序员使用这样的元素,通常是因为它很危险(过时)或者存在更好地选择。
3、@SuppressWarnings : 定义在java.lang.SuppressWrnings中, 也叫正压警告,用来抑制编译时的警告信息。
package annotation;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test();
}
@Deprecated // 不推荐程序员使用
public static void test() {
System.out.println("Deprecated!");
}
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public void test02() {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
元注解 meta-annotation
元注解的作用
负责注解其他注解
Java定义了4个标准的meta-annotation类型,他们被用来提供对其他annotaiton类型作说明
这些类型和他们所支持的类放在 java.lang.annotation包中

package annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/*
元注解
*/
@MyAnnotation //not applitable to class
public class Demo03 {
@MyAnnotation
public void test() {
}
}
//定义一个注解类
// Target表示我们的注解可以用在哪些地方
@Target(value ={ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE} )
// Retention 表示注解在什么地方还有效
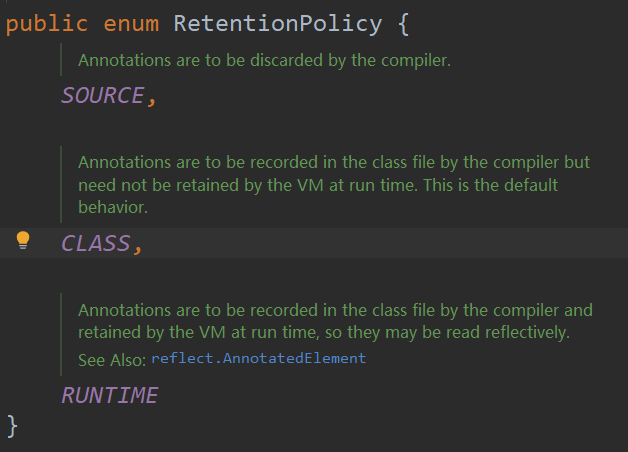
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented // 表示是否将为注解生成在 Javadoc中
@Inherited // 子类可以继承父类的注解
@interface MyAnnotation {
}
自定义注解
1、使用 @interface 自定义注解时,自动继承了java.lang.annotation.Annotation接口
2、细节
@interface 用来声明一个注解
具体格式: public @interface 注解名 { }
其中的每一个方法实际上是声明了一个配置参数
方法的名称就是参数的名称
返回值类型就是参数的类型 (基本数据类型,Class,String,enum)
可以通过default来声明参数的默认值
如果只有一个参数成员,一般参数名为value
注解元素必须要有值 定义注解元素时,经常使用空字符串,0作为默认值
package annotation;
// 自定义注解
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
public class Demo04 {
// 注解可以显示赋值,若没有默认值,就必须给注解赋值,否则将报错
@MyAnnotation01(name = "lzh")
public void test() {
}
@MyAnnotation02("lzh")
public void test2() {
}
}
@Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface MyAnnotation01 {
// 注解的参数 : 参数类型 + 参数名();
String name() default "";
int age() default 0;
int id() default -1; // 如果默认值为-1,代表不存在
String[] schools() default {"清华大学"};
}
@Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface MyAnnotation02{
String value(); // 只有一个参数 默认为value
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/xili-sanriyue/p/15037758.html