1、定义
定义一个操作中的算法骨架,而将算法的一些步骤延迟到子类中,使得子类可以不改变该算法结构的情况下重定义该算法的某些特定步骤。它是一种类行为型模式。
2、优缺点分析
优点:
缺点:
3、UML类图
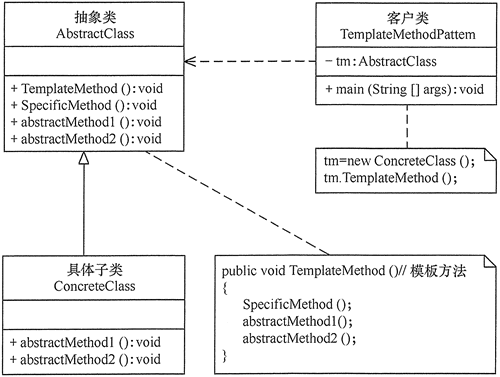
模板方法模式包含以下主要角色:
(1)抽象类/抽象模板(Abstract Class)
抽象模板类:负责给出一个算法的轮廓和骨架,由一个模板方法和若干个基本方法构成。这些方法的定义如下:
①模板方法:定义了算法的骨架,按某种顺序调用其包含的基本方法。
②基本方法:是整个算法中的一个步骤,包含以下几种类型。
( 2)具体子类/具体实现(Concrete Class)
具体实现类,实现抽象类中所定义的抽象方法和钩子方法,它们是一个顶级逻辑的一个组成步骤。
4、代码实现
1 /** 2 * @author it-小林 3 * @desc 抽象类 4 * @date 2021年08月03日 11:33 5 */ 6 public abstract class AbstractClass { 7 8 //模板方法 9 public void templateMethod(){ 10 specificMethod(); 11 abstractMethod1(); 12 abstractMethod2(); 13 } 14 15 //具体方法 16 public void specificMethod(){ 17 System.out.println("抽象类中的具体方法被调用"); 18 } 19 20 //抽象方法1 21 public abstract void abstractMethod1(); 22 23 //抽象方法2 24 public abstract void abstractMethod2(); 25 }
1 /** 2 * @author it-小林 3 * @desc 具体子类 4 * @date 2021年08月03日 11:37 5 */ 6 public class ConcreteClass extends AbstractClass{ 7 8 @Override 9 public void abstractMethod1() { 10 System.out.println("抽象方法1的实现被调用..."); 11 } 12 13 @Override 14 public void abstractMethod2() { 15 System.out.println("抽象方法2的实现被调用..."); 16 } 17 }
1 /** 2 * @author it-小林 3 * @desc 测试类 4 * @date 2021年08月03日 11:38 5 */ 6 public class Client { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 AbstractClass template = new ConcreteClass(); 9 template.templateMethod(); 10 } 11 }
4、应用场景
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/linruitao/p/15067838.html