SEO,EPO 问题全文的思想精神就是:
The basic idea is to extract triples in two cascade steps.
采用的方法是pipeline,先抽取subject,然后再抽取与这个relation-specific 相关的object
we model the relations as functions that map subjects to object, which makes it crucially different from previous works.
这句话读着十分生硬,也不懂是什么意思。感觉有点儿故弄玄虚
directly model the triples and design a traning objective right at the triple level.at the triple level,是因为之前的模型都是将二者但需训练。$$
\begin{gather}
& \prod{j=1}^{|D|} [\prod{(s,r,o)\in T_j} p((s,r,o)|xj)] \
& = \prod{j=1}^{|D|} [\prod_{(s,\in T_j} p(s|xj) \prod{(r,o)\in T_j | s} p((r,o)|s,xj)] \
& = \prod{j=1}^{|D|} [\prod_{(s,\in T_j} p(s|xj) \prod{r\in T_j | s} p(o|s,xj) \prod{(r \in R \backslash T_j|s)} p((r,o)|s,x_j)] \
\end{gather}
$$
上面这个公式无非就是一个条件概率公式。
公式(3)便是这个模型标注想法的来源:
subject以这种方式,我们就可以将每种relation 建模成一个函数,这个函数可以将subjects 映射成 objects,这种方式正和将(subject,object)对分类的方法相反。
所以我们就得到了模型的两个步骤:
step 1: first run the subject tagger to find all possible subjects in the sentence
for each subject found, apply relation-specific object taggers to find all relevant relations and the corresponding objects.先上模型结构图,如下:
其中subject tagger 的损失函数是一个极大似然估计。
在解析subject的时候,采取的方法是最近的start-end匹配。
其实这个与其自身结构有关,因为模型在抽取subject之后,会一次性抽取和某个relation相关的objects,而objects 可不止一个,所以会形成多个三元组。以Figure 2的那张图为例: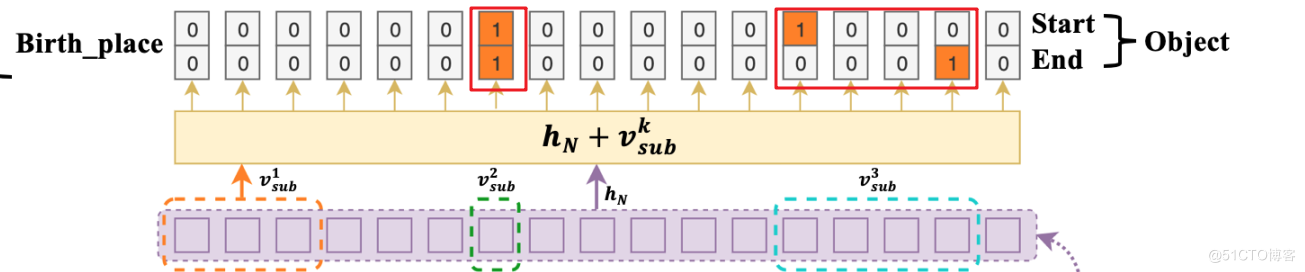
这张图就同时解析出(Jackie R. Brown, Birth_place, Washington) 和 (Jackie R. Brown, Birth_place, United States of America)
原文:https://blog.51cto.com/lawsonabs/3260058