Java语言规定字符串常量必须用双引号“”括起,例如:
System.out.println("JAVA!");
Java的任何字符串常量都是String类的对象,若没有命名,Java自动为其创建一个·匿名String类对象,成为匿名String类的对象。
1.用一个已创建的字符串str创建另一个字符串
1 String s; 2 s=new String("JAVA");
2.用字符数组创建一个字符串对象
1 char[] c={‘h‘,‘e‘,‘l‘,‘l‘,‘o‘}; 2 String str=new String(c); 3 char[] data={‘一‘,‘二‘,‘三‘,‘四‘,‘五‘};//Java中汉字占一个字符 4 String str1=new String(data);
1.求字符串长度
//public int length() String s=new String("JAVA"); int n=s.length();
字符串中字符的位置从0开始最后一个字符的位置时length()-1
2.查找单个字符或字符串
(1)public char charAt(int index):返回当前串对象下标index处的字符
char ch=s.charAt(2);//ch=‘V‘
(2)public int indexOf(String s):串从当前字符串头开始检索字符串s,并返回首次出现s的索引位置。若找不到则返回-1
(3)public int indexOf(String s,int start):从当前下标start处检索,并返回首次出现s的索引位置,若找不到,则返回-1
(4)public String substring(int begin):返回当前串中下标begin开始到串尾的字串
(5)public String substring(int begin,int end):返回当前串中从下标begin开始到end-1结束的字串
3.字符串比较方法
(1)public int compareTo(String s):按字典顺序与参数s指定的字符串比较大小
当前字符串==s,返回0;
当前字符串>s,返回正数;
当前字符串<s,返回负数;
(2)public boolean equals(String str):比较当前字符串对象的实体是否与参数str指定字符串的实体相同,如果相同返回值为true,否则返回值为false。
(3)public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str):在不区分字母的大小写时,比较当前字符串对象的实体是否与参数str指定字符串的实体相同,相同返回true,不同返回false。
代码测试:
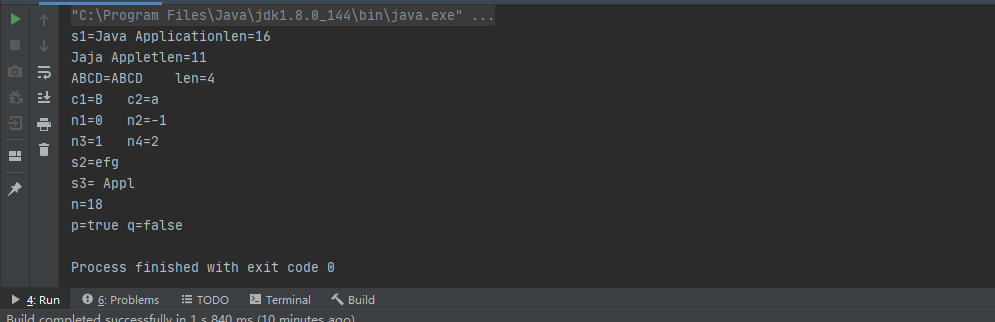
1 package ClassTest; 2 /* 3 类String 4 */ 5 public class StringTest1 { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 String s1="Java Application"; 8 char cc[]={‘J‘,‘a‘,‘j‘,‘a‘,‘ ‘,‘A‘,‘p‘,‘p‘,‘l‘,‘e‘,‘t‘}; 9 String str=new String(cc); 10 //字符串长度 11 int len=str.length(); 12 int len1=s1.length(); 13 int len2="ABCD".length(); 14 //查找单个字符 15 char c1="12ABG".charAt(3); 16 char c2=s1.charAt(3); 17 //查找字符串 18 int n1="abj".indexOf(97); 19 int n2="s1".indexOf(‘d‘); 20 int n3="abj".indexOf("bj",0); 21 int n4=s1.indexOf("va",1); 22 //返回当前串中特定字串 23 String s2="abcdefg".substring(4);//下标到尾 24 String s3=s1.substring(4,9);//下标到下标 25 System.out.println("s1="+s1+"len="+len1); 26 System.out.println(str+"len="+len); 27 System.out.println("ABCD=ABCD"+" len="+len2); 28 System.out.println("c1="+c1+" c2="+c2); 29 System.out.println("n1="+n1+" n2="+n2); 30 System.out.println("n3="+n3+" n4="+n4); 31 System.out.println("s2="+s2); 32 System.out.println("s3="+s3); 33 34 String s="sususush"; 35 int n=s.compareTo("aaaa"); 36 System.out.println("n="+n); 37 38 String s4=new String("ssss"); 39 String s5=new String("ssss"); 40 String s6=new String("asd"); 41 boolean p,q; 42 p=s4.equals(s5); 43 q=s4.equals(s6); 44 System.out.println("p="+p+" q="+q); 45 } 46 }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/jin0622/p/15100768.html