二分图又称作二部图,是图论中的一种特殊模型。 设G=(V,E)是一个无向图,如果顶点V可分割为两个互不相交的子集(A,B),并且图中的每条边(i,j)所关联的两个顶点i和j分别属于这两个不同的顶点集(i in A,j in B),则称图G为一个二分图。
给多组点,我们该如何判断能不能构成二分图呢?
至少有两个顶点且没有奇环的图才能构成二分图
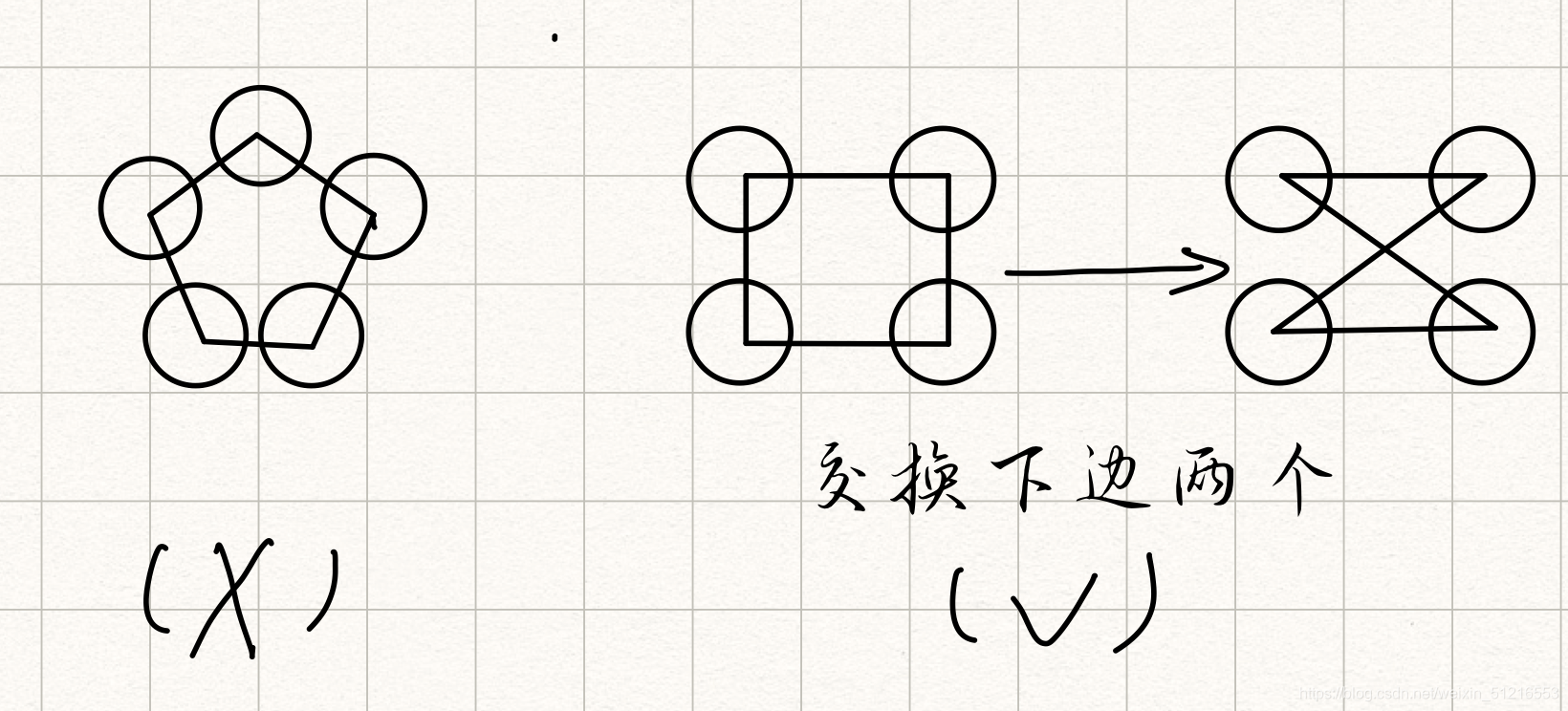
判断二分图最常见的方法就是染色法,顾名思义,染色法就是使用黑白两种颜色对所有点都染上色,且相连的点点颜色不同,如果可以实现,则是二分图
可以用dfs和bfs去写,我这里给出bfs的代码
bool bfs(){
queue<int>q;
q.push(1);//将第一个点塞进去
co[1] = 1;//染色颜色1
while (!q.empty()){
int u = q.front();q.pop();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
if(tr[u][i]){//用的是邻接矩阵,所以判断u到i是否相连
if(!co[i]){//如果没有染色
co[i] = co[u] == 1 ? 2 : 1;//就染上和u不同的颜色
q.push(i);//塞进队列
}
else if(co[i] == co[u])return false;//如果颜色和u相同,说明出现奇环,返回false即可
}
}
}
return true;
}
如果是一边加边,一边询问能否构成二分图
种类并查集
类似于上次那个食物链的题,1-n是假设A是在左边,n+1 - 2*n是假设A在右边,find(A)应该等于find(B+n),find(A + n)应该等于find(B), 每次给出新的边的时候,就判断一下,如果符合,就和类似于上面去emerge一下
给定一个二分图G,在G的一个子图M中,M的边集中的任意两条边都不依附于同一个顶点,则称M是一个匹配。选择这样的边数最大的子集称为图的最大匹配问题(maximal matching problem)。
通俗点讲,就是海王们的配对
有一堆男海王,一堆女海王,各自都有倾慕的对象们,你是月老,负责牵线,在不考虑gay的情况下,要尽可能多的去给男海王与女海王来一一配对,这就是二分图的最大匹配
是不是及其生动形象
有一场宴会,男孩和女孩组成舞伴,并且他们必须互相喜欢才能成为舞伴,一个男孩可能喜欢0个或多个女孩,一个女孩也可以喜欢0个或多个男孩,但一个男孩和他喜欢地女孩成为舞伴以后就不能和其他他喜欢的女孩成为舞伴,女孩亦是如此,问最多可以有多少对舞伴
你以为是 z 绿了y,但一开始其实是 y 要绿了z,所以到底是谁先绿了谁,有待商榷(bushi
代码实现的过程包括两部分:dfs函数与一个for循环
bool dfs(int u){ //邻接矩阵建图的代码
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){//对 u 这个点去循环他喜欢的人
if(!vis[i] && tr[u][i]){//如果他喜欢的 i 没有出现在此次x找舞伴的过程中
vis[i] = 1;
if(!link[i] || dfs(link[i])){//如果 i 没有舞伴,或者 i 的舞伴可以绿他,就安排 i 和 u 在一起
link[i] = u;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
bool dfs(int u){ //链式前向星建图的代码
for(int i = head[u]; i != -1; i = tr[i].next){
int v = tr[i].to;
if(!vis[v]){
vis[v] = 1;
if(link[v] == -1 || dfs(link[v])){
link[v] = u;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){//对每个人都去找舞伴
mem(vis, 0);
if(dfs(i))++ans;
}
邻接矩阵建图法:\(O(n^3)\),n是点数
链式前向星建图法: \(O(n*m)\),m是总边数
二分图中的最大匹配数等于这个图中的最小点覆盖数
什么是最小点覆盖数?
每个点覆盖以他为端点的所有边,选择最少的点来覆盖所有的边,这些点个个数就叫做最小点覆盖数
(选最少点海王,能联系到其他的所有的海王
这里就不证明了,下次一定下次一定(bushi
和上面那个差不多,这里说的是两个人之间有个"romantically involved"的亲密关系,让你找到一个集合,使得所有点没有联系,就是求最大独立集。
最大独立集 = 点总数 - 最大匹配数
我这里使用的是链式前向星建图法
注意??:链式前向星是存边,所以得开大一点的空间,顺便吐槽一下hduoj,数组开的不够大你居然爆TLE,而不是RE,害我我debug一个点都不知道哪里有问题,重写一遍才意识到,可恶至极!
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<sstream>
#include<cstring>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define endl ‘\n‘
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define MAX 500 + 50
#define mod 1000000007
#define lowbit(x) (x & (-x))
#define sd(n) scanf("%d",&n)
#define sdd(n,m) scanf("%d %d",&n,&m)
#define pd(n) printf("%d\n", (n))
#define pdd(n,m) printf("%d %d\n",n, m)
#define sddd(n,m,z) scanf("%d %d %d",&n,&m,&z)
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0)
#define mem(a,b) memset((a),(b),sizeof(a))
typedef long long ll ;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
//不开longlong见祖宗!不看范围见阎王!
inline int IntRead(){char ch = getchar();int s = 0, w = 1;while(ch < ‘0‘ || ch > ‘9‘){if(ch == ‘-‘) w = -1;ch = getchar();}while(ch >= ‘0‘ && ch <= ‘9‘){s = s * 10 + ch - ‘0‘;ch = getchar();}return s * w;}
int k, n, m, x, ans, tot;
int link[MAX];
bool vis[MAX];
int head[MAX];
struct ran{
int to, next;
}tr[100005];
string s;
char y;
void add(int u, int v){//链式前向星建图
tr[++tot].to = v;
tr[tot].next = head[u];
head[u] = tot;
}
bool dfs(int u){
for(int i = head[u]; i != -1; i = tr[i].next){
int v = tr[i].to;
if(!vis[v]){
vis[v] = 1;
if(link[v] == -1 || dfs(link[v])){
link[v] = u;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void init(){//多组输入,一定要记得初始化
mem(link, -1);
mem(head, -1);
ans = tot = 0;
}
int main(){
while (cin>>n) {
init();
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
cin>>s;cin>>y>>k>>y;//这个题的读入真傻逼,奇奇怪怪的
while (k--) {
sd(x);
add(i, x);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
mem(vis, 0);
if(dfs(i))++ans;
}
cout<<n - ans/ 2<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
有一群学生,一些人可能彼此认识,一些人可能不认识,认识不存在传染性,如A认识B,B认识C,但A不能就此认识C
你需要将所有学生分成两组,同一组的学生互不认识,如果可以的话,再将认识的两个人放在一个房间里,问最多能需要多少个房间;如果不能就输出No
这个题首先要判能不能构成二分图
如果可以构成,再继续使用匈牙利算法去进行二分图最大匹配
这次用的是邻接矩阵的建图方法
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<sstream>
#include<cstring>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define endl ‘\n‘
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define MAX 200 + 50
#define mod 1000000007
#define lowbit(x) (x & (-x))
#define sd(n) scanf("%d",&n)
#define sdd(n,m) scanf("%d %d",&n,&m)
#define pd(n) printf("%d\n", (n))
#define pdd(n,m) printf("%d %d\n",n, m)
#define sddd(n,m,z) scanf("%d %d %d",&n,&m,&z)
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0)
#define mem(a,b) memset((a),(b),sizeof(a))
typedef long long ll ;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
//不开longlong见祖宗!提交不看数据范围见祖宗!
inline int IntRead(){char ch = getchar();int s = 0, w = 1;while(ch < ‘0‘ || ch > ‘9‘){if(ch == ‘-‘) w = -1;ch = getchar();}while(ch >= ‘0‘ && ch <= ‘9‘){s = s * 10 + ch - ‘0‘;ch = getchar();}return s * w;}
int n, m, x, y;
bool vis[MAX];
int tr[MAX][MAX];
int co[MAX];
int link[MAX];
bool bfs(){
queue<int>q;
q.push(1);
co[1] = 1;
while (!q.empty()){
int u = q.front();q.pop();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
if(tr[u][i]){
if(!co[i]){
co[i] = co[u] == 1 ? 2 : 1;
q.push(i);
}
else if(co[i] == co[u])return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
bool dfs(int u){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
if(!vis[i] && tr[u][i]){
vis[i] = 1;
if(!link[i] || dfs(link[i])){
link[i] = u;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void init(){
mem(tr, 0);
mem(link, 0);
mem(co, 0);
}
int main(){
while (sdd(n, m) != EOF) {
init();
while (m--) {
sdd(x, y);
tr[x][y] = 1;
}
if(!bfs() || n == 1)cout<<"No\n";//n=1有坑!
else{
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
mem(vis, 0);
if(dfs(i))++ans;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/chelsea0901/p/15110294.html