来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/nxf-rabbit75/p/11276195.html
1.tf.gather
|
1
|
tf.gather(params, indices, validate_indices=None, name=None, axis=0) |
功能:根据提供的
indices在axis这个轴上对params进行索引,拼接成一个新的张量。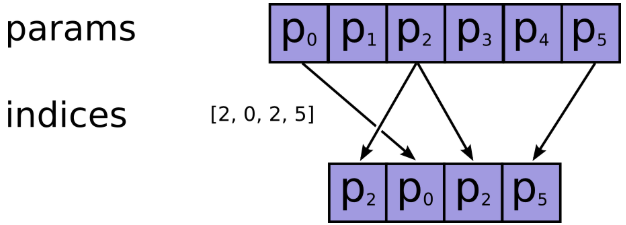
参数:
- params:需要被索引的张量
- indices:必须为整数类型,如int32,int64等,注意检查不要越界了,因为如果越界了,如果使用的
CPU,则会报错,如果在GPU上进行操作的,那么相应的输出值将会被置为0,而不会报错,因此认真检查是否越界。 - name:返回张量名称
返回维度: params.shape[:axis] + indices.shape + params.shape[axis + 1:]
举例:
|
1
2
|
import tensorflow as tftemp4=tf.reshape(tf.range(0,20)+tf.constant(1,shape=[20]),[2,2,5]) |
(1)当indices是向量时,输出的形状和输入形状相同,不改变
|
1
|
temp5=tf.gather(temp4,[0,1],axis=0) #indices是向量 |
(2)当indices是数值时,输出的形状比输入的形状少一维
|
1
|
temp6=tf.gather(temp4,1,axis=1) #indices是数值<br># (2,2,5)[:1]+()+(2,2,5)[2:]=(2,5) |
(3)当indices是多维时
|
1
|
temp8=tf.gather(temp4,[[0,1],[3,4]],axis=2) #indices是多维的<br># (2,2,5)[:2]+(2,2)+(2,2,5)[3:]=(2,2,2,2)<br>temp8: |
bert源码:
2.tf.gather_nd
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
tf.gather_nd( params, indices, name=None, batch_dims=0) |
功能:类似于tf.gather,不过后者只能在一个维度上进行索引,而前者可以在多个维度上进行索引,
参数:
- params:待索引输入张量
- indices:索引,int32,int64,indices将切片定义为params的前N个维度,其中N = indices.shape [-1]
- 通常要求indices.shape[-1] <= params.rank(可以用np.ndim(params)查看)
- 如果等号成立是在索引具体元素
- 如果等号不成立是在沿params的indices.shape[-1]轴进行切片
- name=None:操作的名称(可选)
返回维度: indices.shape[:-1] + params.shape[indices.shape[-1]:],前面的indices.shape[:-1]代表索引后的指定形状
举例:
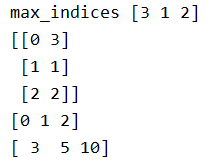
3.tf.batch_gather
作用:支持对张量的批量索引.注意因为是批处理,所以indices要有和params相同的第0个维度。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
import tensorflow as tftensor_a = tf.Variable([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]])tensor_b = tf.Variable([[0],[1],[2]],dtype=tf.int32)tensor_c = tf.Variable([[0],[0],[0]],dtype=tf.int32)with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) print(‘gather‘) print(sess.run(tf.gather(tensor_a,tensor_b))) print(sess.run(tf.gather(tensor_a,tensor_c))) print(‘gather_nd‘) print(sess.run(tf.gather_nd(tensor_a, tensor_b))) print(sess.run(tf.gather_nd(tensor_a, tensor_c))) print(‘batch_gather‘) print(sess.run(tf.batch_gather(tensor_a, tensor_b))) print(sess.run(tf.batch_gather(tensor_a, tensor_c))) |
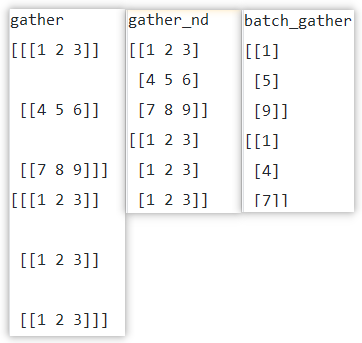
4.tf.where
|
1
|
tf.where(condition, x=None, y=None, name=None) |
作用: 返回condition为True的元素坐标(x=y=None)
- condition:布尔型张量,True/False
- x:与y具有相同类型的张量,可以使用条件和y进行广播。
- y:与x具有相同类型的张量,可以在条件和x的条件下进行广播。
- name:操作名称(可选)
返回维度: (num_true, dim_size(condition)),其中dim_size为condition的维度。
(1)tf.where(condition)
- condition是bool型值,True/False
- 返回值,是condition中元素为True对应的索引
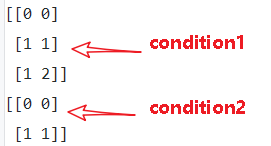
(2)tf.where(condition, x=None, y=None, name=None)
- condition, x, y 相同维度,condition是bool型值,True/False
- 返回值是对应元素,condition中元素为True的元素替换为x中的元素,为False的元素替换为y中对应元素
- x只负责对应替换True的元素,y只负责对应替换False的元素,x,y各有分工
- 由于是替换,返回值的维度,和condition,x , y都是相等的。

5.tf.slice()
|
1
|
tf.slice(inputs, begin, size, name) |
作用:用来进行切片操作,实现在python中的a[:,2:3,5:6]类似的操作,从列表、数组、张量等对象中抽取一部分数据
- begin和size是两个多维列表,他们共同决定了要抽取的数据的开始和结束位置
- begin表示从inputs的哪几个维度上的哪个元素开始抽取
- size表示在inputs的各个维度上抽取的元素个数
- 若begin[]或size[]中出现-1,表示抽取对应维度上的所有元素
bert源码:
参考文献:
【1】tf.gather, tf.gather_nd和tf.slice_机器学习杂货铺1号店-CSDN博客
【2】tf.where/tf.gather/tf.gather_nd - 知乎
【3】tenflow 入门 tf.where()用法_ustbbsy的博客-CSDN博客
【4】tf.gather tf.gather_nd 和 tf.batch_gather 使用方法_张冰洋的天空-CSDN博客
tf.gather()、tf.gather_nd()、tf.batch_gather()、tf.where()和tf.slice()
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/yibeimingyue/p/15114855.html
