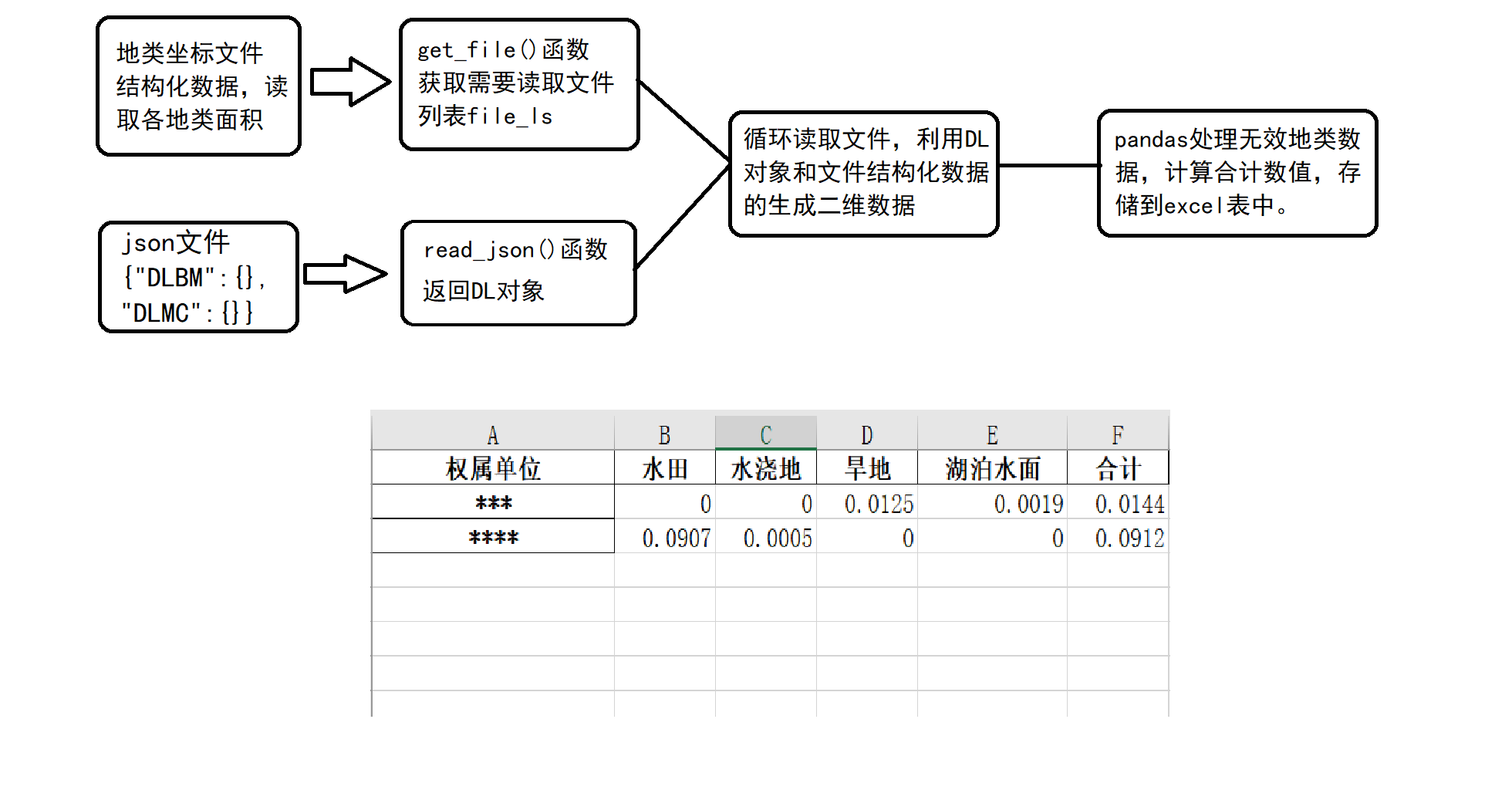
程序功能的阐述,定义read_json()函数,将json格式文件固定的对象读入到程序中。以便后期对数据利用生成pandas的DataFrame对象,完成结构化数据的分列存储。

1 import os,sys 2 from functools import reduce 3 import pandas as pd 4 import json 5 6 ENCODE = "utf8" 7 CWD_PATH = os.path.dirname(sys.argv[0]) 8 9 10 def func(i): 11 m,n = os.path.splitext(i) 12 if n == ".json": 13 return i 14 #加载JSON数据 15 def read_json(PATH): 16 lst = os.listdir(PATH) 17 lstt = list(map(lambda x:os.path.join(PATH, x), lst)) 18 lsf = list(filter(lambda x:os.path.isfile(x), lstt)) 19 lsj = list(filter(func,lsf)) 20 print(lsj) 21 if len(lsj) == 1: 22 for f in lsj: 23 with open(f,‘r‘,encoding=ENCODE) as jsonfile: 24 DL = json.load(jsonfile) 25 jsonfile.close() 26 else: 27 raise ValueError 28 return DL 29 30 #加载文件 31 def get_file(dirpath,file_ls): 32 slogn = 0 33 if not os.path.exists(dirpath): #如果文件不存在,输出错误 34 print("目录不存在,请确认!!!") 35 return file_ls, slogn 36 elif os.path.isfile(dirpath): 37 file_ls.append(dirpath) 38 slogn = 1 39 return file_ls, slogn 40 else: 41 file_t_ls = os.listdir(dirpath) 42 for file_item in file_t_ls: 43 file_p = dirpath + "\\" + file_item 44 if os.path.isfile(file_p): 45 i,j = os.path.splitext(file_p) 46 if j == ".txt"or j == ".TXT": 47 file_ls.append(file_p) 48 print("文件路径已加载完毕...") 49 return file_ls, slogn 50 51 #转换列名为对应地类名称 52 def convent_col(dict_1, index_name, DL): 53 print(‘***文件处理中***‘) 54 df = pd.DataFrame(dict_1,index=index_name) 55 map_columns = DL["DLMC"] 56 df.rename(columns=map_columns, inplace=True) 57 df[‘合计‘]=df.sum(axis=1, numeric_only=True) 58 #print(df) 59 data = df.groupby(‘权属单位‘).agg(‘sum‘) 60 return data 61 62 #生成表格 63 def deal_file(file_ls, dir_path): 64 if len(file_ls) == 0: 65 print("所选择的路径名为空") 66 return ‘error‘ 67 else: 68 print("总共{}个文件".format(len(file_ls))) 69 for file_item in file_ls: 70 #将文件名字作为首列索引(index_col) 71 base_name = os.path.basename(file_item) 72 #定义一个默认的值为列表的字典可以方便后期转化为DataFream二维表,以便向其中添加数据(地类模板) 73 DL = read_json(CWD_PATH) 74 tmp_dict = DL[‘DLBM‘] #defaultdict(list) 75 with open(file_item, ‘r‘, encoding=ENCODE) as file: 76 for line in file: 77 if ‘@‘ in line: 78 tmp_ls = line.strip().split(‘,‘) 79 area = tmp_ls[1] #地类面积 80 qs = tmp_ls[4] #地类权属 81 dlbm = tmp_ls[3] #地类编码 82 tmp_dict["权属"].append(qs) 83 if isinstance(tmp_dict.get(str(dlbm)),list): 84 tmp_dict[dlbm.strip()].append(float(area)) #坐标文件中出现的地类编码都会创建一个键值对,键为地类编码,值为面积列表 85 count = len(tmp_dict.get("权属")) 86 for v in tmp_dict.values(): 87 if len(v) == count: 88 continue 89 else: 90 v.append(0.0) 91 else: 92 print(str(dlbm)) 93 print(tmp_dict) 94 del_key_ls = [] 95 for key,value in tmp_dict.items(): 96 sum = reduce(lambda x, y : x + y, value) 97 if sum == 0: 98 del_key_ls.append(key) 99 for i in del_key_ls: 100 tmp_dict.pop(i) 101 index_name = tmp_dict["权属"] 102 data = convent_col(tmp_dict, index_name, DL) 103 #print(data) 104 save_single_data(data, dir_path, base_name) 105 106 #存储表格 107 def save_single_data(data, s_path, name): 108 print(‘***文件正在保存***‘) 109 save_path = s_path + ‘\\‘ + name + ‘.xlsx‘ 110 data.to_excel(save_path,sheet_name=‘S_FLB‘,float_format=‘%.4f‘) 111 print(‘DataFrame is written successfully to the Excel File.‘) 112 113 #主程序 114 def main_app(dirpath): 115 file_ls = [] 116 f_ls, s = get_file(dirpath,file_ls) 117 if s: 118 dirpath = os.path.dirname(dirpath) 119 deal_file(f_ls, dirpath) 120 return "生成地类分类报表成功" 121 122 if __name__ == "__main__": 123 dirpath = input("请输入要处理的文件路径:") 124 main_app(dirpath)
由于二维表数据列名(地类编码)是固定的,之前是写死在处理程序中,考虑到功能设计上的专一,将这部分写死的数据改存到json文件中读取利用。
由于之前对程序功能考虑疏忽,在数据处理前期即读取了json对象,导致后面程序处理空值列数据时将一些数据改动了,(python程序中要注意可变数据的引用)到循环遍历阶段,循环读取到第二个坐标文件时,报出了KeyError错误,找不到Key。(原因:在第一个坐标文件处理时,将空列删除了,导致了KeyError)
改变,将readjson()函数放入到循环遍历坐标对象下面,每次读取一个文件对象时,重新读取json文件,重新创建空值的DL对象。
注意点:在python程序中对可变数据对象使用时,一定要谨慎,因为它不会在一开始就抛出错误,但在之后又要用到此对象时可能会产生意想不到的问题。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/metaxman/p/15149175.html