
菜鸟写法:
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; //普通实现页面 ? //Java页面 class Java { public: void header() { cout << "首页、公开课、登陆、注册...(公共头部)" << endl; } void footer() { cout << "帮助中心、交流合作、站内地图...(公共底部)" << endl; } void left() { cout << "Java、Python、C++、...(公共分类列表)" << endl; } void content() { cout << "Java 学科视频" << endl; } }; ? //Python页面 class Python { public: void header() { cout << "首页、公开课、登陆、注册...(公共头部)" << endl; } void footer() { cout << "帮助中心、交流合作、站内地图...(公共底部)" << endl; } void left() { cout << "Java、Python、C++、...(公共分类列表)" << endl; } void content() { cout << "Python 学科视频" << endl; } }; ? //C++页面 class CPP { public: void header() { cout << "首页、公开课、登陆、注册...(公共头部)" << endl; } void footer() { cout << "帮助中心、交流合作、站内地图...(公共底部)" << endl; } void left() { cout << "Java、Python、C++、...(公共分类列表)" << endl; } void content() { cout << "C++ 学科视频" << endl; } }; ? void test01() { cout << "Java 下载视频页面如下: " << endl; Java ja; ja.header(); ja.footer(); ja.left(); ja.content(); ? cout << "-----------------------" << endl; cout << "Python 下载视频页面如下: " << endl; Python py; py.header(); py.footer(); py.left(); py.content(); ? cout << "-----------------------" << endl; cout << "C++ 下载视频页面如下: " << endl; CPP cpp; cpp.header(); cpp.footer(); cpp.left(); cpp.content(); ? } ? int main() { test01(); system("pause"); return 0; }
继承写法:
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; ? /* 继承实现页面: 好处:减少重复代码 语法: class 子类:继承方式 父类 子类也称为 派生类 父类也称为 基类 */ ? class BasePage { public: void header() { cout << "首页、公开课、登陆、注册...(公共头部)" << endl; } void footer() { cout << "帮助中心、交流合作、站内地图...(公共底部)" << endl; } void left() { cout << "Java 、Python、C++、...(公共分类列表)" << endl; } }; ? //Java页面 class Java :public BasePage { public: void content() { cout << "Java 学科视频" << endl; } }; ? //Python页面 class Python :public BasePage { public: void content() { cout << "Python 学科视频" << endl; } }; ? //C++页面 class CPP :public BasePage { public: void content() { cout << "C++ 学科视频" << endl; } }; ? void test01() { cout << "Java 下载视频页面如下: " << endl; Java ja; ja.header(); ja.footer(); ja.left(); ja.content(); ? cout << "-----------------------" << endl; cout << "Python 下载视频页面如下: " << endl; Python py; py.header(); py.footer(); py.left(); py.content(); ? cout << "-----------------------" << endl; cout << "C++ 下载视频页面如下: " << endl; CPP cpp; cpp.header(); cpp.footer(); cpp.left(); cpp.content(); } ? int main() { test01(); system("pause"); return 0; }


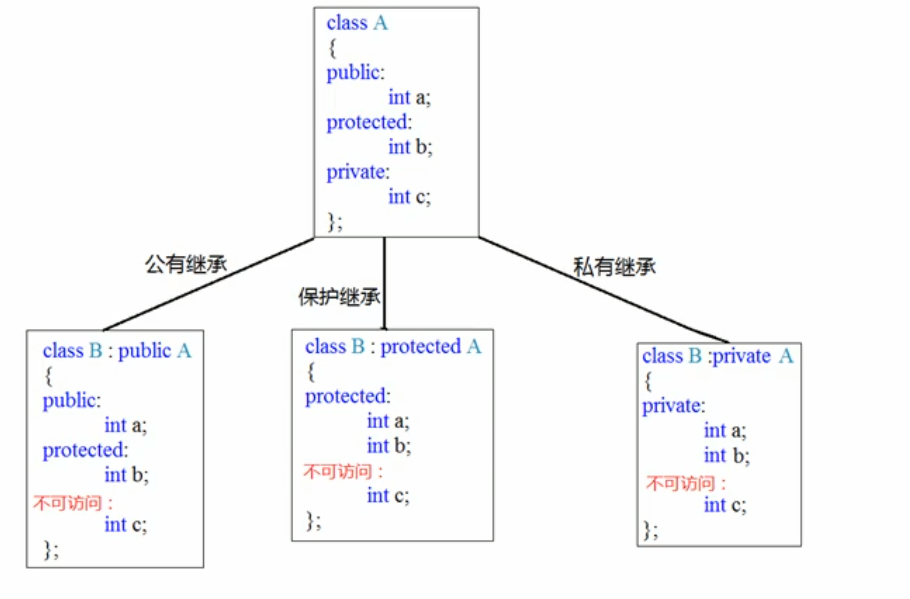
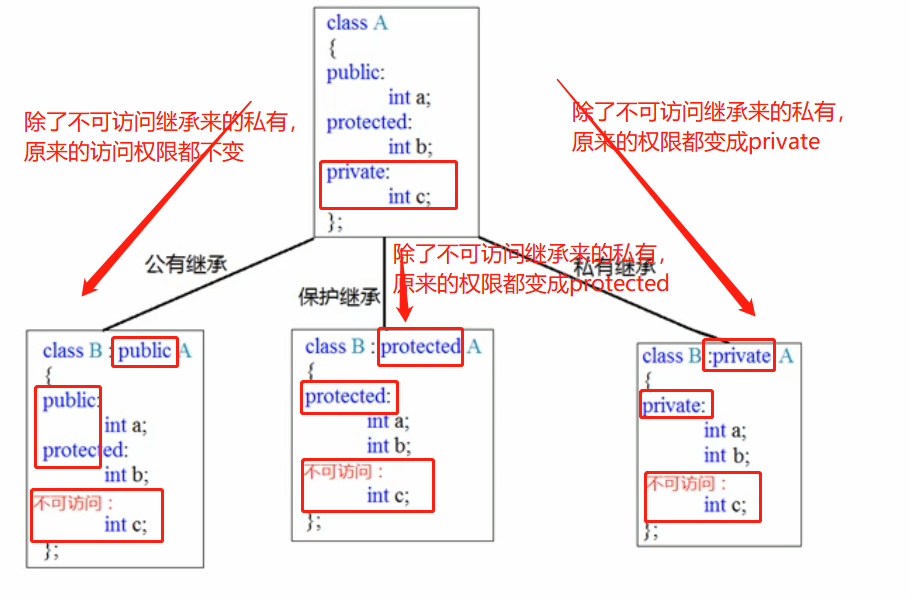
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; ? //继承方式 //公共继承 class Base1 { public: int m_A; protected: int m_B; private: int m_C; ? }; ? //public继承 class Son1 :public Base1 { public: void func() { m_A = 10; //父类中的public成员 ,子类中 public m_B = 10; //父类中的protected成员 ,子类中 protected //m_C = 10;//父类中的private成员 ,子类中访问不到 ? } }; ? //protected继承 class Son2:protected Base1 { public: void func() { m_A = 100; //父类中的public成员, 子类中 protected m_B = 100; //父类中的protected成员 ,子类中 protected //m_C = 10;//父类中的private成员 ,子类中访问不到 } }; ? //private继承 class Son3 :private Base1 { public: void func() { m_A = 100; //父类中的public成员, 子类中 private m_B = 100; //父类中的protected成员 ,子类中 private //m_C = 10;//父类中的private成员 ,子类中访问不到 } }; ? class GrandSon3 :public Son3{ public: void func() { //m_A = 100; //子类访问不到父类Son3的私有 //m_B = 100; //子类访问不到父类Son3的私有 //m_B = 100; //子类访问不到父类Son3的私有 } }; ? void test01() { Son1 s1; s1.m_A = 100; //s1.m_B = 100; //类外访问不到protected 成员 ? Son2 s2; //s2.m_A = 100; //m_A 变为了protected,类外访问不到 ? Son3 s3; //s3.m_A = 100; //m_A 变为了private,类外访问不到 //s3.m_B = 100; //m_B 变为了private,类外访问不到 } ? int main() { test01(); system("pause"); return 0; }

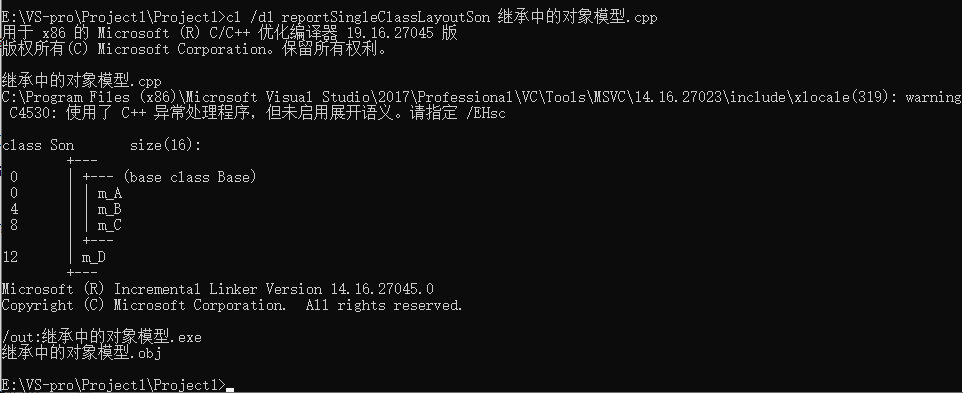
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; ? //继承中的对象模型 class Base { public: int m_A; protected: int m_B; private: int m_C; }; ? class Son :public Base { public: int m_D; }; ? void test01() { //16 //父类中所有非静态的成员属性都会被子类继承下去 //父类中私有成员属性 是被编译器给隐藏了,因此访问不到,但是确实是被继承下去了 cout << "size of son = " << sizeof(Son) << endl; } ? int main() { test01(); system("pause"); return 0; }
利用开发人员命令提示工具查看对象模型
跳转盘符 E
跳转到文件路径 cd 具体路径下
查看命令
cl /d1 reportSingleClassLayout类名 文件名

#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; ? //继承中的构造和析构顺序 class Base { public: Base() { cout << "Base 构造函数!" << endl; } ~Base() { cout << "Base 析构函数!" << endl; } }; ? class Son :public Base { public: public: Son() { cout << "Son 构造函数!" << endl; } ~Son() { cout << "Son 析构函数!" << endl; } }; ? void test01() { //继承中的构造和析构顺序如下: //先构造父类,再构造子类,析构的顺序与构造的顺序相反 Son s; } ? int main() { test01(); ? system("pause"); return 0; }

#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; ? //继承中同名成员处理 class Base { public: Base() { m_A = 100; } void func() { cout << "Base 下的 func() 函数调用 " << endl; } ? void func(int a) { cout << "Base 下的 func(int a) 函数调用 " << endl; } int m_A; }; ? class Son :public Base { public: Son() { m_A = 200; } void func() { cout << "Son 下的 func() 函数调用 " << endl; } int m_A; }; ? //同名成员属性的处理方式 void test01() { Son s; cout << "Son 下的 m_A = " << s.m_A << endl; //如果通过子类对象访问到父类同名成员,需要加作用域 cout << "Base 下的 m_A = " << s.Base::m_A << endl; } ? //同名成员函数的处理方式 void test02() { Son s; //同名时,直接调用是子类中的同名成员 s.func(); //如何调用到父类中的同名成员函数? s.Base::func(); //如果子类中出现和父类同名的成员函数,子类的同名成员会隐藏 //掉父类中所有同名成员(重载)函数 //如果相访问到父类中被隐藏的同名成员函数,需要加作用域 s.Base::func(100); } ? int main() { test01(); test02(); ? system("pause"); return 0; }

static关键字加上后变成静态成员
静态成员变量:所有对象共享同一份数据,定义阶段分配内存,类内声明,类外初始化
静态成员函数:只能访问静态成员变量,不能访问非静态成员变量,只有一份,所有的对象共享同一份函数实例

#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; ? //继承中的同名静态成员处理方式 class Base { public: static int m_A; static void func() { cout << "Base -- static void func()" << endl; } ? static void func(int a) { cout << "Base -- static void func(int a)" << endl; } }; int Base::m_A = 100; ? class Son :public Base { public: static int m_A; static void func() { cout << "Son -- static void func()" << endl; } }; int Son::m_A = 200; ? //同名静态成员属性 void test01() { //1.通过对象访问数据 cout << "通过对象访问 :" << endl; Son s; cout << "Son 下 m_A = " << s.m_A << endl; cout << "Base 下 m_A = " << s.Base::m_A << endl; //2.通过类名访问数据 cout << "通过类名访问 :" << endl; cout << "Son 下 m_A = " << Son::m_A << endl; ? //两个::的含义 //第一个::代表通过类名方式访问 //第二个::代表访问父类作用域下 cout << "Base 下 m_A = " << Son::Base::m_A << endl; ? } //同名静态成员函数 void test02() { //1.通过对象访问数据 cout << "通过对象访问 :" << endl; Son s; s.func(); s.Base::func(); ? //2.通过类名访问数据 cout << "通过类名访问 :" << endl; Son::func(); //子类出现和父类同名静态成员函数,也会隐藏父类中所有同名成员函数 //如果想访问父类中被隐藏同名成员,需要加作用域 Son::Base::func(); Son::Base::func(100); } ? int main() { test01(); test02(); ? system("pause"); return 0; }


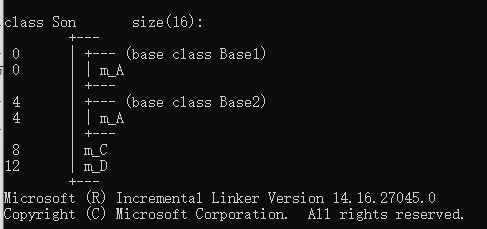
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; ? //多继承语法 class Base1 { public: Base1() { m_A = 100; } int m_A; }; ? ? class Base2 { public: Base2() { m_A = 200; } int m_A; }; ? //子类 需要继承Base1和Base2 //语法:class 子类:继承方式 父类1,继承方式 父类2 class Son :public Base1, public Base2 { public: Son() { m_C = 300; m_D = 400; } int m_C; int m_D; }; ? ? void test01() { Son s; cout << "sizeof(Son) = " << sizeof(s) << endl; //当父类中出现同名成员,需要加作用域区分 //实际开发中不建议做多继承 cout << "Base1::m_A = " << s.Base1::m_A << endl; cout << "Base2::m_A = " << s.Base2::m_A << endl; } ? int main() { test01(); ? system("pause"); return 0; }

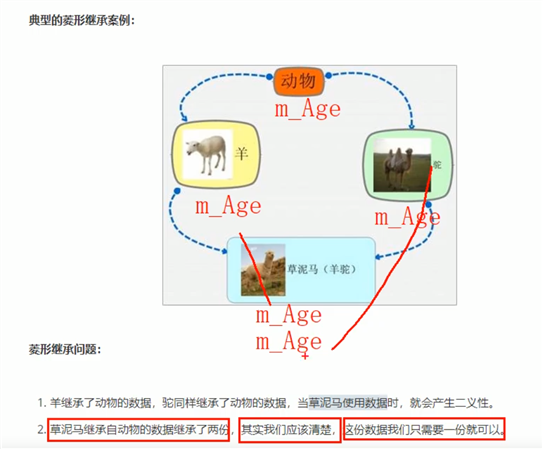
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; ? //菱形继承 //动物类 class Animal { public: int m_Age; }; ? //羊类 //在继承前加上关键字virtual class Sheep :virtual public Animal {}; ? //驼类 //在继承前加上关键字virtual 变为虚继承 //Animal类称为 虚基类 class Camels :virtual public Animal {}; ? //羊驼类 class Alpacas :public Sheep, public Camels {}; ? void test01() { Alpacas as; //当出现菱形继承时,两个父类拥有相同数据,需要加以作用域区分 as.Sheep::m_Age = 18; as.Camels::m_Age = 28; ? cout << "as.Sheep::m_Age = " << as.Sheep::m_Age << endl; cout << "as.Camels::m_Age = " << as.Camels::m_Age << endl; //对于羊驼类这份数据只要有一份就可以了,菱形继承导致数据有两份,资源浪费 //利用虚继承,解决以上问题 //当使用虚继承后,只有一份数据 cout << "as.m_Age = " << as.m_Age << endl; } ? int main() { test01(); ? system("pause"); return 0; }
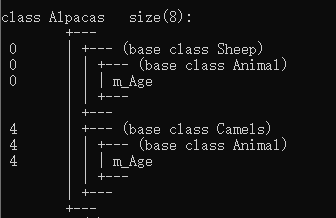
虚继承解决菱形继承的问题

原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/d1012181765/p/15156103.html