HttpSession与Cookie的使用条件相同,都是同一个网站且为同一个浏览器/用户,那么它们有什么区别呢?

在同一个网站【MyWeb】下OneServlet将数据传递给TwoServlet
浏览器访问MyWeb下的OneServlet
public class OneServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1.调用请求对象向Tomcat索要当前用户在服务端的会话作用域对象(私人储物柜)
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
//2.将数据添加到用户私人储物柜
session.setAttribute("key1",共享数据【任意类型】);
}
}
浏览器访问MyWeb下的TwoServlet
public class TwoServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1.调用请求对象向Tomcat索要当前用户在服务端的私人储物柜【会话作用域对象】
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
//2.从会话作用域对象中得到OneServlet提供的共享数据
Object 存储共享数据变量 = session.getAttribute("key1");
}
}


<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>购物</title>
<style type="text/css">
* {
font-size: 18px;
}
th {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<table border="1" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0"
align="center" width="700px" height="300px" style="color: green">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>商品名称</th>
<th width="25%">图片展示</th>
<th>商品描述</th>
<th>商品单价(元)</th>
<th>添加至购物车</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody align="center">
<tr>
<td>笔记本电脑</td>
<td><img src="https://pic.imgdb.cn/item/611d1bf44907e2d39c64783e.jpg" width="50%" /></td>
<td>流畅运行3A大作</td>
<td>9999</td>
<td><a href="/MyWeb/one?tradeName=笔记本电脑">添加至购物车</a></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>压缩饼干</td>
<td><img src="https://pic.imgdb.cn/item/611d1ca64907e2d39c675c3c.jpg" width="50%"></td>
<td>一块顶一天</td>
<td>10</td>
<td><a href="/MyWeb/one?tradeName=压缩饼干">添加至购物车</a></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>牛肉罐头</td>
<td><img src="https://pic.imgdb.cn/item/611d1d324907e2d39c69d5f9.jpg" width="50%"/></td>
<td>囤货必备</td>
<td>50</td>
<td><a href="/MyWeb/one?tradeName=牛肉罐头">添加至购物车</a></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="5" align="left"><a href="/MyWeb/two">点击查看我的购物车</a></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</body>
</html>
package com.tsccg.controller;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
/**
* @Author: TSCCG
* @Date: 2021/08/19 13:55
*/
public class OneServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1.调用请求对象获取请求头中的请求参数【商品名】
String tradeName = request.getParameter("tradeName");
//2.调用请求对象向服务器索要当前用户在服务端的【私人储物柜】
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
//3.将商品信息添加到【私人储物柜】中
//获取当前【私人储物柜】中当前商品的数量
Integer tradeNums = (Integer)session.getAttribute(tradeName);
if (tradeNums == null) {
//如果【私人储物柜】中没有当前商品,则添加一个
session.setAttribute(tradeName,1);
} else {
//如果【私人储物柜】中存在当前商品,则在原有数量上加一
session.setAttribute(tradeName,tradeNums + 1);
}
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.print("<center>");
out.print("<font color=‘green‘ size=‘20px‘>添加成功</font>");
out.print("<br>");
out.print("<input type=\"button\" value=\"继续购物\" onclick=\"window.open(‘/MyWeb/index.html‘,‘_self‘)\" >");
out.print("</center>");
}
}
package com.tsccg.controller;
import org.omg.PortableInterceptor.INACTIVE;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Enumeration;
/**
* @Author: TSCCG
* @Date: 2021/08/19 13:55
*/
public class TwoServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1.调用请求对象向服务器索要当前用户在服务端的【私人储物柜】
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
//2.调用请求对象将【私人储物柜】中所有商品名都取出,存放在一个枚举对象中
Enumeration<String> tradeNames = session.getAttributeNames();
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
//向服务器索要获取输出流
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.print("<table border=‘1‘ cellpadding=‘0‘ cellspacing=‘0‘ align=‘center‘ width=‘300px‘ height=‘150px‘ style=‘color:red;font-size:18px‘>\n");
out.print("<tr>");
out.print("<th>商品名</th>");
out.print("<th>商品数量</th>");
out.print("<th>总价</th>");
out.print("</tr>");
//定义所有商品的总价
int finalPrice = 0;
//3.遍历枚举对象
while (tradeNames.hasMoreElements()) {
//获取当前商品名
String tradeName = tradeNames.nextElement();
//获取当前商品数量
int tradeNums = (int) session.getAttribute(tradeName);
//计算当前商品的总价
int totalPrice = calculation(tradeName,tradeNums);
//统计所有商品的总价
finalPrice += totalPrice;
out.print("<tr>");
out.print("<td>" + tradeName + "</td>");
out.print("<td>" + tradeNums + "</td>");
out.print("<td>" + totalPrice + "元</td>");
out.print("</tr>");
}
out.print("<tr>");
out.print("<td colspan=\"2\">合计</td>");
out.print("<td>" + finalPrice + "</td>");
out.print("</tr>");
out.print("<tr>");
out.print("<td colspan=\"2\"><input type=\"button\" value=\"继续购物\" onclick=\"window.open(‘/MyWeb/index.html‘,‘_self‘)\"></td>");
out.print("<td><input type=\"button\" value=\"结账\"></td>");
out.print("</tr>");
out.print("</table>");
// <table border="1" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" align="center" width="300px" height="150px">
// <tr>
// <th>商品名</th>
// <th>商品数量</th>
// <th>总价</th>
// </tr>
// <tr>
// <td>笔记本电脑</td>
// <td>2</td>
// <td>19998元</td>
// </tr>
// <tr>
// <td colspan="2">合计</td>
// <td>19998元</td>
// </tr>
// <tr>
// <td colspan="2"><input type="button" value="继续购物" onclick="window.open(‘/MyWeb/index.html‘,‘_self‘)"></td>
// <td><input type="button" value="结账"></td>
// </tr>
// </table>
}
/**
* 计算当前商品的总价
* @param tradeName 商品名
* @param tradeNums 商品数量
* @return 商品总价
*/
private static Integer calculation(String tradeName,int tradeNums) {
//电脑单价
final int computerPrice = 9999;
//压缩饼干单价
final int biscuitsPrice = 10;
//牛肉罐头单价
final int beefCanPrice = 50;
//定义当前商品的总价
int totalPrice = 0;
if ("笔记本电脑".equals(tradeName)) {
totalPrice = computerPrice * tradeNums;
} else if ("压缩饼干".equals(tradeName)) {
totalPrice = biscuitsPrice * tradeNums;
} else if ("牛肉罐头".equals(tradeName)) {
totalPrice = beefCanPrice * tradeNums;
}
return totalPrice;
}
}
使用chrome浏览器:

同时使用其他浏览器访问网站:

可见,当使用不同浏览器访问网站时,使用的购物车是不同的。
这说明浏览器/用户是和各自使用的HttpSession绑定的。
这是如何实现的呢?
Http服务器通过Cookie将用户和HttpSession关联起来。
当浏览器第一次访问网站时,Http服务器生成一个HttpSession对象,同时为其分配一个唯一id。
服务器将这个id放进响应头中的Cookie中,发送到浏览器的缓存,作为当前浏览器与生成的HttpSession对象之间的关联符。
当浏览器再次访问网站时,会将这个id一并发送过去,服务器根据这个id找到与其对应的HttpSession对象。

下面我们通过一次完整的会话来加深理解。
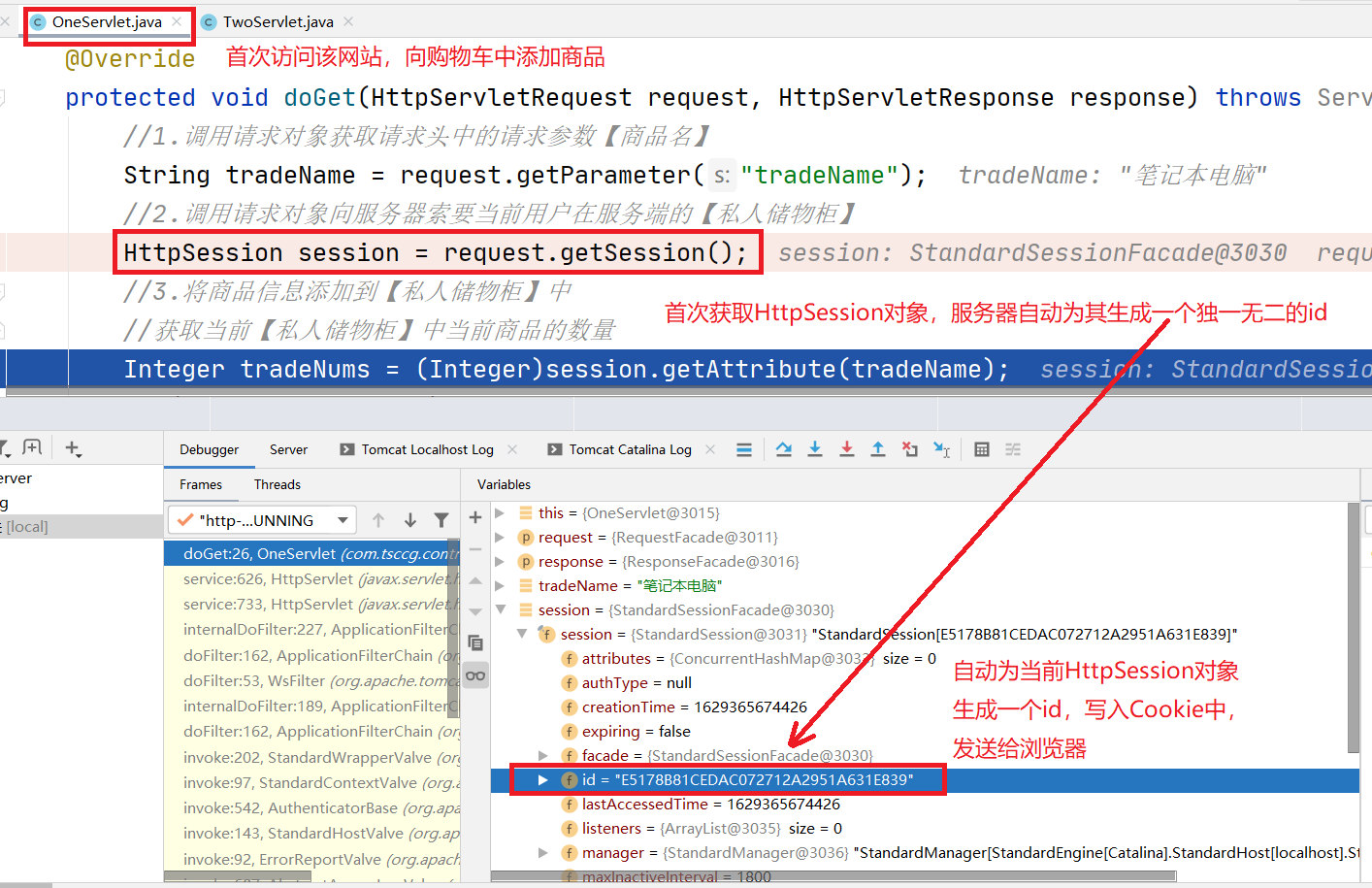
浏览器收到响应包后,将响应头中存有HttpSession对象id的Cookie存入缓存中。等待下次重新访问该网站时调用。

当浏览器再次向网站发起请求时,会把存放在其缓存中的id发送过去。
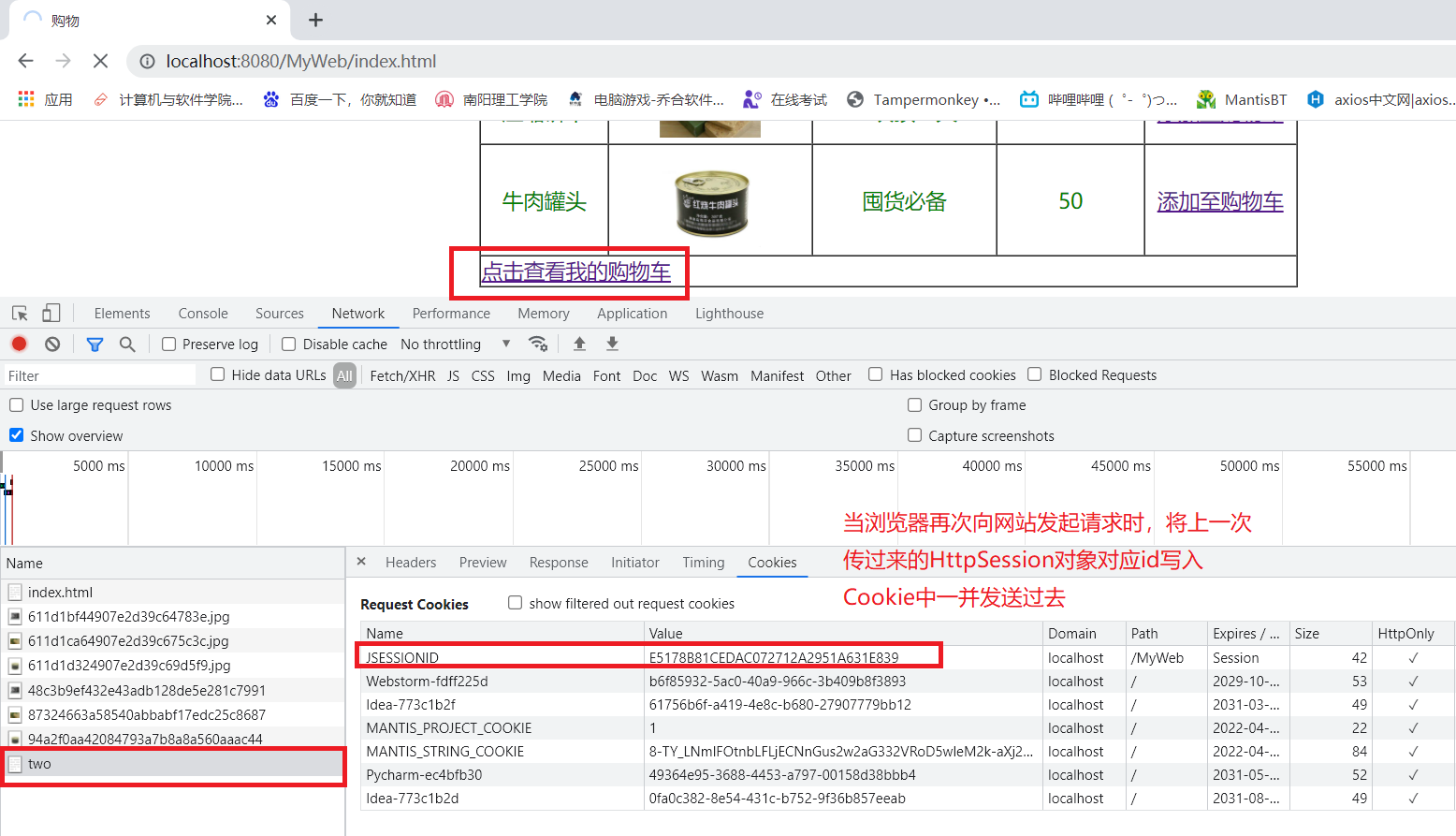
根据浏览器发送过来的id向服务器索要向对应的HttpSession对象,得到的是第一次访问网站时的HttpSession对象。
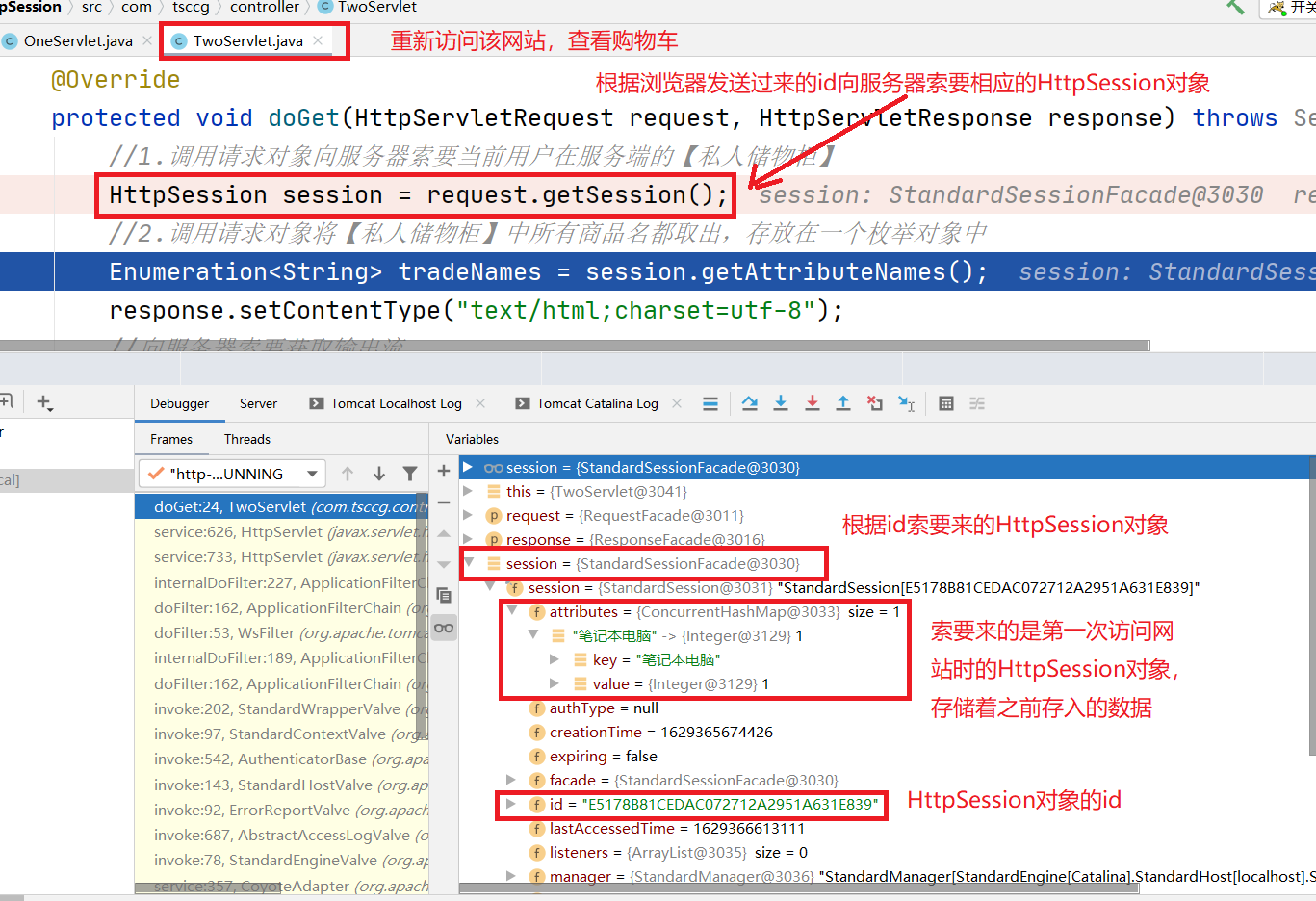
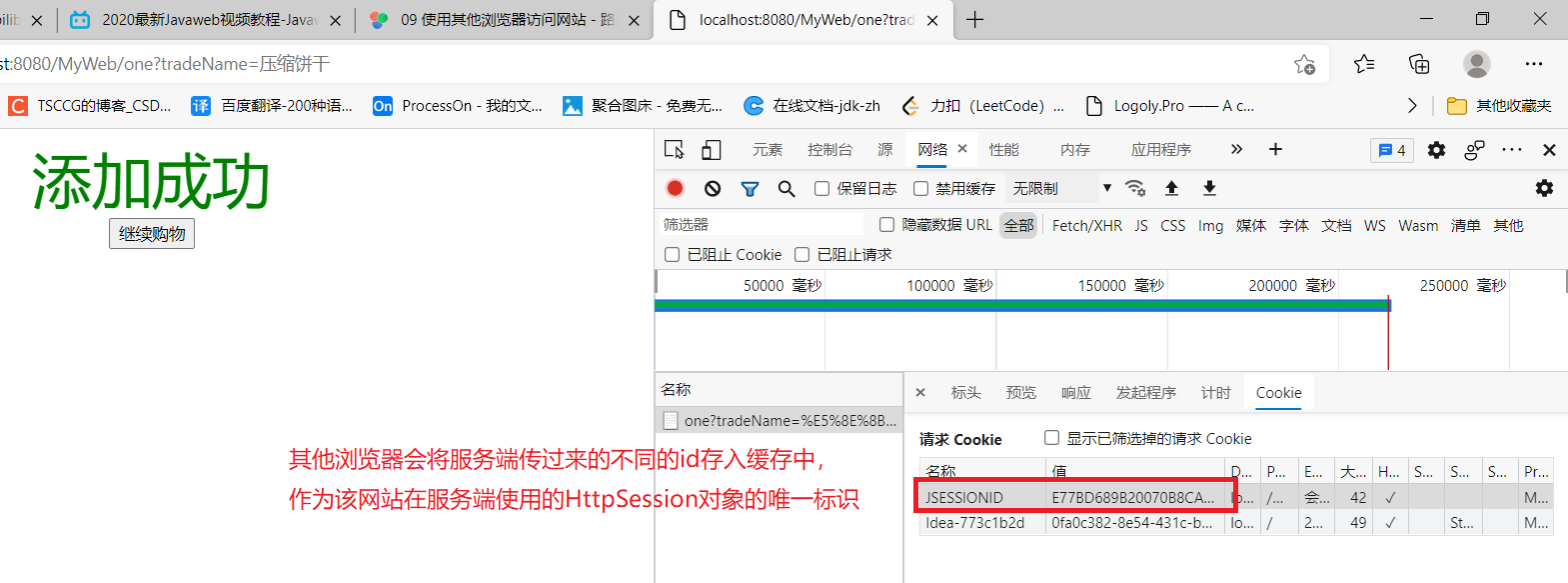
此时,使用其他的浏览器访问网站,生成不同id
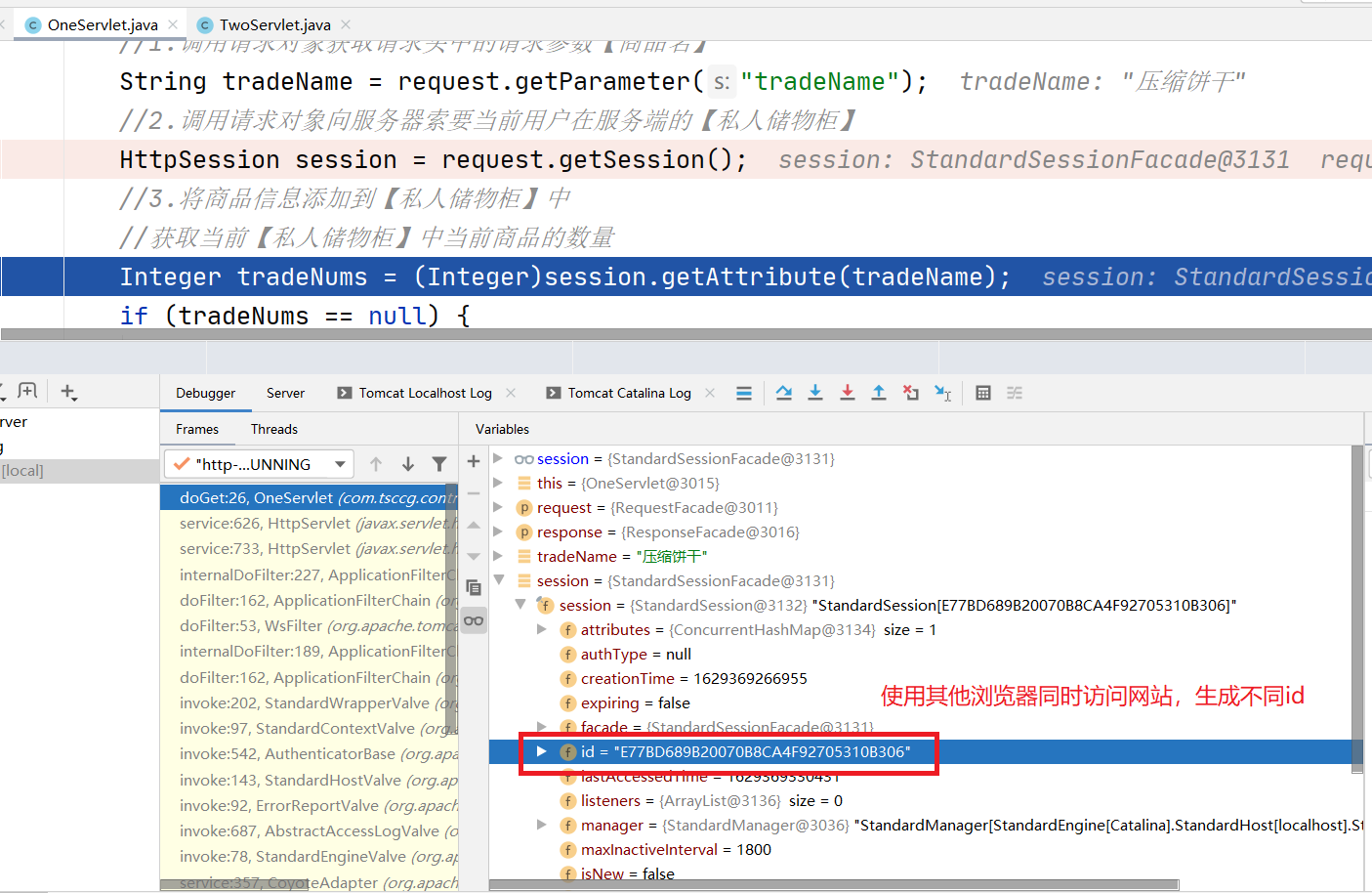
其他浏览器会将服务端传过来的不同id存入缓存中,作为其在服务端使用的HttpSession对象的唯一标识。
getSession():
getSession(false):
那么如何选择呢?
1.用户与HttpSession关联时使用的Cookie只能存放在浏览器缓存中
2.在浏览器关闭时,用户与他的HttpSession对象的关系被切断
3.由于Tomcat无法检测浏览器何时会关闭,所以在浏览器关闭时,Tomcat并不会将浏览器关联的HttpSession对象销毁。
4.为了解决这个问题,Tomcat为每一个HttpSession对象设置一个【空闲时间】。这个空闲时间默认30分钟。如果当前HttpSession对象在30分钟内未被调用,Tomcat就会认为用户已经放弃了自己的HttpSession对象,此时Tomcat就会销毁这个HttpSession对象。
在当前网站/web/WEB_INF/web.xml
<session-config>
<!-- 在当前网站中,设置每一个HttpSession对象的最大空闲时间为10分钟 -->
<session-timeout>10</session-timeout>
</session-config>
JavaWeb-03-Servlet-11-多个Servlet之间的数据共享-02HttpSession接口
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/TSCCG/p/15164379.html