import numpy
import numpy as np
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
import torchvision
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import tensorboard
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
# print(tensorboard.__version__)
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# Assuming that we are on a CUDA machine, this should print a CUDA device:
# print(device)
‘‘‘
device="cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
# print(device)
‘‘‘
torch.set_printoptions(linewidth=120) # Display options for output
torch.set_grad_enabled(True) # Already on by default
print(torch.__version__, torchvision.__version__, sep=‘\n‘)
def get_num_correct(preds, labels):
return preds.argmax(dim=1).eq(labels).sum().item()
class Network(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=6, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=6, out_channels=12, kernel_size=5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features=12 * 4 * 4, out_features=120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(in_features=120, out_features=60)
self.out = nn.Linear(in_features=60, out_features=10)
def forward(self, t):
# (1) input layer
t = t
# (2) hidden conv layer
t = self.conv1(t)
t = F.relu(t)
t = F.max_pool2d(t, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# (3) hidden conv layer
t = self.conv2(t)
t = F.relu(t)
t = F.max_pool2d(t, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# (4) hidden Linear layer
t = t.reshape(-1, 12 * 4 * 4) # -1表示对行没约束,反正是12*4*4列
t = self.fc1(t)
t = F.relu(t)
# (5) hidden Linear layer
t = self.fc2(t)
t = F.relu(t)
# (6) output layer
t = self.out(t)
# t=F.softmax(t,dim=1) #此处不使用softmax函数,因为在训练中我们使用了交叉熵损失函数,而在torch.nn函数类中,已经在其输入中隐式的
# 执行了一个softmax操作,这里我们只返回最后一个线性变换的结果,也即是 return t,也即意味着我们的网络将使用softmax操作进行训练,但在
# 训练完成后,将不需要额外的计算操纵。
return t
# get data
train_set = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(
root=‘./data/FashionMNIST‘,
train=True,
download=True,
transform=transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor()])
)
data_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_set,batch_size=100,shuffle=True) # shuffle=True
# from collections import Iterable
#
# print(isinstance(data_loader,Iterable)) #返回True
#####################
# starting out with TensorBoard(Network Graph and Images) 下面一段为生成日志文件的代码,直到tb.close()
#####################
tb=SummaryWriter()
network=Network()
images,labels=next(iter(data_loader))
grid=torchvision.utils.make_grid(images)#网格效用函数
tb.add_image(‘images‘,grid)
tb.add_graph(network,images)
tb.close()
# optimizer = optim.Adam(network.parameters(), lr=0.01)
‘‘‘
for epoch in range(3):
total_loss = 0
total_correct = 0
for batch in data_loader: # get batch
images, labels = batch
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
preds = network(images) # pass batch
loss = F.cross_entropy(preds, labels) # calculate loss
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward() # calculate gradients
optimizer.step() # update weights using the gradient and the learning rate
total_loss += loss.item()
total_correct += get_num_correct(preds, labels)
print(‘epoch:‘, epoch, ‘total_correct:‘, total_correct, ‘total_loss:‘, total_loss)
print(total_correct / len(train_set))
‘‘‘
其中 runs为该代码所在文件夹中位置,日志文件生成后也在这个文件夹里
如下图:
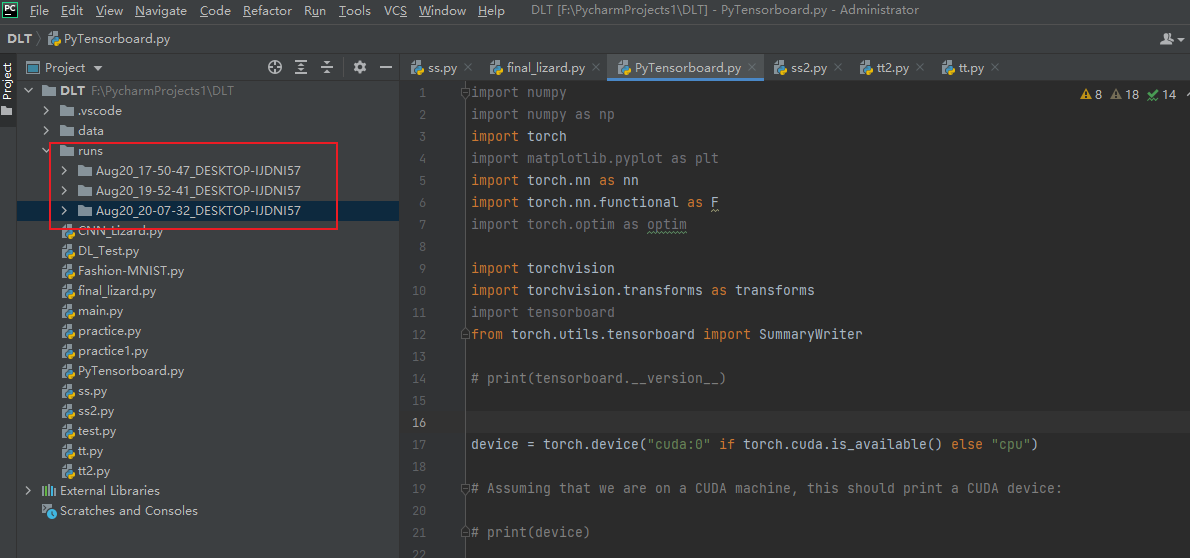
在runs文件夹上点击鼠标右键 有一个open in terminal 点击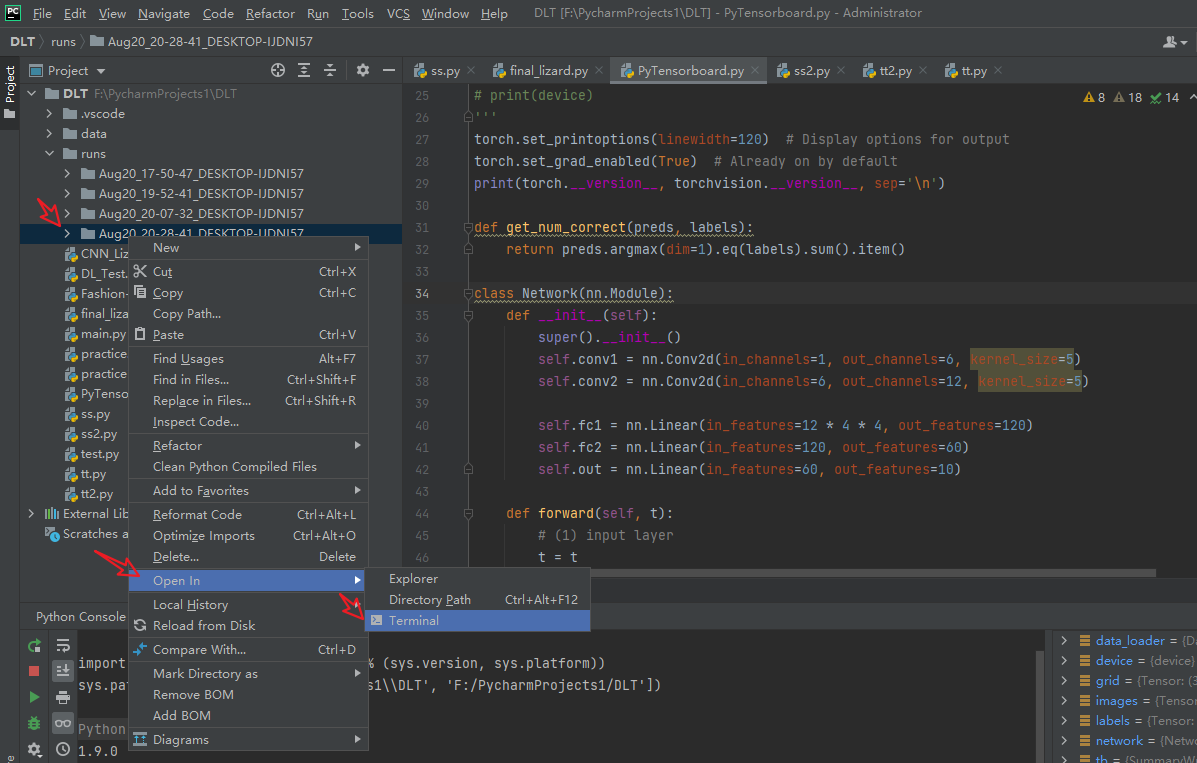
打开后如下图所示:
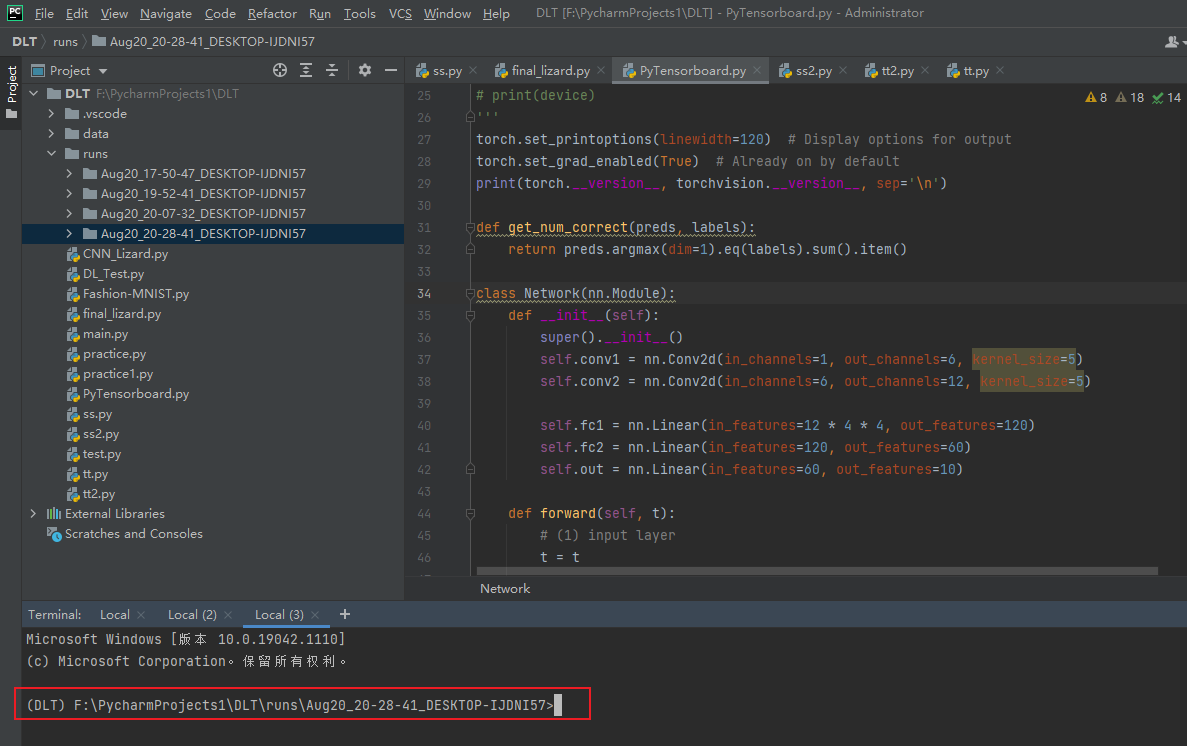
然后再再上图红框右边输入:tensorboard --logdir=日志文件所在的绝对路径
日志文件绝对路径可以直接在runs文件夹右击 有一个copy path 即可
回车后出现一个网址,点击就可以看到tensorboard图:
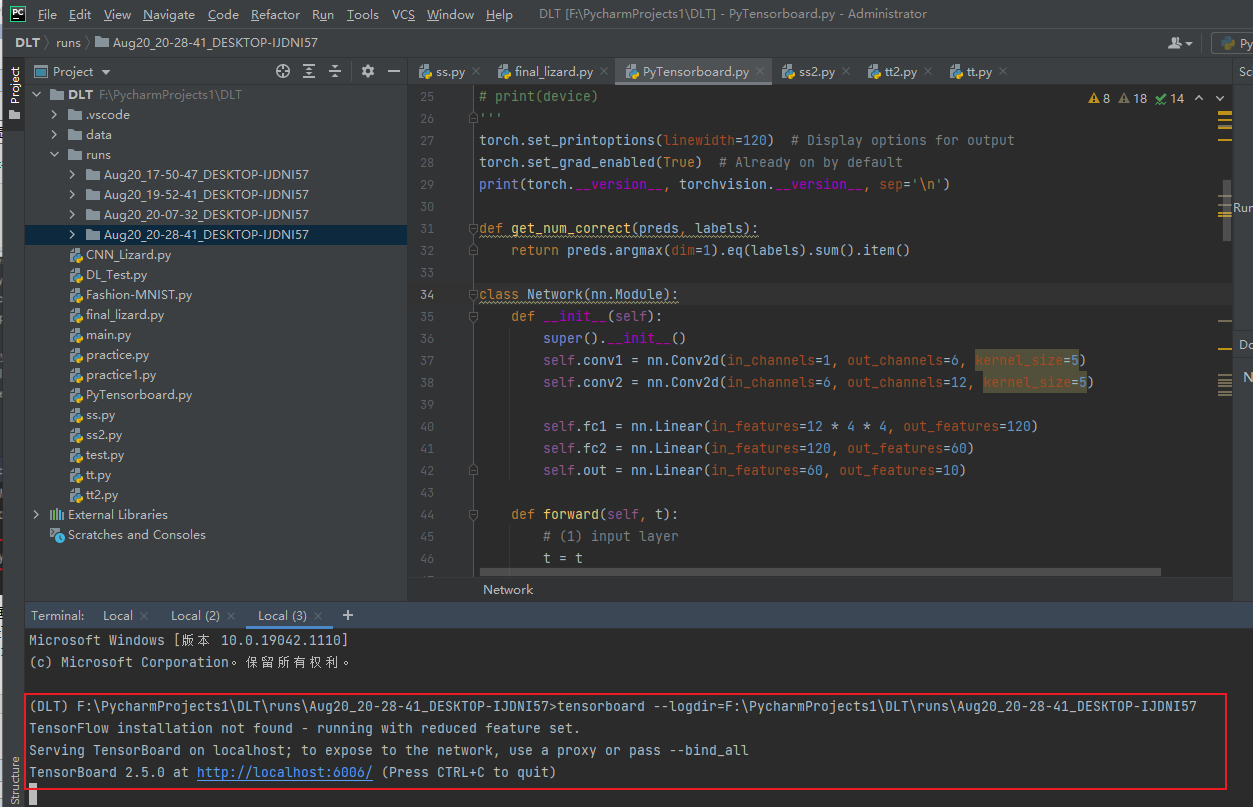
Win10 pycharm中显示PyTorch tensorboard图
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/Li-JT/p/15168086.html