给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
进阶:
你可以在 O(n log n) 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序吗?
示例 1:
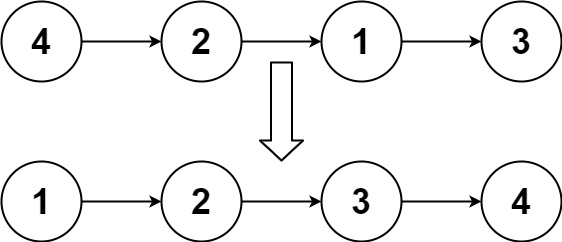
输入:head = [4,2,1,3]
输出:[1,2,3,4]
示例 2:
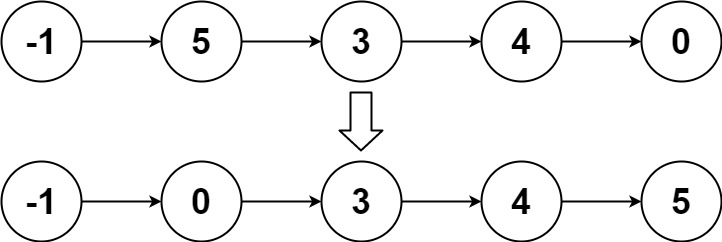
输入:head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
输出:[-1,0,3,4,5]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示:
链表中节点的数目在范围 [0, 5 * 104] 内
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-list
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
归并排序
1:采用归并排序
2:先采用双指针的方式,找链表的中点。
3:按照中点,把链表分割成两部分,分别进行归并排序。
4:把排序好的两个链表,按照大小组成一个新的排序好的链表,并返回此链表。
5:若链表为null或者只有一个节点,则直接返回
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) { return head; } ListNode a = head; ListNode b = head.next; while (b != null && b.next != null) { a = a.next; b = b.next.next; } b = a.next; a.next = null; a = sortList(head); b = sortList(b); ListNode h = new ListNode(0); ListNode item = h; while (a != null && b != null) { if (a.val < b.val) { item.next = a; item = a; a = a.next; item.next = null; } else { item.next = b; item = b; b = b.next; item.next = null; } } if (a != null) { item.next = a; } if (b != null) { item.next = b; } return h.next; }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/wangzaiguli/p/15188821.html