IO模型在Richard Stevens的《UNIX网络编程,第一卷》(程序猿必备!)一书中有非常详尽的描述,以下简要介绍,并给出代码示例。
另外比较好的总结性blog,推荐:
使用异步 I/O
大大提高应用程序的性能
IO
- 同步,异步,阻塞,非阻塞 (亡羊补牢篇)
常见网络IO模型:阻塞式IO、无阻塞式IO、IO复用、异步IO、信号驱动
阻塞式IO:
在一个进程发出IO请求后,进入阻塞状态,直到内核返回数据,才重新运行,如图: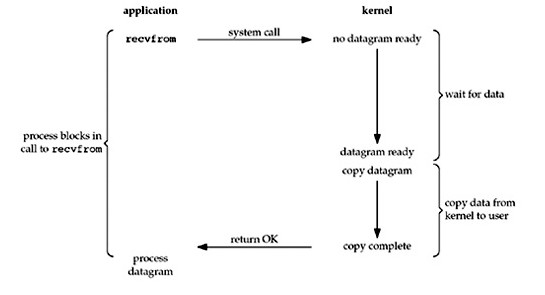
代码
sever端:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83 |
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <errno.h> #include <string.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <unistd.h> int main() { int
sockfd, new_fd; int
sin_size, numbytes; struct
sockaddr_in addr, cliaddr; //创建socket if((sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) < 0) { perror("createSocket"); return
-1; } //初始化socket结构 memset(&addr, 0, sizeof(addr)); addr.sin_family = AF_INET; addr.sin_port = htons(7092); addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); //绑定套接口 if(bind(sockfd,(struct
sockaddr *)&addr,sizeof(struct
sockaddr))==-1) { perror("bind"); return
-1; } //创建监听套接口 if(listen(sockfd,10)==-1) { perror("listen"); return
-1; } printf("server is running!\n"); char
buff[1024]; //等待连接 while(1) { sin_size = sizeof(struct
sockaddr_in); //接受连接 if((new_fd = accept(sockfd, (struct
sockaddr *)&cliaddr, (socklen_t*)&sin_size))==-1) { perror("accept"); return
-1; } //生成一个子进程来完成和客户端的会话,父进程继续监听 if(!fork()) { //读取客户端发来的信息 memset(buff,0,sizeof(buff)); if((numbytes = recv(new_fd,buff,sizeof(buff),0))==-1) { perror("recv"); return
-1; } printf("buff=%s\n",buff); //将从客户端接收到的信息再发回客户端 if(send(new_fd,buff,strlen(buff),0)==-1) { perror("send"); } close(new_fd); return
0; } //父进程关闭new_fd close(new_fd); } close(sockfd); } |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63 |
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <errno.h> #include <string.h> #include <netdb.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <unistd.h> int
main(int
argc,char
*argv[]) { if(argc!=3) { printf("%s: input IP & port\n",argv[0]); return
1; } int
sockfd,numbytes; char
buf[100] = "hello world"; struct
hostent *he; struct
sockaddr_in their_addr; //将基本名字和地址转换 he = gethostbyname(argv[1]); //建立一个TCP套接口 if((sockfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0))==-1) { perror("socket"); exit(1); } //初始化结构体 their_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; their_addr.sin_port = htons(atoi(argv[2])); their_addr.sin_addr = *((struct
in_addr *)he->h_addr); bzero(&(their_addr.sin_zero),8); //和服务器建立连接 if(connect(sockfd,(struct
sockaddr *)&their_addr,sizeof(struct
sockaddr))==-1) { perror("connect"); exit(1); } //向服务器发送字符串 if(send(sockfd,buf,strlen(buf),0)==-1) { perror("send"); exit(1); } memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf)); //接受从服务器返回的信息 if((numbytes = recv(sockfd,buf,100,0))==-1) { perror("recv"); exit(1); } close(sockfd); return
0; } |
运行:
$ ./bin/server
server is running!
buff=hello
world
buff=hello world
$ ./bin/client 10.32.49.10 7092
$
./bin/client 10.32.49.10 7092
无阻塞式IO:
在一个进程发出IO请求后,不阻塞,如果数据没有准备好,就直接返回错误码,如图:

可以通过fcntl控制socket描述符属性。
int flags;
flag=fcntl(sockfd,F_GETFL,0);
fcntl(sockfd,F_SETFL,flag|O_NONBLOCK)
非阻塞式I/O模型对4种I/O操作返回的错误
读操作:接收缓冲区无数据时返回EWOULDBLOCK
写操作:发送缓冲区无空间时返回EWOULDBLOCK;空间不够时部分拷贝,返回实际拷贝字节数
建立连接:启动3次握手,立刻返回错误EINPROGRESS;服务器客户端在同一主机上connect立即返回成功
接受连接:没有新连接返回EWOULDBLOCK
代码:
server端:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119 |
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <errno.h> #include <string.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> int
main() { int
sockfd, new_fd; int
sin_size; struct
sockaddr_in addr, cliaddr; //创建socket if((sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) < 0) { perror("createSocket"); return
-1; } //初始化socket结构 memset(&addr, 0, sizeof(addr)); addr.sin_family = AF_INET; addr.sin_port = htons(7092); addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); //绑定套接口 if(bind(sockfd,(struct
sockaddr *)&addr,sizeof(struct
sockaddr))==-1) { perror("bind"); return
-1; } //创建监听套接口 if(listen(sockfd,10)==-1) { perror("listen"); return
-1; } printf("server is running!\n"); char
buff[1024]; //等待连接 while(1) { sin_size = sizeof(struct
sockaddr_in); //接受连接 if((new_fd = accept(sockfd, (struct
sockaddr *)&cliaddr, (socklen_t*)&sin_size))==-1) { perror("accept"); return
-1; } //生成一个子进程来完成和客户端的会话,父进程继续监听 if(!fork()) { //设置new_fd无阻塞属性 int
flags; if((flags=fcntl(new_fd, F_GETFL, 0))<0) { perror("fcntl F_GETFL"); } flags |= O_NONBLOCK; if(fcntl(new_fd, F_SETFL,flags)<0) { perror("fcntl F_SETFL"); } //读取客户端发来的信息 memset(buff,0,sizeof(buff)); while(1) { if((recv(new_fd,buff,sizeof(buff),0)) < 0) { if(errno==EWOULDBLOCK) { perror("recv error, wait...."); sleep(1); continue; } } else { printf("buff=%s\n",buff); } break; } //发送数据 while(1) { if(send(new_fd,buff,strlen(buff),0) < 0) { if(errno==EWOULDBLOCK) { perror("send error, wait...."); sleep(1); continue; } } else { printf("buff=%s\n",buff); } break; } close(new_fd); return
0; } //父进程关闭new_fd close(new_fd); } close(sockfd); } |
client端:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68 |
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <errno.h> #include <string.h> #include <netdb.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <unistd.h> int
main(int
argc,char
*argv[]) { if(argc!=3) { printf("%s: input IP & port\n",argv[0]); return
1; } int
sockfd,numbytes; char
buf[100] = "hello world"; struct
hostent *he; struct
sockaddr_in their_addr; //将基本名字和地址转换 he = gethostbyname(argv[1]); //建立一个TCP套接口 if((sockfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0))==-1) { perror("socket"); exit(1); } //初始化结构体 their_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; their_addr.sin_port = htons(atoi(argv[2])); their_addr.sin_addr = *((struct
in_addr *)he->h_addr); bzero(&(their_addr.sin_zero),8); //和服务器建立连接 if(connect(sockfd,(struct
sockaddr *)&their_addr,sizeof(struct
sockaddr))==-1) { perror("connect"); exit(1); } sleep(5); //向服务器发送字符串 if(send(sockfd,buf,strlen(buf),0)==-1) { perror("send"); exit(1); } memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf)); sleep(5); //接受从服务器返回的信息 if((numbytes = recv(sockfd,buf,100,0))==-1) { perror("recv"); exit(1); } close(sockfd); return
0; } |
运行:
$ ./bin/server
server is running!
recv error,
wait....: Resource temporarily unavailable
recv error, wait....: Resource
temporarily unavailable
recv error, wait....: Resource temporarily
unavailable
recv error, wait....: Resource temporarily unavailable
recv
error, wait....: Resource temporarily unavailable
buff=hello world
buff=hello world
$ ./bin/client 10.32.49.10 7092
IO复用:
IO复用阻塞在select、poll或epoll这样的系统调用上,通过这种方式,在不使用多线程的前提下,单个进程可以同时处理多个网络连接的IO。如图:
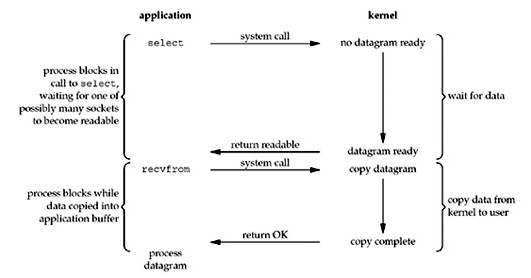
代码
sever端:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222 |
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <errno.h> #include <string.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <netdb.h> #include <sys/epoll.h> #define MAXEVENT 1024 int
create_server_socket(int& sockfd) { struct
sockaddr_in addr; //创建socket if((sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) < 0) { perror("createSocket"); return
-1; } //初始化socket结构 memset(&addr, 0, sizeof(addr)); addr.sin_family = AF_INET; addr.sin_port = htons(7092); addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); //绑定套接口 if(bind(sockfd,(struct
sockaddr *)&addr,sizeof(struct
sockaddr))==-1) { perror("bind"); return
-1; } //创建监听套接口 if(listen(sockfd,10)==-1) { perror("listen"); return
-1; } return
0; } int
set_socket_non_blocking(int
fd) { int
flags, s; flags = fcntl (fd, F_GETFL, 0); if
(flags == -1) { perror
("fcntl F_GETFL failed"); return
-1; } flags |= O_NONBLOCK; s = fcntl (fd, F_SETFL, flags); if
(s == -1) { perror
("fcntl F_SETFL failed"); return
-1; } return
0; } int
main() { int
sockfd, efd; struct
epoll_event event; struct
epoll_event *events; int
s; if(create_server_socket(sockfd) != 0) { perror("create server sock failed\n"); return
1; } set_socket_non_blocking(sockfd); printf("server is running!\n"); //创建一个epoll的句柄 //int epoll_create(int size) //Since Linux 2.6.8, the size argument is unused. (The kernel dynamically sizes the required data structures without needing this initial hint.) efd = epoll_create(MAXEVENT); if
(efd == -1) { perror
("epoll_create"); abort
(); } //注册新事件到epoll efd event.data.fd = sockfd; event.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET; s = epoll_ctl(efd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, sockfd, &event); if
(s == -1) { perror
("epoll_ctl EPOLL_CTL_ADD failed"); abort
(); } events = (epoll_event*)calloc(MAXEVENT, sizeof(event)); while
(1) { int
n, i; n = epoll_wait(efd, events, MAXEVENT, -1); for
(i = 0; i < n; i++) { //fd error if
((events[i].events & EPOLLERR) || (events[i].events & EPOLLHUP) || (!(events[i].events & EPOLLIN))) { perror("epoll error\n"); close (events[i].data.fd); continue; } //新连接 else
if (sockfd == events[i].data.fd) { while
(1) { struct
sockaddr in_addr; socklen_t in_len; int
infd; char
hbuf[NI_MAXHOST], sbuf[NI_MAXSERV]; //接受连接 in_len = sizeof(in_addr); infd = accept(sockfd, &in_addr, &in_len); if
(infd == -1) { if
((errno
== EAGAIN) || (errno
== EWOULDBLOCK)) { //已接受所有连接 break; } else { perror
("accept"); break; } } s = getnameinfo (&in_addr, in_len, hbuf, sizeof
hbuf, sbuf, sizeof
sbuf, NI_NUMERICHOST | NI_NUMERICSERV); if
(s == 0) { printf("Accepted connection on descriptor %d " "(host=%s, port=%s)\n", infd, hbuf, sbuf); } /* 设置新接受的socket连接无阻塞*/ s = set_socket_non_blocking (infd); if
(s == -1) { return
1; } //注册新事件到epoll event.data.fd = infd; event.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET; s = epoll_ctl(efd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, infd, &event); if
(s == -1) { perror
("epoll_ctl"); return
1; } } continue; } //数据可读 else { int
done = 0; while
(1) { ssize_t count; char
buf[512]; count = read(events[i].data.fd, buf, sizeof(buf)); if(count == -1) { //数据读完 if
(errno
!= EAGAIN) { perror
("read"); done = 1; } break; } else
if(count == 0) { /* End of file. The remote has closed the connection. */ done = 1; break; } printf("recv: %s\n", buf); } if
(done) { printf
("Closed connection on descriptor %d\n", events[i].data.fd); close (events[i].data.fd); } } } } free
(events); close(sockfd); return
0; } |
client端:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61 |
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <errno.h> #include <string.h> #include <netdb.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <unistd.h> int
main(int
argc,char
*argv[]) { if(argc!=3) { printf("%s: input IP & port\n",argv[0]); return
1; } int
sockfd,numbytes; char
buf[100] = "hello world"; struct
hostent *he; struct
sockaddr_in their_addr; //将基本名字和地址转换 he = gethostbyname(argv[1]); //建立一个TCP套接口 if((sockfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0))==-1) { perror("socket"); exit(1); } //初始化结构体 their_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; their_addr.sin_port = htons(atoi(argv[2])); their_addr.sin_addr = *((struct
in_addr *)he->h_addr); bzero(&(their_addr.sin_zero),8); //和服务器建立连接 if(connect(sockfd,(struct
sockaddr *)&their_addr,sizeof(struct
sockaddr))==-1) { perror("connect"); exit(1); } //向服务器发送字符串 while(1) { if(send(sockfd,buf,strlen(buf),0)==-1) { perror("send"); exit(1); } sleep(2); } memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf)); close(sockfd); return
0; } |
运行:
$ ./bin/server
server is running!
Accepted
connection on descriptor 5 (host=10.32.49.10, port=39001)
recv: hello
world
recv: hello world
recv: hello world
recv: hello world
./bin/client 10.32.49.10 7092
异步IO:
在一个进程发出IO请求后直接返回,内核在整个操作(包括将数据复制到进程缓冲区)完成后通知进程,如图:

代码
server端:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118 |
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <errno.h> #include <string.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <aio.h> #include <pthread.h> #define BUF_SIZE 1024 void
aio_completion_handler(sigval_t sigval); void
setup_io(int
fd, aiocb& my_aiocb) { //初始化AIO请求 bzero( (char
*)&my_aiocb, sizeof(struct
aiocb) ); my_aiocb.aio_fildes = fd; my_aiocb.aio_buf = malloc(BUF_SIZE+1); my_aiocb.aio_nbytes = BUF_SIZE; my_aiocb.aio_offset = 0; //设置线程回调函数 my_aiocb.aio_sigevent.sigev_notify = SIGEV_THREAD; my_aiocb.aio_sigevent.sigev_notify_function = aio_completion_handler; my_aiocb.aio_sigevent.sigev_notify_attributes = NULL; my_aiocb.aio_sigevent.sigev_value.sival_ptr = &my_aiocb; } //回调函数 void
aio_completion_handler(sigval_t sigval) { struct
aiocb *req; int
ret; req = (struct
aiocb *)sigval.sival_ptr; if
(aio_error(req) == 0) { if((ret = aio_return(req)) > 0) { printf("Thread id %u recv:%s\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self(), (char*)req->aio_buf); } } char* buf = (char*)req->aio_buf; if(send(req->aio_fildes, buf, strlen(buf), 0) == -1) { perror("send"); return; } close(req->aio_fildes); return; } int
main() { int
sockfd; int
sin_size; struct
sockaddr_in addr, cliaddr; //创建socket if((sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) < 0) { perror("createSocket"); return
-1; } //初始化socket结构 memset(&addr, 0, sizeof(addr)); addr.sin_family = AF_INET; addr.sin_port = htons(7092); addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); //绑定套接口 if(bind(sockfd,(struct
sockaddr *)&addr,sizeof(struct
sockaddr))==-1) { perror("bind"); return
-1; } //创建监听套接口 if(listen(sockfd,10)==-1) { perror("listen"); return
-1; } printf("server is running!\n"); //等待连接 while(1) { int
new_fd; struct
aiocb my_aiocb; sin_size = sizeof(struct
sockaddr_in); //接受连接 if((new_fd = accept(sockfd, (struct
sockaddr *)&cliaddr, (socklen_t*)&sin_size))==-1) { perror("accept"); return
-1; } printf("Thread id %u accept connect, fd: %d\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self(), new_fd); setup_io(new_fd, my_aiocb); aio_read(&my_aiocb); } close(sockfd); } |
client端:
运行:
$ ./bin/server
server is running!
Thread id 2505492000
accept connect, fd: 4
Thread id 1084246368 recv:hello world
(注意:线程ID不一样)
$ ./bin/client
10.32.49.10 7092
recv: hello world
信号驱动IO:
使用信号驱动I/O时,当网络套接字可读后,内核通过发送SIGIO信号通知应用进程,于是应用可以开始读取数据。如图: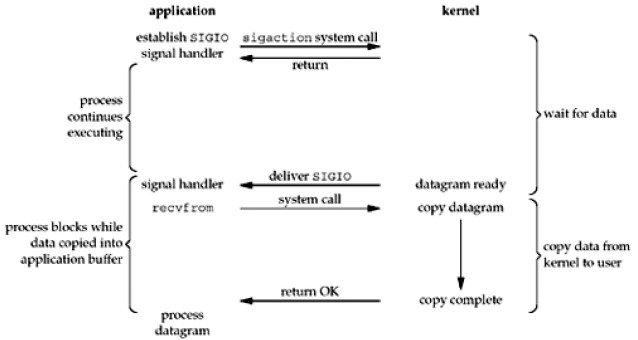
为了让套接字描述符可以工作于信号驱动I/O模式,应用进程必须完成如下三步设置:
1.注册SIGIO信号处理程序。(安装信号处理器)
2.使用fcntl的F_SETOWN命令,设置套接字所有者。(设置套接字的所有者)
3.使用fcntl的F_SETFL命令,置O_ASYNC标志,允许套接字信号驱动I/O。(允许这个套接字进行信号输入输出)
注意,必须保证在设置套接字所有者之前,向系统注册信号处理程序,否则就有可能在fcntl调用后,信号处理程序注册前内核向应用交付SIGIO信号,导致应用丢失此信号。
在UDP编程中使用信号驱动I/O,此时SIGIO信号产生于下面两种情况:
套接字收到一个数据报。
套接字上发生了异步错误。
因此,当应用因为收到一个UDP数据报而产生的SIGIO时,要么可以调用recvfrom读取该数据报,要么得到一个异步错误。
对于TCP编程,信号驱动I/O就没有太大意义了,因为对于流式套接字而言,有很多情况都可以导致SIGIO产生,而应用又无法区分是什么具体情况导致该信号产生的
信号驱动IO模型在网络编程中极少使用,这里不写例子了,有兴趣的同学可以参考:http://blog.csdn.net/yskcg/article/details/6021275
例子源码打包下载:
http://download.csdn.net/detail/yfkiss/4288465
本文转自:http://blog.csdn.net/yfkiss/article/details/7516589
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/labi/p/3574709.html