【数据结构】——排序算法——2.2、直接插入排序
一、先上维基的图:

图一、快速排序效果
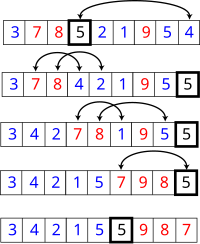
图二、快速排序实例
| 分类 | 排序算法 |
|---|---|
| 数据结构 | 不定 |
| 最差时间复杂度 |  |
| 最优时间复杂度 |  |
| 平均时间复杂度 |  |
| 最差空间复杂度 | 根据实现的方式不同而不同 |
步骤为:
递归的最底部情形,是数列的大小是零或一,也就是永远都已经被排序好了。虽然一直递归下去,但是这个算法总会退出,因为在每次的迭代(iteration)中,它至少会把一个元素摆到它最后的位置去。
三、Java程序import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Random;
public class Quicksort {
public static final Random RND = new Random();
private static void swap(Object[] array, int i, int j) {
Object tmp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = tmp;
}
private static <E> int partition(E[] array, int begin, int end, Comparator<? super E> cmp) {
int index = begin + RND.nextInt(end - begin + 1);
E pivot = array[index];
swap(array, index, end);
for (int i = index = begin; i < end; ++ i) {
if (cmp.compare(array[i], pivot) <= 0) {
swap(array, index++, i);
}
}
swap(array, index, end);
return (index);
}
private static <E> void qsort(E[] array, int begin, int end, Comparator<? super E> cmp) {
if (end > begin) {
int index = partition(array, begin, end, cmp);
qsort(array, begin, index - 1, cmp);
qsort(array, index + 1, end, cmp);
}
}
public static <E> void sort(E[] array, Comparator<? super E> cmp) {
qsort(array, 0, array.length - 1, cmp);
}
}
/*
* more efficient implements for quicksort. <br />
* use left, center and right median value (@see #median()) for the pivot, and
* the more efficient inner loop for the core of the algorithm.
*/
class Sort {
public static final int CUTOFF = 11;
/**
* quick sort algorithm. <br />
*
* @param arr an array of Comparable items. <br />
*/
public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void quicksort( T[] arr ) {
quickSort( arr, 0, arr.length - 1 );
}
/**
* get the median of the left, center and right. <br />
* order these and hide the pivot by put it the end of
* of the array. <br />
*
* @param arr an array of Comparable items. <br />
* @param left the most-left index of the subarray. <br />
* @param right the most-right index of the subarray.<br />
* @return T
*/
public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> T median( T[] arr, int left, int right ) {
int center = ( left + right ) / 2;
if ( arr[left].compareTo( arr[center] ) > 0 )
swapRef( arr, left, center );
if ( arr[left].compareTo( arr[right] ) > 0 )
swapRef( arr, left, right );
if ( arr[center].compareTo( arr[right] ) > 0 )
swapRef( arr, center, right );
swapRef( arr, center, right - 1 );
return arr[ right - 1 ];
}
/**
* internal method to sort the array with quick sort algorithm. <br />
*
* @param arr an array of Comparable Items. <br />
* @param left the left-most index of the subarray. <br />
* @param right the right-most index of the subarray. <br />
*/
private static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void quickSort( T[] arr, int left, int right ) {
if ( left + CUTOFF <= right ) {
//find the pivot
T pivot = median( arr, left, right );
//start partitioning
int i = left, j = right - 1;
for ( ; ; ) {
while ( arr[++i].compareTo( pivot ) < 0 ) ;
while ( arr[--j].compareTo( pivot ) > 0 ) ;
if ( i < j )
swapRef( arr, i, j );
else
break;
}
//swap the pivot reference back to the small collection.
swapRef( arr, i, right - 1 );
quickSort( arr, left, i - 1 ); //sort the small collection.
quickSort( arr, i + 1, right ); //sort the large collection.
} else {
//if the total number is less than CUTOFF we use insertion sort instead (cause it much more efficient).
insertionSort( arr, left, right );
}
}
/**
* method to swap references in an array.<br />
*
* @param arr an array of Objects. <br />
* @param idx1 the index of the first element. <br />
* @param idx2 the index of the second element. <br />
*/
public static <T> void swapRef( T[] arr, int idx1, int idx2 ) {
T tmp = arr[idx1];
arr[idx1] = arr[idx2];
arr[idx2] = tmp;
}
/**
* method to sort an subarray from start to end
* with insertion sort algorithm. <br />
*
* @param arr an array of Comparable items. <br />
* @param start the begining position. <br />
* @param end the end position. <br />
*/
public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void insertionSort( T[] arr, int start, int end ) {
int i;
for ( int j = start + 1; j <= end; j++ ) {
T tmp = arr[j];
for ( i = j; i > start && tmp.compareTo( arr[i - 1] ) < 0; i-- ) {
arr[ i ] = arr[ i - 1 ];
}
arr[ i ] = tmp;
}
}
}原文:http://blog.csdn.net/waycaiqi/article/details/44540711