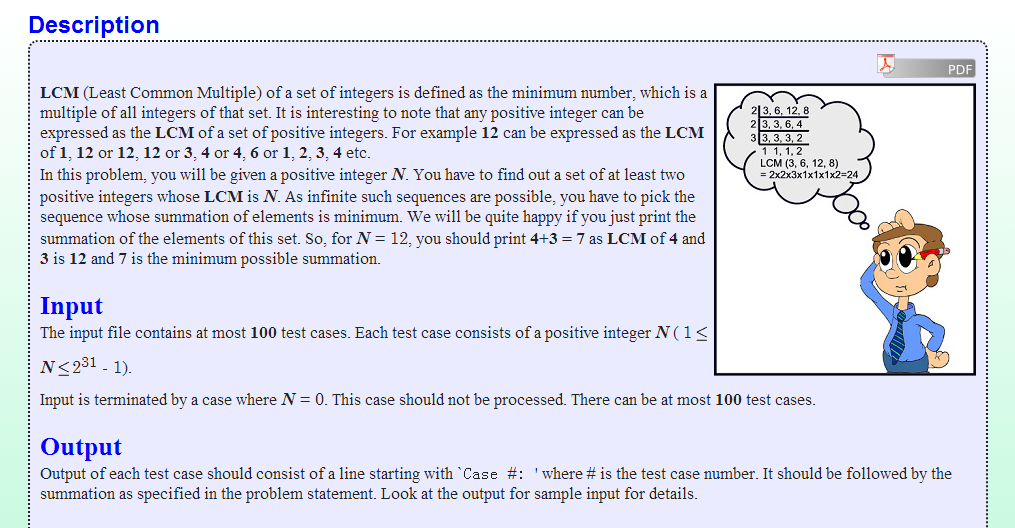
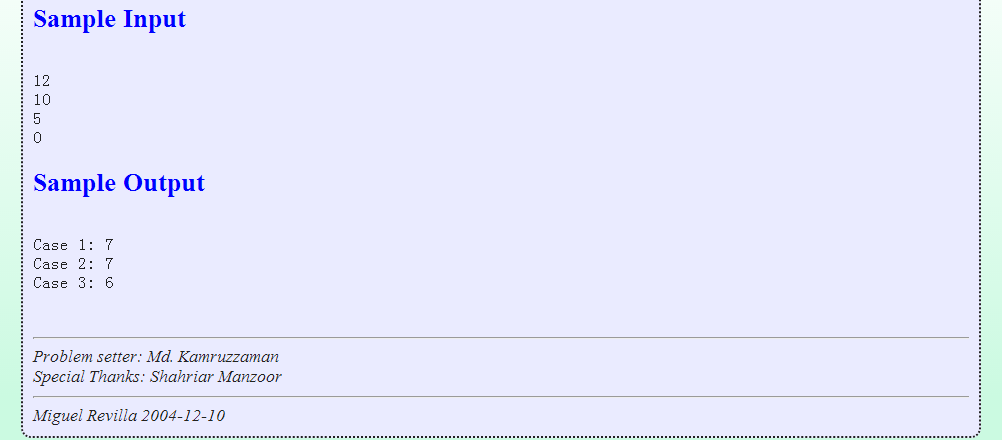
 寻找&星空の孩子
寻找&星空の孩子
AC代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
LL n,sum;
inline LL divisor(LL x)
{
int t=0,cnt;
LL tp;
for(int i=2; i<=sqrt(n); i++)
{
cnt=0;
tp=1;
if(x%i==0&&i!=n)
{
while(x)
{
if(x%i==0)
{
cnt++;
x=x/i;
tp=tp*i;
}
else {sum+=tp;break;}
}
t++;
}
if(!x) break;
}
if(x>1){sum+=x;t++;}
// printf("sum=%lld\n",sum);
return t;
}
int main()
{
int ca=1;
while(scanf("%lld",&n),n)
{
sum=0;
LL m=divisor(n);
if(sum==0||m==1)sum=n+1;
printf("Case %d: %lld\n",ca++,sum);
}
return 0;
}
超时代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
LL n,sum;
inline LL divisor(LL x)
{
int t=0,cnt;
LL tp;
for(int i=2; i<=x; i++)//这么写,就超时 了。。。。。
{
cnt=0;
tp=1;
if(x%i==0&&i!=n)
{
while(x)
{
if(x%i==0)
{
cnt++;
x=x/i;
tp=tp*i;
}
else {sum+=tp;break;}
}
t++;
}
if(!x) break;
}
return t;
}
int main()
{
int ca=1;
while(scanf("%lld",&n),n)
{
sum=0;
LL m=divisor(n);
if(sum==0||m==1)sum=n+1;
printf("Case %d: %lld\n",ca++,sum);
}
return 0;
}
Minimum Sum LCM(uva10791+和最小的LCM+推理)
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/u010579068/article/details/46462003