Mike is a bartender at Rico‘s bar. At Rico‘s, they put beer glasses in a special shelf. There are n kinds of beer at Rico‘s numbered from 1to n. i-th kind of beer has ai milliliters of foam on it.

Maxim is Mike‘s boss. Today he told Mike to perform q queries. Initially the shelf is empty. In each request, Maxim gives him a number x. If beer number x is already in the shelf, then Mike should remove it from the shelf, otherwise he should put it in the shelf.
After each query, Mike should tell him the score of the shelf. Bears are geeks. So they think that the score of a shelf is the number of pairs (i,?j) of
glasses in the shelf such that i?<?j and 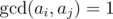 where
where 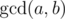 is
the greatest common divisor of numbers aand b.
is
the greatest common divisor of numbers aand b.
Mike is tired. So he asked you to help him in performing these requests.
The first line of input contains numbers n and q (1?≤?n,?q?≤?2?×?105), the number of different kinds of beer and number of queries.
The next line contains n space separated integers, a1,?a2,?... ,?an (1?≤?ai?≤?5?×?105), the height of foam in top of each kind of beer.
The next q lines contain the queries. Each query consists of a single integer integer x (1?≤?x?≤?n), the index of a beer that should be added or removed from the shelf.
For each query, print the answer for that query in one line.
5 6 1 2 3 4 6 1 2 3 4 5 1
0 1 3 5 6 2
题意:
输入n,m,然后输入n个数,之后是m次操作,每次操作输入一个下标i,下标i第一次出现,代表把数组第i个数放进架子中,第二次出现,代表取出来,
每次操作完之后,输出架子中的数字钟,有几个是互质的
思路:
先取出所有质因子,这样可以大大减少计算时间,枚举质因子的过程时间消耗几乎可以忽略不计
然后使用质因子得到其他因子,并且记录个数来计算最后的值
#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stack> #include <queue> #include <map> #include <set> #include <vector> #include <math.h> #include <bitset> #include <algorithm> #include <climits> using namespace std; #define LS 2*i #define RS 2*i+1 #define UP(i,x,y) for(i=x;i<=y;i++) #define DOWN(i,x,y) for(i=x;i>=y;i--) #define MEM(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof(a)) #define W(a) while(a) #define gcd(a,b) __gcd(a,b) #define LL long long #define N 500005 #define MOD 1000000007 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f #define EXP 1e-8 #define lowbit(x) (x&-x) LL n,q; LL ans; bool vis[N]; LL a[N],s[N]; LL num[1000005],tot,cnt; //num[i]记录包含因子i的数的个数 void _set(LL n)//求出质因子 { LL i; tot = 0; for(i = 2; i<=n/i; i++) { if(n%i==0) { s[tot++] = i; while(n%i==0) n/=i; } } if(n!=1) s[tot++] = n; } LL _add() { LL i,j,k; LL ret = 0; for(i = 1; i<(1<<tot); i++)//枚举状态 { LL mul = 1,c = 0; for(j = 0; j<tot; j++) { if((1<<j)&i) mul*=s[j],c++; } if(c%2) ret+=num[mul];//因为偶数个质数相乘得出的数量能根据奇数得到,所以采用奇数增加,偶数减去的方法来使得总数不变 else ret-=num[mul]; num[mul]++; } ans += (cnt-ret);//总数减去不互质的对数 cnt++; return ans; } LL _sub() { LL i,j,k; LL ret = 0; for(i = 1; i<(1<<tot); i++) { LL mul = 1,c = 0; for(j = 0; j<tot; j++) { if((1<<j)&i) mul*=s[j],c++; } num[mul]--; if(c%2) ret+=num[mul]; else ret-=num[mul]; } cnt--; ans -= (cnt-ret); return ans; } int main() { LL i,j,k,x; cnt = ans = 0; scanf("%I64d%I64d",&n,&q); for(i = 1; i<=n; i++) scanf("%I64d",&a[i]); while(q--) { scanf("%I64d",&x); _set(a[x]); if(vis[x]) { vis[x] = false; printf("%I64d\n",_sub()); } else { vis[x] = true; printf("%I64d\n",_add()); } } return 0; }
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/libin56842/article/details/46474103